
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
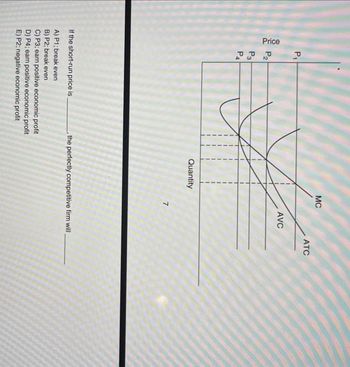
Transcribed Image Text:Price
P₁
P2
P3
PA
Quantity
MC
If the short-run price is.
, the perfectly competitive firm will
A) P1; break even
B) P2; break even
C) P3; earn positive economic profit
D) P4; earn positive economic profit
E) P2; negative economic profit
AVC
ATC
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Question 16 Refer to Figure 5-1 The firm will earn positive economic profits if the price is P4 only O P4 or P3 only P4, P3, or P2 only O any of P4, P3, P2, or P1arrow_forwardIn the short run, a perfectly competitive firm's economic profits Question 7 options: must be negative, that is the firm must incur an economic loss. might be positive, negative (an economic loss), or zero (a normal profit). must be positive. must equal zero, that is, the firm earns a normal profit.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- MC АТС $25.00 AVC $19.50 -- $15.00 $12.50 - - 30 40 50 60 Output (Q) For the firm shown in the diagram above, its Long Run Supply Curve is its curve for any price greater than ATC; $19.50 MC; $12.50 AVC; $12.50 MC; $19.50arrow_forwards 1, 12 & 13 Assignment Saved Help Save & Exit Assume a purely competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If a decline in demand occurs, firms will Multiple Choice leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will rise. enter the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will fall.arrow_forwardP P₂ B C Q₂ D MC Firm entry occurs. Output Quantity Refer to the above figures for the typical firm in a competitive market. If the market demand curve is D3, what happens in the long run? A Firm exit occurs. ATC Most firms do nothing. D₂ Some existing firms increase capital input. D₂ D₁ Quantityarrow_forward
- 39) If a perfectly competitive firm operates in the short run but exits the industry in the long run, then the firm's short run condition isA) TR > TVC and TR < TC. B) TR > TC.C) TR < TVC. D) TR < TFC.arrow_forwardMarginal revenue is A) the change in total revenue from a one-unit increase in the quantity sold. B) less than price for a perfectly competitive firm. C) another name for total revenue. D) the economic profit from producing an additional unit of output. E) the change in total cost from producing an additional unit of output.arrow_forwardume the pizza market is a perfectly competitive constant cost industry, and all firms have identical homogenous firms). The market demand and market supply functions for this perfectly competit stry are given below. L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 q=TP 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 TC 100 205 2.45 280 340 430 545 720 930 1190 P = 30.5-.005Q P = 1.7+.003Q TFC TVC 100 0 100 105 20.50 10.50 100 145 12.25 7.25 100 180 9.33 6.00 100 240 8.50 6.00 100 330 8.60 6.60 100 445 9.08 7.42 100 620 10.29 8.86 100 830 11.63 10.38 100 1090 13.22 12.11 ATC AVC MC 10.50 4.60 3.50 6.00 9.00 11.5 17.50 21.00 26.00arrow_forward
- 20) What will a firm in a perfectly competitive industry do in the short-run if the price of its product decreases below the firm's average variable costs but still above average total costs? A) Do nothing B) Increase production C) Decrease production D) Shut downarrow_forwardSuppose that the demand curve faced by a firm is downward sloping. Which of the following statements is true? Question 5Answer a. The firm faces constantly changing production technology b. The firm operates in a perfectly competitive market c. The firm’s marginal revenue is equal to the market price d. The firm is not a price-takerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education