
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:6.
7.
8.
9.
20.
O
O
ICT
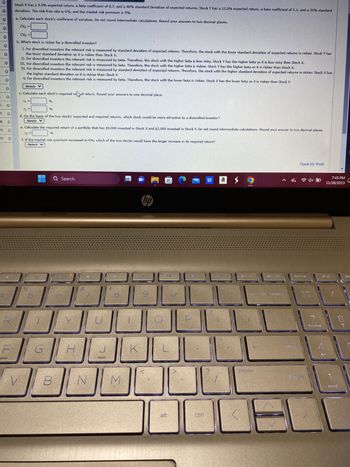
Stock X has a 9.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.7, and a 40% standard deviation of expected returns. Stock Y has a 12.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 1.1, and a 30% standard
deviation. The risk-free rate is 6%, and the market risk premium is 5%.
a. Calculate each stock's coefficient of variation. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places.
CVx =
CVy
b. Which stock is riskier for a diversified investor?
-
the lower standard deviation so it is riskier than Stock X.
I. For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by standard deviation of expected returns. Therefore, the stock with the lower standard deviation of expected returns is riskier. Stock Y has
II. For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by beta. Therefore, the stock with the higher beta is less risky. Stock Y has the higher beta so it is less risky than Stock X.
III. For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by beta. Therefore, the stock with the higher beta is riskier. Stock Y has the higher beta so it is riskier than Stock X.
IV. For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by standard deviation of expected returns. Therefore, the stock with the higher standard deviation of expected returns is riskier. Stock X has
the higher standard deviation so it is riskier than Stock Y.
V. For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by beta. Therefore, the stock with the lower beta is riskier. Stock X has the lower beta so it is riskier than Stock Y.
V
-Select-
c. Calculate each stock's required raof return. Round your answers to one decimal place.
Tx =
2
Ty
-
%
%
d. On the basis of the two stocks' expected and required returns, which stock would be more attractive to a diversified investor?
-Select-
e. Calculate the required return of a portfolio that has $9,000 invested in Stock X and $3,000 invested in Stock Y. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places.
гр =
%
f. If the market risk premium increased to 6%, which of the two stocks would have the larger increase in its required return?
-Select-
B
Q Search
H
N
U
Ľ
M
hp
K
JL
alt
ctrl
a
0
HISTOR
prt sc
pause
delete
backspace
Check My Work
home
enter
4x
num
lock
T shit
7
home
7:45 PM
11/28/2023
end
1
end
004
po
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the index model for stocks A and B is estimated from excess returns with the following results: RA = 3.6% + 1.2RM + eA RB = -1.6% + 1.5RM + eB OM = 16%; R-squarea = 0.25; R-square; = 0.15 What is the covariance between each stock and the market index? (Calculate using numbers in decimal form, not percentages. Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) Covariance Stock A Stock Barrow_forwardStock Y has a beta of 0.9 and an expected return of 9.46 percent. Stock Z has a beta of 2.1 and an expected return of 15.59 percent. What would the risk-free rate (in percent) have to be for the two stocks to be correctly priced relative to each other? Answer to two decimals.arrow_forwardConsider the following information on Stocks I and II: The market risk premium is 8 percent and the risk-free rate is 40.5 percent. a-1. What is the beta of each stock? Note: Do not round Intermedlate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. a-2. Which stock has the most systematic risk? Stock I Stock II b-1. What is the standard deviation of each stock? Note: Do not round Intermedlate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b.2. Which one has the most unsystemstic risk? Stock I Stock II c. Which stock is "riskier"? Stock I Stock IIarrow_forward
- The index model has been estimated for stocks A and B with the following results: = 0.12 +0.670RM+еA RA= RB=0.04 +1.512RM + еB °M= 0.330 σ(eд) = 0.20 σ(eB) = 0.10 What is the covariance between each stock and the market index? (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.) Stock A covariance Stock B covariancearrow_forward6) see picarrow_forwardStock X has a 9.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.7, and a 40% standard deviation of expected returns. Stock Y has a 12.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 1.1, and a 20% standard deviation. The risk-free rate is 6%, and the market risk premium is 5%. Calculate each stock's coefficient of variation. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Calculate each stock's required rate of return. Round your answers to one decimal place. rx = % ry = % Calculate the required return of a portfolio that has $7,500 invested in Stock X and $2,500 invested in Stock Y. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. rp = %arrow_forward
- An analyst has modeled the stock of Crisp Trucking using a two-factor APT model. The risk-free rate is 5%, the expected return on the first factor (r₁) is 14%, and the expected return on the second factor (r2) is 8%. If bil 0.5 and bi2 = 0.8, what is Crisp's required return? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to one decimal place. % =arrow_forwardSuppose that the Index model for stocks A and B is estimated from excess returns with the following results: RA 3.5% 8.65RM + A Rg -1.6% +0.88RM + ep OM 21%; R-squareд 0.22; R-squareg 0.14 What are the covariance and the correlation coefficient between the two stocks? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Calculate using numbers in decimal form, not percentages. Round your answers to 4 decimal places. Covariance Correlation coefficientarrow_forwardYou are given the returns for the following three stocks: Stock B Stock C Stock A 14.00% 14.00% -19.00% 14.00 14.00 34.00 14.00 22.00 37.00 14.00 14.00 14.00 4.00 Year 1 2 3 4 5 7.00 13.00 Calculate the arithmetic return, geometric return, and standard deviation for each stock. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Arithmetic return Standard deviation Geometric return Stock A 14.01 % 0.00 % 14.01 % Stock B 14.00 % 14.01 % Stock C 14.00 % 14.02 %arrow_forward
- Suppose that the index model for stocks A and B is estimated from excess returns with the following results: RA= 5.0% + 1.30RM + eA RB= -2.0% + 1.6RM + eB sigmaM= 20% ; R-squareA= 0.20 ; R-squareB= 0.12 What is the standard deviation of each stock (write as percentage, rounded to 2 decimal places)?arrow_forwardCrimson Co. has a beta equal to 1.29 and a required return of 0.147 based on the CAPM. If the market risk premium is 0.041, the risk-free rate of return is Instruction: Type your answer as a decimal, and round to three decimal placesarrow_forwardPlease do stepwise and correct please ill like.. pls correctarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education