
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
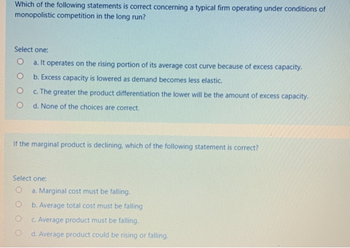
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following statements is correct concerning a typical firm operating under conditions of
monopolistic competition in the long run?
Select one:
O
O
O
O
a. It operates on the rising portion of its average cost curve because of excess capacity.
b. Excess capacity is lowered as demand becomes less elastic.
c. The greater the product differentiation the lower will be the amount of excess capacity.
d. None of the choices are correct.
If the marginal product is declining, which of the following statement is correct?
Select one:
a. Marginal cost must be falling.
b. Average total cost must be falling
c. Average product must be falling.
d. Average product could be rising or falling.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Why are oligopolistic firms not allocatively efficient? A. They face a downward-sloping demand curve. B. They produce below the point where average total costs are lowest C. They produce at a point where there's deadweight loss. OD. They are able to earn positive economic profits. ← PREVIOUS ubmission SUBMIT VIEWarrow_forwardQ50arrow_forwardIn an monopolistic competitive industry, firms can earn positive economic profits Select one: a. In the short run and in the long run. b. In the short run but not in the long run. c. Both in the short run and long run as he does not lose money. d. In the long run but not in the short run.arrow_forward
- . Which market condition (Monopoly, Perfect Competition, Duopoly, or monopolistic competition) is good for customers and why? Illustrate your choice with an appropriate scenarioarrow_forwardQuestion 4 All of these are characteristic of monopolistic competition, EXCEPT: O A. free entry and exit. O B. barriers to entry. OC. product differentiation. OD. price maker.arrow_forwardExhibit 10.5 Price 3.25 3.00 2.50 0 700 1,000 MC MR ATC D = AR Quantity Exhibit 10.5 shows the demand, marginal revenue, and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output and price, the firm would O a. have to expand to stay in business in the long run. O b. be better off shutting down, since total revenue does not cover fixed costs. O c. be experiencing an economic loss. O d. be earning an economic profit. O e. be earning zero economic profit.arrow_forward
- What issues do the online businesses face? How are they similar to offline competition? How are these issues resolved (market v. nonmarket) in the online and offline business? Use the theory fo the 4 Is. Issues are understood as moral concerns, consequences, justice, and rights at stake which can be resolved by either market or non-market action.arrow_forwardFill in the blank and answer in 5-6 sentence onlyarrow_forwardThe firm in the figure below is in monopolistic competition. It will set a price equal to MC ATC MR D 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Quantity (units per day) O a. $1. O b. $3. O c. more than $3. O d. $2. Price and costs (dollars per unit)arrow_forward
- Refer to Figure 17-5. Efficient scale is reached O a. at 100 units. O b. beyond 133.33 units. O c. at 133.33 units. O d. between 100 and 133.33 units. 13 Figure 17-5 The figure is drawn for a monopolistically competitive firm. PRICE MC 140 123.33 ATC Demand 90 56.67 100 133.33 QUANTITY MRarrow_forwardWhich of the following market types has all firms selling products so identical that buyers do not care from which firm they buy? Select one: O a. monopolistic competition O b. oligopoly O c. monopoly O d. perfect competitionarrow_forwarda. Compared to pure monopoly and pure competition, monopolistically competitive industries O might have economic profits, they will diminish as competitors enter, and there will be productive inefficiency. O will have economic profits, they will remain constant as competitors enter, and there will be productive efficiency. O will have economic profits, they will diminish constant as competitors enter, and there will be productive efficiency. O might have economic profits, they will remain constant as competitors enter, and there will be productive efficiency.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education