
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
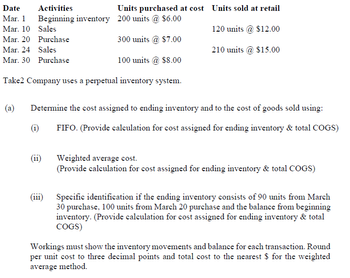
Transcribed Image Text:Date Activities
Mar. 1
Mar. 10
Mar. 20
Mar. 24
Mar. 30 Purchase
Beginning inventory 200 units @ $6.00
Sales
Purchase
300 units @ $7.00
Sales
100 units @ $8.00
Take2 Company uses a perpetual inventory system.
(a) Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to the cost of goods sold using:
FIFO. (Provide calculation for cost assigned for ending inventory & total COGS)
(1)
Units purchased at cost Units sold at retail
120 units @ $12.00
210 units @ $15.00
(11)
(111)
Weighted average cost.
(Provide calculation for cost assigned for ending inventory & total COGS)
Specific identification if the ending inventory consists of 90 units from March
30 purchase, 100 units from March 20 purchase and the balance from beginning
inventory. (Provide calculation for cost assigned for ending inventory & total
COGS)
Workings must show the inventory movements and balance for each transaction. Round
per unit cost to three decimal points and total cost to the nearest $ for the weighted
average method.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for tennis rackets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 19 units @ $18 11 Purchase 16 units @ $16 14 Sale 20 units 21 Purchase 12 units @ $21 25 Sale 14 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using LIFO. Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Purchases Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Date Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 11 $ 14 $ 21 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Rand Company produces dry fertilizer. At the beginning of the year, Rand had the following standard cost sheet: Direct materials (8 lbs. @ $1.25) $10.00 Direct labor (0.15 hr. @ $18.00) 2.70 Fixed overhead (0.20 hr. @ $3.00) 0.60 Variable overhead (0.20 hr. @ $1.70) 0.34 Standard cost per unit $13.64 Overhead rates are computed using practical volume, which is 49,000 units. The actual results for the year are as follows: Units produced: 53,000 Direct materials purchased: 408,000 pounds at $1.32 per pound Direct materials used: 406,800 pounds Direct labor: 10,500 hours at $17.95 per hour Fixed overhead: $36,570 Variable overhead: $18,000 MPV=28,560 UNFAV MUV=21,500 FAV LRV=525 FAV LEV=45,900 UNFAV FIXED SPENDING VARIANCE= 7,170 UNFAV FIXED VOLUME VARIANCE= 2,400 FAV VARIABLE SPENDING= 150 UNFAV VARIABLE EFFICIENCY= 4,335 UNFAV Prepare journal entries for the following: The purchase of direct materials The issuance…arrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forwardUsing a perpetual system, what is the cost of the goods sold for November if the company uses LIFO? Nov. 01 Inventory 16 units at $20.00 Nov. 04 Sold 11 units Nov. 10 Purchased 33 units at $21.00 Nov. 17 Sold 25 units Nov. 30 Purchased 23 units at $25.00 Using the perpetual LIFO system, what is the cost of the merchandise sold for November? Select the correct answer. A. $745.00 B. $848.00 C. $845.00 D. $740.00arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for portable game players are as follows: Apr. 1 Inventory 60 units @ $81 10 Sale 49 units 15 Purchase 31 units @ $85 20 Sale 20 units 24 Sale 14 units 30 Purchase 31 units @ $89 The business maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the first-in, first-out method. Question Content Area a. Determine the cost of the merchandise sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 3. Under FIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Cost of Merchandise Sold Unit Cost column and in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Perpetual Inventory AccountFirst-in, First-out MethodPortable Game Players Date QuantityPurchased PurchasesUnitCost PurchasesTotalCost QuantityCost ofMerchandiseSold Cost ofMerchandiseSoldUnit Cost Cost ofMerchandiseSoldTotal…arrow_forwardUse the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. Аpril 1 Inventory 100 units @ $40 Sale 60 units 10 Purchase 40 units $42 15 Sale 50units Purchase 60 units $45 Assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system, calculate the cost of merchandise sold on April 5 as well as ending inventory as of April 30th, using FIFO, Enter as whole numbers! Do not use decimals or dollar signs. COMS April 5h $ COMS April 15th $ Ending Inventory April 30th $ 20arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for tennis rackets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 18 units @ $14 11 Purchase 12 units @ $18 14 Sale 25 units 21 Purchase 13 units @ $19 25 Sale 8 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO. Cost of Purchases Goods Sold Inventory Date Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 %$4 11 $4 $ 14 21 $4 25 $4 $4 $4 Total Cost of goods sold $4 Ending inventory value %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Please do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardRequired information Use the following information for the Exercises below. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Activities Units Acquired at Cost 215 units @ $14.00 = $3,010 Date Units sold at Retail Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Jan. 10 Sales 165 units @ $23.00 Jan. 20 Purchase 160 units @ $13.00 = 2,080 Jan. 25 Sales 190 units @ $23.00 Jan. 30 Purchase 330 units @ $12.50 = 4,125 Totals 705 units $9,215 355 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 350 units, where 330 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory. Exercise 5-3 Perpetual: Inventory costing methods LO P1 Required: 1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification. 2. Determine the cost assigned to…arrow_forwardCalculator Beginning inventory, purchases and sales data for widgets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 15 units @ $30 11 Purchase 12 units @ $27 14 Sale 18 units 21 Purchase 7 units @ $25 25 Sale 10 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and calculates the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO. Purchases Cost ofGoods Sold Inventory Date Qty Unit Cost Total Cost Qty Unit Cost Total Cost Qty Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 $ $ 11 $ $ $ $ $ 14 $ $ $ $ $ 21 $ $ $ $ $ 25 $ $ $ $ $ Total Cost of goods sold $ Ending inventory value $arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education