
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
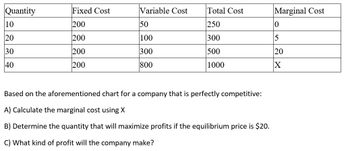
Transcribed Image Text:Quantity
10
20
30
40
Fixed Cost
200
200
200
200
Variable Cost
50
100
300
800
Total Cost
250
300
500
1000
Based on the aforementioned chart for a company that is perfectly competitive:
A) Calculate the marginal cost using X
B) Determine the quantity that will maximize profits if the equilibrium price is $20.
C) What kind of profit will the company make?
Marginal Cost
0
5
20
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If a perfectly competitive firm's average total cost is less than the price, then the firm A) incurs an economic loss. B) makes an economic profit. C) makes zero economic profit. D) makes either zero economic profit or an economic profit depending on whether the marginal revenue is equal to or greater than the price. E) None of these answers is correct because the relationship between the price and average total cost has nothing to do with the firm's profit.arrow_forwardWhich of the following are perfectly competitive markets? Market Tomato Growing Coffee vendor Manufacturing computers Constructing new homes Perfectly Competitive? Yes Yes No Yes Number of Firms Few Many Few Many Type of Product Identical or Differentiated Identical Differentiated Identical Ease of Entry High High Low Higharrow_forwardThe graph on the right shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. Firm's Supply Curve Use the point drawing tool to identify price-quantity combinations for the prices of $20, $30, $50, and $80 per unit of output. 120- MC 110- Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects. 100- AC 90- If there are 100 identical firms in the market, what will be the market supply (to the 80- nearest 100) at these prices? 70- AVC Price Market Supply 2 60- $20 9 50- $30 40- $50 30 20- $80 10- 0- 100 120 140 160 180 Output 20 40 60 80 étv 20 MacBook Air DII 80 F9 F5 F3 F2 #3 $ & 3 4 5 6 9 { E R Y P F G H J K > C V N M command op レレ .... P. AC, AVC, MC B トarrow_forward
- The table below shows the price and cost information for a firm that operates in a perfectly competitive market. Based on this information, what is the profit-maximizing output quantity? Price Quantity Total Cost $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $6 $10 $15 $21 $28 $35 $45 1 2 3 4 5 6 Profit is maximized at a quantity of type your answer. units, where it is equal to $ type your answer. Is the long run price in this market likely to be higher or lower than the current price of $8? type your answer.arrow_forwardUniversity Economics, Theory of Productionarrow_forwardAccording to the graph below answer the following questions: 1. What is the profit-maximizing quantity 2. What is the total revenue at that quantity 3. What is the total cost at that quantity 4. How much is the total profit at that quantity Perfect Competition with a price of $18. Price $25 $18 $15 70 Quantity 130 MC 160 ATCarrow_forward
- The graph below shows a perfectly competitive firm in short run equilibrium, where the firm has chosen the output level maximizing its profit. Consider the level of profits being earned here, and what will happen over time. What will happen in the long run? Note that the horizontal demand curve, D1, is also equivalent to marginal revenue and price. Group of answer choices The market price will increase causing economic profits to increase Demand will increase causing economic profits to increase The market price will decrease until economic profit is zeroarrow_forwarda) What is the profit maximising condition in a market with perfect competition?b) Explain what is meant by abnormal profit? What is the adjustment process from short-run abnormal profit to long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market?c) Please find below Pricing options for firm A and B, along with individual payoffs (Firm A’s payoff/Firm B’s payoff)Firm BFirm APrice £2 Price £1Price £2 £20,000/£20,000 £10,000/£24,000Price £1 £24,000/£10,000 £12,000/£12,000Assume you are the pricing manager at Firm A;i) What is your payoff for a ‘maximin’ strategy?ii) What is your payoff for a ‘maximax’ strategy?iii) Does a dominant strategy exist within this prisoners’ dilemma?arrow_forwardConsider the perfectly competitive market for sports jackets. The following graph shows the marginal cost ( MCMC ), average total cost ( ATCATC ), and average variable cost ( AVCAVC ) curves for a typical firm in the industry.arrow_forward
- The figure below depicts the market supply and demand for the perfectly competitive rollerblade industry. S Price per pair of Rollerblades 1,140 070 50 150 Number of pairs of Rollerblades per week Based on the figure above, if the current quantity demanded of rollerblades is 150 per week, you accurately predict that in the short run, Q Select one: a. price and quantity supplied will increase and quantity demanded will decrease. b. price and quantity supplied will decrease and quantity demanded will increase. c. price, quantity supplied and quantity demanded will increase. d. price, quantity supplied and quantity demanded will decrease.arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm has total revenue and total cost curves given by: TR = 800Q TC = 4,000 + 12Q + 2 Q2 a. Find the profit-maximizing output for this firm. b. What profit does the firm makearrow_forwardUse the following graphs for questions 22 and 23. At what price would a firm exit the market? (a) Relationship of total cost to total variable cost and total fixed cost (b) Relationship of marginal cost to average total cost, average variable cost, and average fixed cost Total Costs (dollars) 700 Cost 150 Per 140 TC Unit 130 TVC (dollars) 120 MC 600 110 100 500 90 80 400 70 60 ATC 300 TFC 50 AVC 40 AFC 200 30 20 TFC 100 10 AFC 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity of Output Quantity of Output (units per hour) (units per hour) O $20 O $30 $45 $50arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education