
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
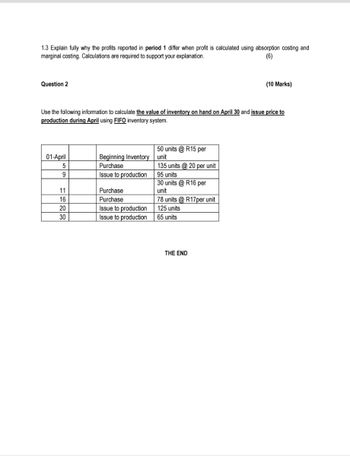
Transcribed Image Text:1.3 Explain fully why the profits reported in period 1 differ when profit is calculated using absorption costing and
marginal costing. Calculations are required to support your explanation.
(6)
Question 2
(10 Marks)
Use the following information to calculate the value of inventory on hand on April 30 and issue price to
production during April using FIFO inventory system.
50 units @ R15 per
01-April
5
Beginning Inventory
Purchase
unit
135 units @20 per unit
9
Issue to production
95 units
11
Purchase
30 units @ R16 per
unit
16
Purchase
78 units @ R17per unit
20
Issue to production
125 units
30
Issue to production
65 units
THE END
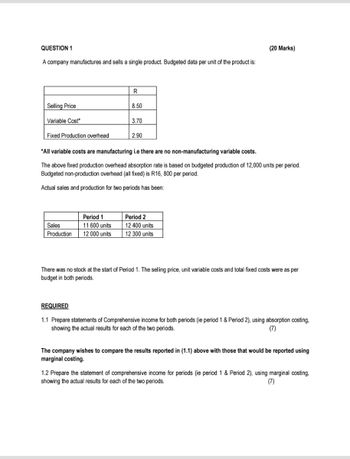
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 1
A company manufactures and sells a single product. Budgeted data per unit of the product is:
(20 Marks)
Selling Price
Variable Cost*
Fixed Production overhead
R
8.50
3.70
2.90
*All variable costs are manufacturing i.e there are no non-manufacturing variable costs.
The above fixed production overhead absorption rate is based on budgeted production of 12,000 units per period.
Budgeted non-production overhead (all fixed) is R16, 800 per period.
Actual sales and production for two periods has been:
Sales
Production
Period 1
11 600 units
12 000 units
Period 2
12 400 units
12 300 units
There was no stock at the start of Period 1. The selling price, unit variable costs and total fixed costs were as per
budget in both periods.
REQUIRED
1.1 Prepare statements of Comprehensive income for both periods (ie period 1 & Period 2), using absorption costing,
showing the actual results for each of the two periods.
(7)
The company wishes to compare the results reported in (1.1) above with those that would be reported using
marginal costing.
1.2 Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for periods (ie period 1 & Period 2), using marginal costing,
showing the actual results for each of the two periods.
(7)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardRequired information Use the following information for the Exercises below. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Activities Units Acquired at Cost 215 units @ $14.00 = $3,010 Date Units sold at Retail Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Jan. 10 Sales 165 units @ $23.00 Jan. 20 Purchase 160 units @ $13.00 = 2,080 Jan. 25 Sales 190 units @ $23.00 Jan. 30 Purchase 330 units @ $12.50 = 4,125 Totals 705 units $9,215 355 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 350 units, where 330 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory. Exercise 5-3 Perpetual: Inventory costing methods LO P1 Required: 1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification. 2. Determine the cost assigned to…arrow_forwardhelppppp Hemming Co. uses a perpetual inventory system A.) Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to the cost of goods sold using FIFO. B.) Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to the cost of goods sold using LIFO. c.) Compute the gross margin for FIFO and LIFO methodarrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardOmega Company reports the following for the month of June. Units Unit Cost June 1 Beg Inventory 300 $4 12 Purchase 450 $6 23 Purchase 750 $5 30 Ending Inventory 222 Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under • FIFO • LIFO average-cost method. Answer:arrow_forwardI need help with this accounting questionarrow_forward
- Homework i s Date January 1 January 10 March 14 March 15 July 30 October 5 October 26. Date Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Hemming Company reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Units Acquired at Cost @$13.20 = @$18.20 = @$23.20 = @$28.20 Activities Beginning inventory Sales Purchase Sales Purchase. Sales Purchase. Totals a) Cost of Goods Sold using Specific Identification Available for Sale Activity Saved # of units 8,372 11,136 5,076 $28,280 Cost of Goods Sold Cost Per Unit Hemming uses a periodic inventory system. Ending inventory consists of 40 units from the March 14 purchase, 80 units from the July 30 purchase, and all 180 units from the October 26 purchase. Using the specific identification method, calculate the following. Help COGS Save & Exit Subre Units Sold at Retail 240 units 410 units 450 units 1,100 units Check my work Ending Inventory Units @ $43.20 @$43.20 @$43.20 Ending…arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward-/ 1 Question 3 of 6 Pearl Industries uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 Inventory 130 $4 $ 520 12 Purchases 520 6 3,120 23 Purchases 325 2,600 30 Inventory 305 (a) Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (For calculation purposes, round average cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.275. Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.) FIFO LIFO Average-Cost The cost of the ending inventory The cost of goods sold !!! %24 %24 %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Cost Flow Methods The following three identical units of Item JC07 are purchased during April: Item Beta Units Cost April 2 Purchase 1 $177 April 15 Purchase 1 179 April 20 Purchase 1 181 Total 3 $537 Average cost per unit $179 ($537 ÷ 3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 27 for $234. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost method. Gross Profit Ending Inventory a. First-in, first-out (FIFO) $fill in the blank 1 $fill in the blank 2 b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) $fill in the blank 3 $fill in the blank 4 c. Weighted average cost $fill in the blank 5 $fill in the blank 6arrow_forwardMatch the term with its definition. Cost-To-Retail Ratio [Choose ] Choose Time Elapsed: Hide Time Attempt due: Apr 7 at 11:59pm 15 Hours, 11 Minutes, 4 Seconds Designated Market Value Gross Profit Method Gross Profit Percentage The cost to replace an item. Also known as "Replacement Cost". Correct Answer Gross profit divided by Sales. Correct Answer Used in the Retail Inventory Method to restate endinding inventory to a cost basis. Correct Answer An addition to the original sales price Correct Answer A method of estimating inventory. Can not be used for an annual financial staement. Correct Answer Net Realizable Value minus a normal profit margin Correct Answer Sales price minus costs to complete or dispose. Also called "Net Realizable Value" Correct Answer An inventory valuation method that compares cost to designated market and records inventory at the lower of the two amounts. Correct Answer An inventory valuation method that compiles inventory at sales prices and converts the…arrow_forwardQuestion 3 Wario Widgets uses a perpetual inventory system and it uses the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) costing method. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail Price Mar 1 Opening inventory 400 units at RM100/unit Mar 5 Purchases 300 units at RM150/unit Mar 10 Sales 600 units at RM500/unit Mar 15 Purchases 400 units at RM180/unit Mar 20 Sales 400 units at RM500/unit Mar 25 Purchases 200 units at RM180/unit 100 units at RM170/unit Required: Apply the FIFO costing method to compute the gross profit, the cost of goods purchased, cost of goods sold, and inventory balance for each transaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education