
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
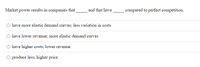
Transcribed Image Text:Market power results in companies that
and that have
compared to perfect competition.
have more elastic demand curves; less variation in costs
have lower revenue; more elastic demand curves
have higher costs; lower revenue
produce less; higher price
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 12 Examine the graph below. Assume this firm is producing at its profit-maximizing output. In the long run, if prices remain as shown here, this firm will SA MC ATC 13 12 11 10 AVC 6 6 0 3 8 0 12 15 18 21 q stay in the market and make a profit have zero economic profit O exit the market shut down have losses equal to fixed costs 9 B 7arrow_forwardEconomic theory would suggest that the profitability of an industry would be O inversely related to the number of firms competing in the industry. O unrelated to the number of firms competing in the industry. O zero in the long run, regardless of market structure. O directly related to the number of firms competing in the industry.arrow_forwardIn a perfect market the TR and TC create a ___________________breakeven quantity whenever the MC is constant and the potential profit is ___________________________________?arrow_forward
- What are the three conditions for a market to be perfectly competitive? For a market to be perfectly competitive, there must be O A. many buyers and a small number of firms that compete, selling identical products, and barriers to new firms entering the market. O B. many buyers and one seller, with the firm producing a product that has no close substitutes, and barriers to new firms entering the market. OC. many buyers and a few sellers, with all firms selling identical products, and no barriers to new firms entering the market. O D. many buyers and sellers, with all firms selling identical products, and no barriers to new firms entering the market. O E. many buyers and sellers, with firms selling similar but not identical products, with low barriers new firms entering the market.arrow_forwardHi hlo Expert Hand written solution is not allowed.arrow_forwardWhich one of these goods is likely to have the largest substitution effect? Select one: a. Skittles candy b. Honda Accord c. Flour d. Electricity e. Gasolinearrow_forward
- this question is too confusing for me please helparrow_forwardWhat is a price taker? A price taker is O A. a firm with a downward-sloping demand curve. O B. a firm that is unable to affect the market price. Oc. a firm with a perfectly inelastic demand curve. O D. a firm that has the ability to charge price greater than marginal cost. O E. a firm that does not seek to maximize profits. When are firms likely to be price takers? A firm is likely to be a price taker when O A. it sells a differentiated product. O B. barriers to entry are substantial. OC. it has market power. O D. it represents a small fraction of the total market,. O E. firms in the industry collude.arrow_forwardHow to sovle these? What's the right answer?arrow_forward
- Consider a firm with market power. As firms exit the industry: D O the firm's supply curve will shift leftward. O the firm's demand curve will become flatter. O the firm's average cost curve will shift upward. O the firm's demand curve will become steeper.arrow_forwardThe table shown displays the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. Price $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $56 When one unit is produced exceed O marginal costs, marginal revenue, more O marginal revenue; marginal costs more O marginal revenue, marginal costs; less Omarginal costs, marginal revenue, less and the fem should produce Quantity 0 1 2 3 4 15 TC $10.00 $20.00 $2750 $77 50 $147.50 $250 00arrow_forwardExplanation it correctly and detailsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education