
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
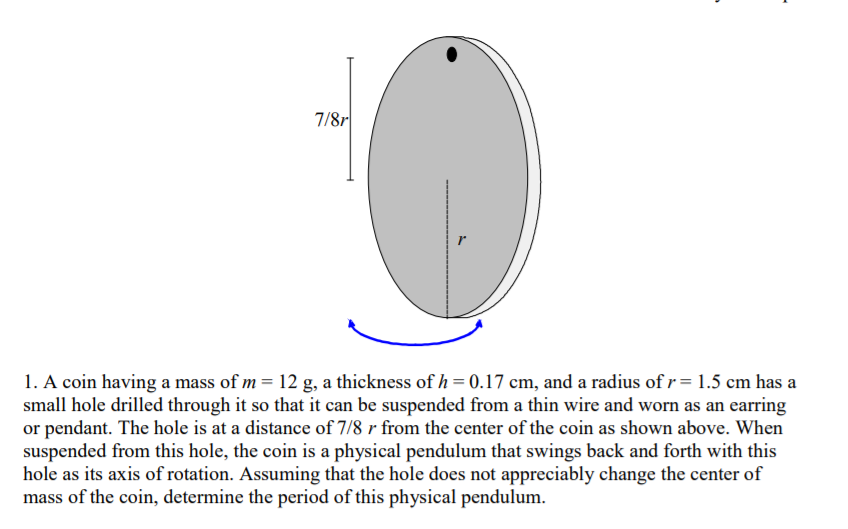
Transcribed Image Text:1. A coin having a mass of m = 12 g, a thickness of h = 0.17 cm, and a radius of r= 1.5 cm has a
small hole drilled through it so that it can be suspended from a thin wire and worn as an earring
or pendant. The hole is at a distance of 7/8 r from the center of the coin as shown above. When
suspended from this hole, the coin is a physical pendulum that swings back and forth with this
hole as its axis of rotation. Assuming that the hole does not appreciably change the center of
mass of the coin, determine the period of this physical pendulum.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A physical pendulum is constructed such that two spheres of different radii are welded together. A rod is then welded to the top of these two spheres as shown. The length of the rod is 2.90 m while the mass is 2.00 kg. The radius of the small (upper) sphere is 0.790 m with a mass of 8.20 kg. The radius of the lower (larger) sphere is 0.960 m with a mass of 11.6 kg. The entire system is hung from the end of the rod. a. what is the rotational intertia of the rod? b. what is the rotational intertial of the small sphere? c. what is the rotational intertia of the large sphere? d. what is the distance from the pivot point to the center of mass of the system? e. what is the period of oscillation of the pendulum?arrow_forwardIn the figure, a solid cylinder attached to a horizontal spring (k = 5.80 N/m) rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface. If the system is released from rest when the spring is stretched by 0.290 m, find (a) the translational kinetic energy and (b) the rotational kinetic energy of the cylinder as it passes through the equilibrium position. (c) If the cylinder has mass M = 6.20 kg, find the period of the simple harmonic motion that the cylinder's center of mass executes. (Hint: Find the time derivative of the total mechanical energy.) M · k oooooo (a) Number i 0. (b) Number i (c) Number i O. Units Units Unitsarrow_forwardIn the figure, a solid cylinder attached to a horizontal spring (k = 9.00 N/m) rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface. If the system is released from rest when the spring is stretched by 0.250 m, find (a) the translational kinetic energy and (b) the rotational kinetic energy of the cylinder as it passes through the equilibrium position. (c) If the cylinder has mass M = 5.30 kg, find the period of the simple harmonic motion that the cylinder's center of mass executes. (Hint: Find the time derivative of the total mechanical energy.) (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units >arrow_forward
- Most injuries to the shoulder will require rehab and physical therapy. Pendulum exercises are a great way to increase strength and improve flexibility and range of motion in an injured shoulder. Here, the patient bends forward until their back is horizontal. The injured arm is hung vertically downward and is allowed to swing freely back and forth like a pendulum (see the figure). Treat the arm (length of 69 cm) in the figure as a physical pendulum – a uniform rod rotating about an axis through one of its ends – and calculate the period of the arm’s small oscillations.arrow_forward3. A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string of length 1.60 m. Now you start with the pendulum at 16.6 degrees with respect to the vertical, but rather than releasing it from rest, you give it a push downward. It swings to the other side, and reaches a maximum angle of 55.4 degrees with respect to the vertical. What must have been the initial speed of the pendulum just after you pushed it? 4.78 m/s 3.50 m/s 3.68 m/s 1.14 m/sarrow_forwardA 0.41-kg metal sphere oscillates at the end of a vertical spring. As the spring stretches from 0.12 m to 0.23 m (relative to its unstrained length), the speed of the sphere decreases from 7.0 to 4.5 m/s. What is the spring constant of the spring? Number i 306.17 Units N/narrow_forward
- A 0.200-m uniform bar has a mass of 0.676 kg and is released from rest in the vertical position, as the drawing indicates. The spring is initially unstrained and has a spring constant of k = 28.0 N/m. Find the tangential speed with which end A strikes the horizontal surface. Number i Units 0.100 m Pivot (friction less) 0.100 m 0.100 marrow_forwardThe equations used to describe the physical pendulum will lead us directly to an answer. Part 3 of 3 - Analyze We are givenf = 0.685 Hz, d 0.510 m, and m = 2.10 kg. We have the following equation for the period. T = 2n V mgd This gives 4721 T2 = mgd and, solving for the moment of inertia, we have the following. T?mgd mgd %3D kg )(9.80 m/s?) m Hz kg - m2 Submit Skip (you cannot come back) Need Help? Read it O Show My Work (Optional) ?arrow_forwardThe pendulum in the figure consists of a uniform disk with radius r = 10.0 cm and mass 560 g attached to a uniform rod with length L = 390 mm and mass 270 g. (a) Calculate the rotational inertia of the pendulum about the pivot point. (b) What is the distance between the pivot point and the center of mass of the pendulum? (c) Calculate the period of oscillation. (a) Number Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON