
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
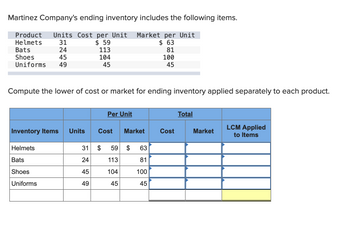
Transcribed Image Text:Martinez Company's ending inventory includes the following items.
Product Units Cost per Unit Market per Unit
Helmets
31
$59
$ 63
24
113
81
104
100
45
45
Bats
Shoes
45
Uniforms 49
Compute the lower of cost or market for ending inventory applied separately to each product.
Inventory Items Units
Helmets
Bats
Shoes
Uniforms
31
24
45
49
Per Unit
Cost
Market
$ 59 $ 63
113
81
104
100
45
45
Cost
Total
Market
LCM Applied
to Items
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 76 Company, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Number of Units Unit Cost Sales Beginning Inventory 260 $100 Sold 160 $140 Purchased 500 103 Sold 400 142 Purchased 420 110 Sold 370 174 Ending Inventory 250 Cost of Goods Sold FIFO $111,100 LIFO 97,900 AVG 96,805 Compare the ealculations for gross margin for A76 Company, based on the results of the perpetual inventory calculations using FIFO, LIFO, and AVG. Round intermediate calculation to 2 decimal places and final answer to nearest whole dollar. Comparison of FIFO, LIFO, AVG; Perpetual FIFO LIFO AVG Sales Revenue 24 Cost of Goods Sold Gross Marginarrow_forward! Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Trey Monson starts a merchandising business on December 1 and enters into the following three inventory purchases. Monson uses a perpetual inventory system. Also, on December 15, Monson sells 15 units for $39 each. Purchases on December 7 Purchases on December 14 Purchases on December 21 10 units @ $25.00 cost 20 units@ $31.00 cost 15 units @ $33.00 cost Of the units sold, 8 are from the December 7 purchase and 7 are from the December 14 purchase. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on specific identification.arrow_forwardAmes Trading Company has the following products in its ending inventory Cost per Unit Product Mountain bikes. Skateboards Gliders Inventory Items Quantity 12 22 12 Mountain bikes Skateboards Gliders $ 580 330 960 Compute lower of cost or market for inventory applied separately to each product. Units Market per Unit $ 510 370 910 Per Unit Cost Market Cost Total Market LCM applied to each productarrow_forward
- Skysong Company follows the practice of pricing its inventory at the lower-of-cost-or-market, on an individual-item basis. Item No. 1320 1333 1426 1437 1510 1522 1573 1626 Quantity 1,500 1,200 1,100 1,300 1,000 800 3,300 1,300 Cost per Unit $3.39 2.86 4.77 3.82 2.39 3.18 1.91 4.98 Cost to Replace $3.18 2.44 3.92 3.29 2.12 2.86 1.70 5.51 Estimated Selling Cost of Completion and Price Disposal $0.37 The amount of Skysong Company's inventory $ $4.77 3.71 5.30 3.39 3.45 4.03 2.65 6.36 From the information above, determine the amount of Skysong Company inventory. 0.53 0.42 0.27 0.85 0.42 0.80 0.53 Normal Profit $1.33 0.53 1.06 0.95 0.64 0.53 0.53 1.06arrow_forwardsssarrow_forwardThe following inventory information is gathered from the accounting records of Tucker Enterprises: # of Units x Unit Cost = Total Beginning Inventory 4000 x 5 Purchases 6000 x 7 Sales 9000 x 10 Ending Inventory 1000 a. Calculate Ending Inventory # of Units Unit Cost Ending Inventory 1.FIFO 0 $- 2.LIFO 0 $- 3.Weighted Average Cost 0 $- $- $- $- b. Cost of Goods Sold # of Units # of Units Unit cost Unit cost Cost of Goods Sold 1.FIFO $- 2.LIFO $- 3.Weighted Average Cost $- $- 0 $- c.Gross profit using each of the following methods: Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit 1.FIFO $- $- $- 2.LIFO $- $- $- 3.Weighted Average Cost $- $- $-arrow_forward
- Han Company has three products in its ending inventory. Specific per unit data at the end of the year for each of the products are as follows: Cost Replacement cost Selling price Selling costs Normal profit Product 1 2 3 $ Cost Required: What unit values should Han use for each of its products when applying the lower of cost or market (LCM) rule to ending inventory? Product 1 $28 26 48 5 13 28 $ 98 58 Q Search Replacement cost 26 93 48 Product 2 $98 93 128 or 30 38 NRV Product 3 $58 48 60 10 20 W ENG 4x D 4:45 PM 11/27/2023arrow_forwardLower-of-Cost-or-Net Realizable Value Method The following data are taken from the Hilton Corporation’s inventory accounts: Item Code Quantity Unit Cost Net Realizable Value Product 1 XKE 100 $32 $28 XKF 400 43 44 Product 2 ZNJ 400 32 29 ZNS 300 43 48 Calculate the value of the company’s ending inventory using the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable method applied to each item of inventory. Applying the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value method to each item of the inventory results in an ending inventory amount of $Answerarrow_forwardGiven the following: Numberpurchased Costper unit Total January 1 inventory 32 $ 4 $ 128 April 1 52 6 312 June 1 42 7 294 November 1 47 8 376 173 $ 1,110 a. Calculate the cost of ending inventory using the FIFO (ending inventory shows 53 units). b. Calculate the cost of goods sold using the FIFO (ending inventory shows 53 units).arrow_forward
- Please do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardOriole Company follows the practice of pricing its inventory at the lower-of-cost-or-market, on an individual-item basis. Item No. 1320 1333 1426 1437 1510 1522 1573 1626 Quantity 1,400 1,100 1,000 1,200 900 700 3,200 1,200 Cost per Unit $3.84 3.24 5.40 4.32 2.70 3.60 2.16 5.64 Cost to Replace $3.60 2.76 The amount of Oriole Company's inventory $ 4.44 3.72 2.40 3.24 1.92 6.24 Estimated Selling Price $5.40 4.20 6.00 3.84 3.90 4.56 3.00 7.20 From the information above, determine the amount of Oriole Company inventory. Cost of Completion and Disposal $0.42 0.60 0.48 0.30 0.96 0.48 0.90 0.60 Normal Profit $1.50 0.60 1.20 1.08 0.72 0.60 0.60 1.20arrow_forwardDetermine the ending inventory amount by applying the lower of cost or market value to a. Each inventory item of inventoryb. Total inventory The following data refer to Froning Company’s ending inventoryItem Code, Quantity, Unit Cost, Unit MarketLXC 60 $45 $48KMT 210 $38 $34MOR 300 $22 $20NES 100 $27 $32arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education