
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
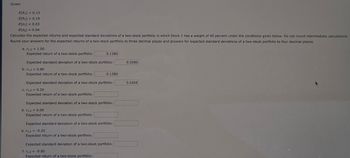
Transcribed Image Text:Given:
E(R1)
= 0.13
E(R2) = 0.19
E(01) = 0.03
E(02) = 0.04
Calculate the expected returns and expected standard deviations of a two-stock portfolio in which Stock 1 has a weight of 40 percent under the conditions given below. Do not round intermediate calculations.
Round your answers for the expected returns of a two-stock portfolio to three decimal places and answers for expected standard deviations of a two-stock portfolio to four decimal places.
a. 1,2=1.00
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
0.1280
0.0280
Expected standard deviation of a two-stock portfolio:
b. 1,2 = 0.80
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
0.1280
0.0266
Expected standard deviation of a two-stock portfolio:
C. 1,2
0.20
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
Expected standard deviation of a two-stock portfolio:
d. 1,2 = 0.00
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
Expected standard deviation of a two-stock portfolio:
e. 1,2 = -0.20
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
Expected standard deviation of a two-stock portfolio:
f. 1,2 = -0.80
Expected return of a two-stock portfolio:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Stocks A and B have the following returns: (Click on the folowing icon a in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Stock A Stock B 0.08 0.06 0.15 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.01 -0.01 0.09 -0.03 a. What are the expected roturns of the two stocks? b. What are the standard deviations of the returns of the two stocks? c. If their correlation is 048, what is the expected return and standard deviation of a portfolio of 75% stock A and 25% stock B? a. What are the expected returns of the two stocks? The expected return for stock A is (Round to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardConsider the following collection of n = 9 closing prices for stock ABC:101.02, 102.23, 100.34, 99.87, 98.65, 96.45, 98.45, 99.00, 100.05Compute the standard estimator of the volatility parameter σ using these closing prices.arrow_forwardThe index model has been estimated from the excess returns for stock A with the following results: = RA 12.00% +1.55RM+ eA °M = 24.00% σ(eд) = 18.50% What is the standard deviation of the return for stock A? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Standard deviation %arrow_forward
- Please do both questions QUESTION 1 Assume the following data for a stock: beta = 0.9; risk-free rate = 4 percent; market rate of return = 24 percent; and expected rate of return on the stock = 23 percent. Then the stock is: correctly priced. overpriced. this is the wrong answer underpriced. The answer cannot be determined. QUESTION 2 Assume the following data for a stock: beta = 1.5; risk-free rate = 8 percent; market rate of return = 18 percent; and expected rate of return on the stock = 22 percent. Then the stock is: overpriced. underpriced. this is the wrong answer correctly priced. cannot be determinedarrow_forwardConsider the three stocks in the following table. Pt represents price at time t, and Qt represents shares outstanding at time t. Stock C splits two-for-one in the last period. A B с Po 81 41 82 Rate of return 20 100 200 200 Divisor P1₁ 86 36 92 21 100 200 200 Required: a. Calculate the rate of return on a price-weighted index of the three stocks for the first period (t = 0 to t= 1). (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) % P2 86 36 46 Q2 100 200 400 b. What will be the divisor for the price-weighted index in year 2? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardData: So 101; X= 114; 1+r= 1.12. The two possibilities for sr are 143 and 85.arrow_forward
- Ο A stock has a required return of 16%, the risk-free rate is 5.5%, and the market risk premium is 4%. a. What is the stock's beta? Round your answer to two decimal places. b. If the market risk premium increased to 7%, what would happen to the stock's required rate of return? Assume that the risk-free rate and the beta remain unchanged. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. I. If the stock's beta is greater than 1.0, then the change in required rate of return will be greater than the change in the market risk premium. II. If the stock's beta is less than 1.0, then the change in required rate of return will be greater than the change in the market risk premium. III. If the stock's beta is greater than 1.0, then the change in required rate of return will be less than the change in the market risk premium. IV. If the stock's beta is equal to 1.0, then the change in required rate of return will be greater than the change in the market risk…arrow_forwardVinayarrow_forwardSuppose that the index model for stocks A and B is estimated from excess returns with the following results: RA = 3.6% + 1.2RM + eA RB = -1.6% + 1.5RM + eB OM = 16%; R-squarea = 0.25; R-square; = 0.15 What is the covariance between each stock and the market index? (Calculate using numbers in decimal form, not percentages. Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) Covariance Stock A Stock Barrow_forward
- Given the following information on five stocks, construct: a. A simple price-weighted average b. A value-weighted average c. A geometric average d. What is the percentage increase in each average if the stock prices change to those in Column I? e. What is the percentage increase in each average if the stock prices change from those in the Price column to those in Column II? f. Why were the percentage changes different in parts (d) and (e)? g. If you were managing a fund and wanted a source to compare your results to, which of the three averages would you prefer to use, and why? Stock Price # of Shares I II A B C D E F $12.00 150,000 $14.00 125,000 $11.00 200,000 $ 22.00 80,000 $8.00 30,000 $29.00 140,000 $12.00 $12.00 $14.00 $14.00 $20.00 $11.00 $ 22,00 $ 22.00 $8.00 $15.00 $29.00 $29.00arrow_forwardConsider the following information on Stocks I and II: The market risk premium is 8 percent and the risk-free rate is 40.5 percent. a-1. What is the beta of each stock? Note: Do not round Intermedlate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. a-2. Which stock has the most systematic risk? Stock I Stock II b-1. What is the standard deviation of each stock? Note: Do not round Intermedlate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b.2. Which one has the most unsystemstic risk? Stock I Stock II c. Which stock is "riskier"? Stock I Stock IIarrow_forwardConsider the three stocks in the following table. Pt represents price at time t, and Qt represents shares outstanding at time t. Stock C splits two-for-one in the last period. A B C Po 82 42 84 00 100 200 200 Divisor P1 87 37 94 01 100 200 200 P2 87 37 47 92 100 200 400 Required: a. Calculate the rate of return on a price-weighted index of the three stocks for the first period (t=0 to t= 1). (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Rate of return I % b. What will be the divisor for the price-weighted index in year 2? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) D c. Calculate the rate of return of the price-weighted index for the second period (t=1 to t = 2).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education