
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
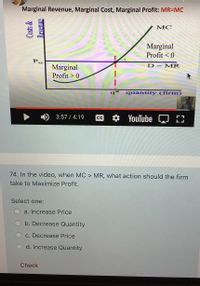
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website**
### Diagram Explanation
The diagram shown in the video illustrates the relationship between Marginal Revenue (MR), Marginal Cost (MC), and Marginal Profit. The graph is labeled with "Costs & Revenue" on the vertical axis and "quantity (firm)" on the horizontal axis.
- **MC Curve**: This upward-sloping green line represents the Marginal Cost, which increases as the quantity produced increases.
- **MR (D=MR) Line**: This horizontal blue line represents the Marginal Revenue, which indicates the constant revenue gained from selling one more unit.
- **Intersection Point (E)**: Point E is where the MR line intersects the MC curve, representing the profit-maximizing output level, denoted as q*.
- **Marginal Profit Regions**:
- To the left of point E, marginal profit is greater than zero, indicating that increasing production will increase profit.
- To the right of point E, marginal profit is less than zero, suggesting that further production will decrease profit.
### Question
**74. In the video, when MC > MR, what action should the firm take to Maximize Profit?**
Select one:
- a. Increase Price
- b. Decrease Quantity
- c. Decrease Price
- d. Increase Quantity
(Select the correct option and click "Check" to verify your answer.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5arrow_forward!arrow_forward22. Suppose the firm in the figure below sets a uniform price for its product. Please show the steps. a. If the firm chooses to set a uniform price for its product, then the profit-maximizing price is $________ and ________ units will be sold. Under this uniform pricing policy, the maximum possible profit is $________. b. The maximum profit the firm could earn if the firm sells 2,000 units and is able to charge the demand price for every one of the 2,000 units it sells is $ ________. c. For the additional number of units sold by expanding output to 2,000 units (from the output level in part a), the consumer surplus that could be captured if it were possible to charge the demand price on every one of those units would amount to $________.arrow_forward
- If firms can easily enter and exit a market, then A. firms will earn zero economic profit in the short run. B. firms will produce at minimum average fixed cost in the long run. C. firms will produce where price is greater than marginal cost. D. firms will produce where price is greater than marginal revenue. E. firms will produce at minimum average cost in the long run.arrow_forwardConsider a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If this firm were to raise its price, its a. revenue would fall dramatically b. profits would increase as long as costs remained constant C. total costs would increase revenue would increase only if market demand were inelastic e. revenue would decrease only if market demand were elasticarrow_forwardIf a firm charges a lower price they will have a lower profit margin but a higher profit; if a firm charges a higher price they will have a higher profit margin but a lower profit. Which of the following statements is accurate? A. The firm should charge a lower price for the higher profit. B. The firm should a higher price for the lower profit. C. The firm should charge a higher price for the higher profit margin. D. Whether the firm should charge a higher price or lower price indeterminate.arrow_forward
- 4. Hundreds of music stores have been closing in the face of stagnant demand for CDs because of new competition by online music vendors. a. How would price competition from these new sources cause a retail store to close? b. In the long run, will CDs remain a viable product? If so, how?arrow_forward5. Restaurants offer related but differentiated products to their consumers. In the long run, new restaurants enter the market and imitate the cuisine and atmosphere of successful competitors. How would you expect a restaurant to set its prices in the long run? Describe the relationship between price and average total cost. Does a restaurant earn economic profits?arrow_forwardNeed clear explanation for your answer...arrow_forward
- 1arrow_forward1.i) Assuming you are the managing director of a firm that produces goods: A,B and C .The price elasticity of demand for A is 1.2, for B it is 1.oo and C is 0.75. It is known that he's firm is experiencing serious cash flow problems and you have to increase total revenue as soon as possible. If you were in a position to set the prices for these goods, what would be your pricing strategy for each product ii) price falls from N$ 16 to N$ 12 per bottle and demand rises from 200 to 300 per bottle.calculate the PED using midpoint formula Output prices average (total)cost Total cost marginal cost Total profit/loss 10 10 -108 20 10 4 -48 30 10 5 3 40 10 6.20 40 50 10 8 60 60 10 10 60 2. i) fill in the gaps ii)in which market structure doess Johnson Electronics (Pty)Ltd operate? iii)what level of output maximizes the firms profitarrow_forwardThe figure below shows the industry demand curve and two possible industry supply curves in the perfectly competitive market for cheeseburgers. Price ($) 8 7 6 51 3 2 1 0 3 5 6 B S₂ A S₁ Select one: ● a. an excess supply of 6 cheeseburgers. b. an excess demand of 4 cheeseburgers. O c. an excess supply of 3 cheeseburgers. d. an excess demand of 6 cheeseburgers. 7 8 Cheeseburgers The market depicted in the figure above is initially at equilibrium at Point A. Suppose firms begin to exit the market, causing the supply curve to shift from S₁ to S₂. 9 10 11 12 Q If the price of cheeseburgers remains constant at $5.00, as a result of the decrease in supply there will bearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education