
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:-/ 1
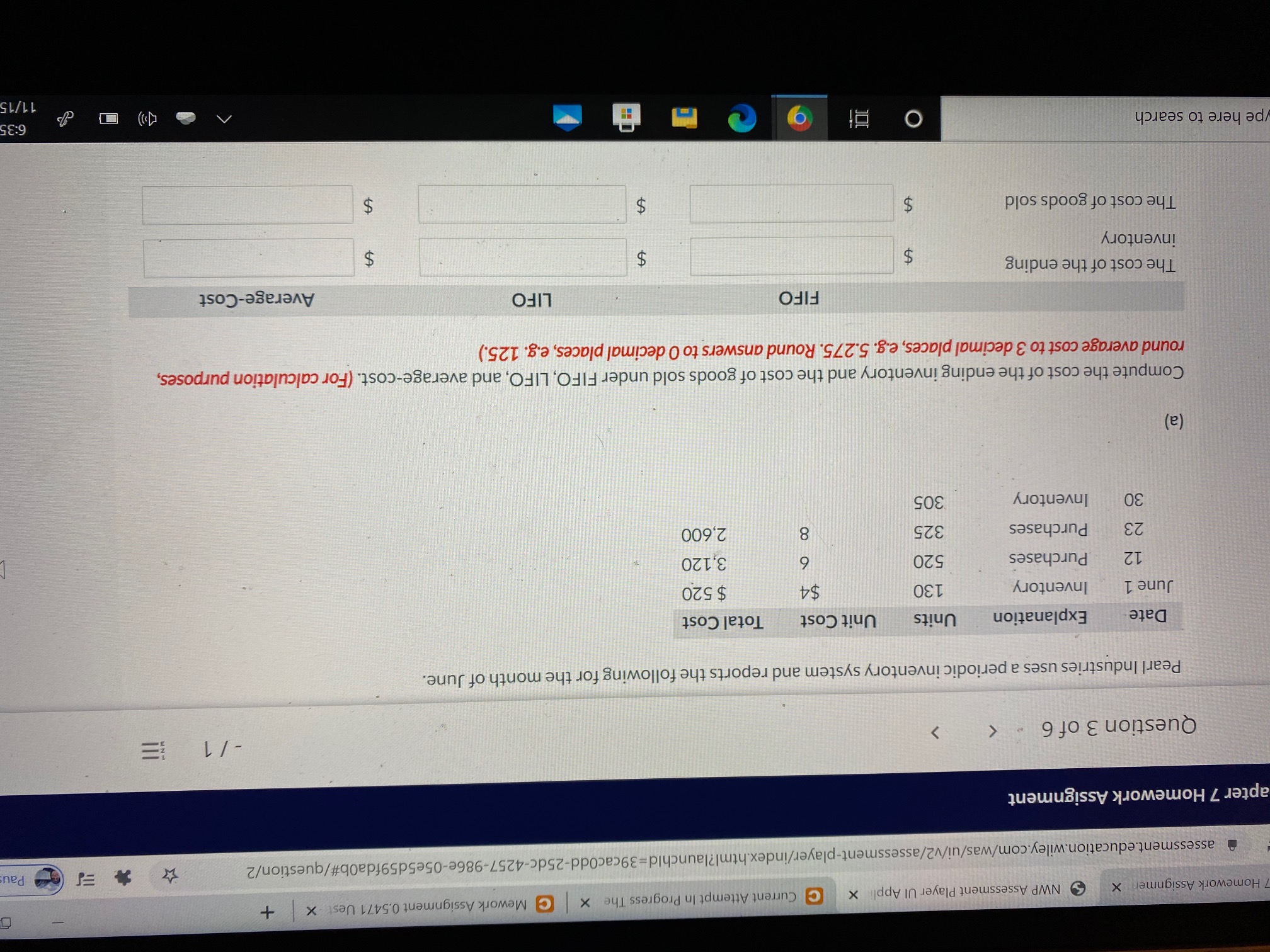
Question 3 of 6
Pearl Industries uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June.
Date
Explanation
Units
Unit Cost
Total Cost
June 1
Inventory
130
$4
$ 520
12
Purchases
520
6
3,120
23
Purchases
325
2,600
30
Inventory
305
(a)
Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (For calculation purposes,
round average cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.275. Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.)
