
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Q2.
A physical pendulum consists of a ring of radius 0.5 m and mass 2 kg. The ring is pivoted at a point on its
perimeter. The ring is pulled out such that its centre of mass makes a small initial angle ?0 = 0.2 rad from
the vertical and released from rest.
(C) Calculate the angular frequency of the oscillation of the ring
(D) Calculate the period of the oscillation of the ring
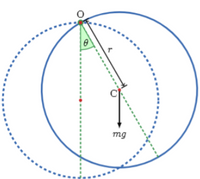
Transcribed Image Text:mg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. What is the translational velocity of the bottom tip of the pendulum at the moment that gravitational potential energy is 50% of its maximum? b. What effect would doubling the mass and length of the physical pendulum have on the answer to part (a) of the problem? c. Draw graphs of angular acceleration, tangential translational acceleration, and centripetal acceleration as functions of the instantaneous angle that the pendulum makes with the vertical. In all three graphs show the behavior of the acceleration from release with theta =38.4 degree until the pendulum is vertical and theta =0 degree.arrow_forwardA 37 kg block on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to a spring. The block is exhibiting SHM. The total energy of the system is 420 J. A.) Determine how much PE it has when its KE is six-sevenths of the PE. PE= w B.) Determine the maximum speed of the block. Vmax=arrow_forwardAn object is attached to a coiled spring. The object begins at its rest position at t = 0 seconds. It is then propelled downward. Write an equation for the distance of the object from its rest position after t seconds, if the amplitude is 7 inches and the period is 5 seconds The equation for the distance d of the object from its resting position isarrow_forward
- MM12.. no handwritten...arrow_forward6. A body is oscillating with simple harmonic motion, with an angular frequency of g rad/s. At time t = 6s, the position of the body is x = 0.40m, and its velocity is v= -0.25m/s. (a) Find the amplitude of the motion. (b) Determine the phase of the motion, (c) What is the position of the body at t = 10.0s?arrow_forward(hrw8c15p89) A vertical spring stretches 7.4 cm when a 2.0 kg block is hung from its end. Calculate the spring constant. Submit Answer Tries 0/5 This block is then displaced an additional 5.5 cm downward and released from rest. Find the period. Submit Answer Tries 0/5 Find the frequency. Submit Answer Tries 0/5 Find the amplitude ( cm). Submit Answer Tries 0/5 Find the maximum speed of the resulting SHM ( cm/s). Submit Answer Tries 0/5arrow_forward
- In the figure, a physical pendulum consists of a uniform solid disk (of radius R = 56.2 cm) supported in a vertical plane by a pivot located a distance d = 22.8 cm from the center of the disk. The disk is displaced by a small angle and released. What is the period of the resulting simple harmonic motion? Number i Units Pivot R 12arrow_forwardWhile visiting the Albert Michelson exhibit at Clark University, you notice that a chandelier (which looks remarkably like a simple pendulum) swings back and forth in the breeze once every T = 6.4 seconds. a)Calculate the frequency of oscillation (in Hertz) of the chandelier. b) Calculate the angular frequency ω of the chandelier in radians/second. c)Determine the length L in meters of the chandelier.arrow_forwardA large block with mass 18 kg executes horizontal simple harmonic motion as it slides across a frictionless surface with a frequency 1.27 Hz. Block smaller block with mass 5 kg rests on it, as shown in the figure, and the coefficient of static friction between the two is flg = 0.401. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s². k -0000² 25 5 kg s=0.401 18 kg What maximum amplitude of oscillation can the system have if the block is not to slip? Answer in units of cm.arrow_forward
- b. An object with a mass of 0.2 kg attached to a spring exhibits simple harmonic motion according to the equation x = 0.04 cos ( 20zt +"). Find the frequency and the period of the oscillation. Find the velocity of the particle, its acceleration and the acting force, as well as the amplitudes of the respective quantities. wwwip Figure 3: Question 2(b) A spring mass systemarrow_forwardThe figure shows the pendulum of a clock in your grandmother's house. The uniform rod of length L = 2.00 m has a mass m = 0.880 kg. Attached to the rod is a uniform disk of mass M = 1.40 kg and radius 0.150 m. The clock is constructed to keep perfect time if the period of the pendulum is exactly 2.50 s. L What should the distance d be so that the period of this pendulum is 2.40 s? Ad = m M 0.150 m Tipler & Mosca, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 6e 2008 W.H. Freeman and Company Suppose that the pendulum clock loses 5.00 min/day. To make sure your grandmother will not be late for her quilting parties, you decide to adjust the clock back to its proper period. What distance Ad and in what direction should you move the disk to ensure that the clock will keep perfect time? d = cm directon of Ad: upward marrow_forwardA pendulum's angular position is given by e = 0.0310 cos(mt), where e is in radians and w = 3.83 rad/s. Find the period (in s) and length (in m) of the pendulum. period -5.29 How does period depend on angular frequency? s length 5.29 How does the angular frequency of a pendulum depend on its length and the free-fall acceleration? marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON