
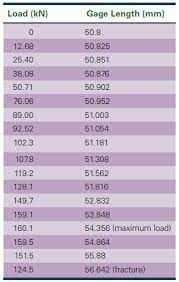
A specimen of an AISI-SAE type 416 stainless steel with a 0.505-in. diameter was machined to a 2.00-in.-gage length and the following data were collected:
After fracture, the gage length was 2.75 in. and the diameter was 0.365 in. Plot the After fracture, the gage length was 2.20 in. and the diameter was 0.325 in. Plot the engineering stress strain curve and calculate
(a) the 0.2% offset yield strength;
(b) the tensile strength;
(c) the modulus of elasticity;
(d) the % elongation;
(e) the % reduction in area;
(f) the engineering stress at fracture;
(g) the true stress at necking;
(h) the modulus of resilience; and
(i) the elastic and plastic strain to fracture.
(j) W hen the sample was loaded to 11,400 lbs, the diameter was measured to be 0.504 in. Calculate the tranverse and axial strains at this load. Compute the Poisson’s ratio.
(k) Obtain the tensile properties for type 416 stainless steel that has been quenched and tempered and compare them to your answers. Discuss the similarities and differences.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

- A three-point bending test was performed on an aluminum oxide specimen having a circular cross section of radius 6.7 mm; the specimen fractured at a load of 3190 N when the distance between support points was 46 mm. Another test is to be performed on a specimen of this same material, but one that has a square cross section of 16 mm in length on each edge. At what load would you expect this specimen to fracture if the support point separation is maintained at 46 mm? Ff = ____________ Narrow_forward2. Please estimate the number of cycles to failure of a steel specimen under tensile fatigue loading with the following parameters. The R ratio is 3, mean stress 200 MPa, yield strength 450 MPa, ultimate tensile strength 560 MPa, Young’s modulus 200 GPa, KIC = 140 MPa . Assume the initial crack length is 0.1 mm.arrow_forwardProb- In a tensile test carried out in the laboratory on a steel specimen for 5 minutes. The strain value noted at that time was 0.30. What is the average strain rate of that steel specimen?arrow_forward
- Question 7: Given a 1050 HR steel, estimate (a) the rotating-beam endurance limit at 106 cycles. (b) the endurance strength of a polished rotating-beam specimen corresponding to 104 cycles to failure (c) the expected life of a polished rotating-beam specimen under a completely reversed stress of 55 kpsi.arrow_forwardZhpe Outine lece Select 834 Anange Oick Create wnd Shane Adobe PO Adite A SydesO upe iects tere Ding teting 1. (a) A tension test was performed on a magnesium alloy specimen having a diameter 12 mm and gauge 50 mm. The resulting stress-strain diagram is shown figure. Determine the approximate modulus of elastic and the yield strength of the alloy using the 0.2% offset method. (MPa) 280 245 (b) A tension test was performed on a magnesium specimen having a diameter 12 mm and gauge 1ength of 50 mm. The resulting stress-strain diagram is shown in the figure. If the specimen is stressed to 210 MPa and unloaded, determine the permanent elongation of the 210 175 140 specimen 105 70 35 (me 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.010 ANatesarrow_forwardI need typing answer urgentarrow_forward
- Please answer d,e,farrow_forwardDrow the shear and bending diagramarrow_forwardQuestion 1 a) A standard mild steel tensile test specimen has a diameter of 16mm and a gauge length of 80mm. the specimen was tested to destruction and the following results obtained, Load at yield point = 87KN Extension at yield point = 173 x 10“ m Ultimate load = 124KN %3D Total extension at fracture = 24mm Diameter of specimen at fracture = 9.8mm Cross-sectional area at fracture = 75.4mm? Cross-sectional area "A" = 200mm² Compute the followings: Modulus of elasticity of steel. Ultimate tensile stress. i. ii. iii. Yield stress iv. Percentage elongation.arrow_forward
- A steel specimen is tested in tension. The specimen is 1" wide by 0.5" thick in the test region. By monitoring the stresses from the testing machine, it was found that the specimen yielded at a stress of 72 ksi and fractured at 96 ksi. (a). Determine the tensile loads at yield and at fracturearrow_forward2. A specimen of steel 25mm diameter witha guage langth of 200 mm is tested to destruction. It has an extension of 0.16mm under a load of 80 kn and the load at elastic limit is 160 kN. The maximum load is 180 kN. The total extension at fracture is 56 mm and diameter at neck is 18 mm. Find a. The stress at elastic limit b. Youngs's Modulus c. Percentage elongation d. Percentage reduction in area e. Ultimate tensile stressarrow_forward2 please include scketcharrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