FIFO
LIFO
Average-Cost
The cost of the ending
inventory
The cost of goods sold
!!!
%24
%24
%24
%24
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4 Cheyenne Corp. uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date June 1 12 23 30 Explanation Units Unit Cost Inventory Purchases Purchases. Inventory 130 370 200 240 $5 Weighted-average unit cost $ 6 7 Total Cost $650 2,220 1,400 Calculate weighted-average unit cost. (Round answer to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.125.)arrow_forwardThe following are the transactions for the month of July. Units Unit Cost Unit Selling Price July 1 Beginning Inventory 55 $ 10 July 13 Purchase 275 11 July 25 Sold (100 ) $ 14 July 31 Ending Inventory 230 Calculate cost of goods available for sale and ending inventory, then sales, cost of goods sold, and gross profit, under FIFO. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. How would i creat a FIFO periodic table?arrow_forwardTeal Mountain Inc. uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 Inventory 130 $5 $ 650 12 Purchases 370 6 2,220 23 Purchases 200 7 1,400 30 Inventory 240 Calculate weighted-average unit cost. (Round answer to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.125.) Weighted-average unit cost $enter a weighted-average unit cost in dollars eTextbook and Media Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.) FIFO LIFO Average-cost The cost of the ending inventory $enter a dollar amount $enter a dollar amount $enter a dollar amount The cost of goods sold $enter a dollar amount $enter a dollar amount $enter a dollar amountarrow_forward
- Use the following information for the Exercises 3-7 below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 385 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 15 units from beginning inventory. Date January 1 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 Activities Beginning inventory Sales Purchase Sales Purchase Totals Units Acquired at Cost 225 units @ $ 15.00- 180 units @ $14.00- 385 units @ $ 12.00 = 790 units $ 3,375 2,520 4,620 $ 10,515 Units sold at Retail 175 units 210 units 385 units Exercise 5-5 (Algo) Perpetual: Gross profit effects of inventory methods LO A1 1. Compute gross profit for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. 2. Which method yields the highest gross profit? 3. Does gross profit…arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for A67 Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for weighted average (AVG). Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answers to the nearest dollar amount. Number of Units Unit Cost Sales Beginning inventory 860 $60 Purchased 650 62 Sold 400 $100 Sold 350 110 Ending inventory 760 AVG (perpetual) Inventory Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Inventory Remaining Cost of Goods Purchased Number Number Number of Units Unit Cost Total Cost of Units Unit Cost Total Cost of Units Unit Cost Total Cost Beginning Purchase Sale Sale Total COGS Total Purchasesarrow_forwardSagararrow_forward
- Jesters company uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June DATE EXPLAINATION UNITS UNIT COST TOTAL COST June 1 Inventory 120 $5 $600 12 Purchase 370 $6 $2220 23 Purchase 200 $7 $1400 30. Inventory. 230 How do the average-cost values for ending inventory and cost of goods sold relate to ending inventory and cost of goods sold for FIFO and LIFO? Explain why the average cost is not $6arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] A company began January with 8,000 units of its principal product. The cost of each unit is $7. Inventory transactions for the month of January are as follows: Date of Purchase January 10 January 18 Totals Sales Units Date of Sale January 5 January 12 January 20 Total 6,000 8,000 14,000 * Includes purchase price and cost of freight. Units Purchases Unit Cost* 4,000 2,000 5,000 11,000 $8 9 11,000 units were on hand at the end of the month. Total Cost $ 48,000 72,000 $ 120,000arrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
- A & B pleasearrow_forwardsarrow_forwardok rint From the following, calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the weighted-average method, ending Inventory is 49 units. Note: Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest cent. 1.0 lerences Beginning inventory and purchases January 1 April 10 May 15 July 22 August 19 Mc Graw Hill September 30 November 10 December 15 Cost of ending inventory Cost of goods sold Units 5 10 12 15 18 20 32 16 -- Unit cost $ 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.25 4.00 4.20 4.40 4.80 < Prev lab caps lock shift BUD fr 7 of 10 control JUL 30 A 2 Z 1 W option Next # S E H D command R C 5 F V G Y B H A 8 N J K M O ge command ontarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education