
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:A
weight (g)
Cmah-/- HFD
--wild type HFD
50- -Cmah-/-NCD
-wild type NCD
40-
30-
20+
0
2
6 8 10 12
study week
B
weight (g)
50-
40-
30-
20-
10-
wild type NCD
40
0.
Cmah-/-NCD
wild type HFD
Cmah-/-HFD
C
250-
E.
200-
150-
100-
glucose (mg/dL)
wild type NCD
0
Cmah-/- NCD
wild type HFD
Cmah-/- HFD

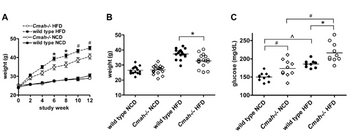
Transcribed Image Text:Next, compare blood glucose concentrations of wild type mice fed NCD to Cmah mice fed NCD.
Do these data support, contradict or say nothing about the hypothesis that the \textit{Cmah} gene
does not affect blood glucose? Explain your answer thoroughly.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer question number 5 asap.arrow_forwardLink: Lack of RAC1 in macrophages protects against atherosclerosis - PMC (nih.gov) Could somone explain exactly what this means below? NOT HW just trying to get a better understanding on what this experiment is about. To produce mice that are deficient for RAC1 in macrophages, female C57BL/6 mice homozygously expressing the floxed Rac1 gene (Rac1fl/fl) [6] were crossbred with male mice homozygously expressing Cre under the monocyte-specific lysozyme M promoter (LC) [12]. Mice were genotyped for Rac1 deficiency as previously describedarrow_forwardFollowing a mutagenesis experiment to identify novel genes affecting the circadian clock in Drosophila melanogaster you discover several mutants. You start considering two of those mutants that you call C and d. The two homozygous C/C and d/d are arrhythmic (arrhythmic is the definition of their phenotype), whereas the two heterozygous C/C and D/d are rhythmic (rhythmic is the definition of their phenotype) with a 24h period. You make two true-breeding stocks: stock 3 homozygous for C and stock 4 homozygous for d. You cross them in both directions and in both cases you observe complementation with no difference between males and females. Then you take the progeny of one cross, for instance the F1 of Females 3 x Males 4, and you perform a Testcross. Out of 1000 flies resulting from the Testcross only 125 are rhythmic. Using the number of flies expected for the Parental and the Recombinant genotypes and the formula that defines recombination frequency, what is the distance between loci C…arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forwardFollowing a mutagenesis experiment to identify novel genes affecting the circadian clock in Drosophila melanogaster you discover several mutants. You start considering two of those mutants that you call c and d. The two homozygous c/c and d/d are arrhythmic (arrhythmic is the definition of their phenotype), whereas the two heterozygous C/c and D/d are rhythmic (rhythmic is the definition of their phenotype) with a 24h period. You make two true-breeding stocks: stock 3 homozygous for c and stock 4 homozygous for d. You cross them in both directions and in both cases you observe complementation with no difference between males and females. Then you take the progeny of one cross, for instance the F1 of Females 3 x Males 4, and you perform a Testcross. Out of 1000 flies resulting from the lestcross only 125 are rhythmic. Using the number of flies expected for the Parental and the Recombinant genotypes and the formula that defines recombination frequency, what is the distance between loci C…arrow_forwardFollowing a mutagenesis experiment to identify novel genes affecting the circadian clock in Drosophila melanogaster you discover several mutants. You start considering two of those mutants that you call c and d. The two homozygous c/c and d/d are arrhythmic (arrhythmic is the definition of their phenotype), whereas the two heterozygous C/c and D/d are rhythmic (rhythmic is the definition of their phenotype) with a 24h period. You make two true-breeding stocks: stock 3 homozygous for c and stock 4 homozygous for d. You cross them in both directions and in both cases you observe complementation with no difference between males and females. Then you take the progeny of one cross, for instance the F1 of Females 3 x Males 4, and you perform a Testcross. Out of 1000 flies resulting from the Testcross only 125 are rhythmic. Comparing the number of flies expected for the Parental and the Recombinant genotypes, what can be concluded about the C and D loci? Select only one answer. 1. The…arrow_forward
- What data have been complied in the Human Protein Atlas? https://www.proteinatlas.org/about A.The Human Protein Atlas was created by integrating different omics technologies such as antibody-based imaging, proteomic analysis by mass spectrometry, transcriptomics and systems biology. B.The Human Protein Atlas was established by examining the distribution of proteins in a diseased tissue and inferring where the protein localize in a healthy tissue. C.The Human Protein Atlas was created by creating a list of all know proteins in alphabetical order. D.The Human Protein Atlas was created immunoblot analysis of proteins in different tissues.arrow_forwardIs it correct to conclude that these data support the notion that missing the Cmah gene causes higher blood glucose in mice no matter what type of diet they are on? Explain your answerarrow_forward1) Are NGN2-induced neurons (NGN2-iNs) the same as the cells in neural organoids? If not, how are they different? 2) Forced expression of the transcription factor neurogenin 2 (NGN2) induces human neurons, but to mature into electrophysiologically active neurons the require the presence of another cell type: what is that? 3)What kind of expression of NGN2 is associated with a central nervous system (CNS)-like cell? How do you know this?arrow_forward
- Standard 7a Rodents can make vocalizations that humans can hear, such as a squeal. But they also can communicate during social interactions using ultrasonic vocalizations - vocalizations at a frequency higher than the human ear is capable of hearing. Sex differences in vocal communication, similar to observations in songbirds, are observed In rats, with adult male rats eliciting a typical type of ultrasonic vocalizations not observed in females. As noted elsewhere in this Problem Set, FOXP2 is involved in the development and neural control of vocalizations in a broad spectrum of species, including rodents. In humans it is linked to human speech and language disorders. In rats, FOXP2 has been related to sex-specific vocalizations, like the male-typical ultrasonic vocalizations. FOXP2 expression in neurons in the brain is greater in males than females. Further, recent research demonstrated that FOXP2 is a target of activated androgen receptors (Le specialize receptors that bind androgens…arrow_forward. You need to prepare 500 μL of a 250 µg/mL bovine gamma globulin solution, for one of your protein standards in the Bradford assay. The available bovine gamma globulin in the lab is in the form of a 2 mg/mL stock solution, and it can be diluted with deionized water. Describe or show below how you would create your desired 250 µg/mL solution.arrow_forwardFollowing a mutagenesis experiment to identify novel genes affecting the circadian clock in Drosophila melanogaster you discover several mutants. You start considering two of those mutants that you call c and d. The two homozygous c/c and d/d are arrhythmic (arrhythmic is the definition of their phenotype), whereas the two heterozygous C/c and D/d are rhythmic (rhythmic is the definition of their phenotype) with a 24h period. You make two true-breeding stocks: stock 3 homozygous for c and stock 4 homozygous for d. You cross them in both directions and in both cases you observe complementation with no difference between males and females. Then you take the progeny of one cross, for instance the F1 of Females 3 x Males 4, and you perform a Testcross. Out of 1000 flies resulting from the Testcross only 125 are rhythmic. Which is the genotype of the rhythmic flies resulting from the testcross? Select only one answer 1. C/C d/d 2. C/c D/d 3. C/c d/d 4. c/c…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education