
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
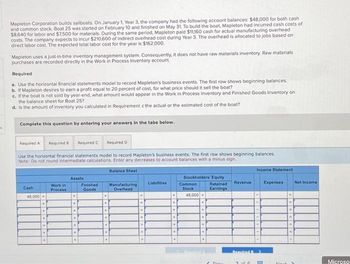
Transcribed Image Text:$
Mapleton Corporation builds sailboats. On January 1, Year 3, the company had the following account balances: $48,000 for both cash
and common stock, Boat 25 was started on February 10 and finished on May 31. To build the boat, Mapleton had incurred cash costs of
$8,640 for labor and $7,500 for materials. During the same period, Mapleton paid $11,160 cash for actual manufacturing overhead
costs. The company expects to incur $210,600 of indirect overhead cost during Year 3. The overhead is allocated to jobs based on
direct labor cost. The expected total labor cost for the year is $162,000.
Mapleton uses a just-in-time inventory management system. Consequently, it does not have raw materials inventory. Raw materials
purchases are recorded directly in the Work in Process Inventory account.
Required
a. Use the horizontal financial statements model to record Mapleton's business events. The first row shows beginning balances.
b. If Mapleton desires to earn a profit equal to 20 percent of cost, for what price should it sell the boat?
c. If the boat is not sold by year-end, what amount would appear in the Work in Process Inventory and Finished Goods Inventory on
the balance sheet for Boat 25?
d. is the amount of inventory you calculated in Requirement c the actual or the estimated cost of the boat?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required A
Required B Required C
Use the horizontal financial statements model to record Mapleton's business events. The first row shows beginning balances.
Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter any decreases to account balances with a minus sign.
Balance Sheet
Cash
48,000+
+
♦
Work in
Process
Assets
Required D
Finished
Goods
Manufacturing
Overhead
Liabilities
Stockholders' Equity
Retained
Earnings
Common
Stock
48,000.
+
Prov
Revenue
Income Statement
Required >
2 of 6
Expenses
blout
Net Income
Microso
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Global Traders purchases a piece of equipment for $1.5 million and incurs the following expenses: Freight charges = $250,000 Installation charges = $25,000 Cost of training machine maintenance staff = $12,000 Cost of strengthening the factory floor = $5,500 Cost of painting factory walls = $7,000 The amounts capitalized and expensed by the company are closest to: Balance Sheet ($) A 1,775,000 B 1,780,500 C 1,792,500 O Row B Row C Row A Income Statement ($) 24,500 19,000 7,000arrow_forwardJurvin Enterprises is a manufacturing company with no beginning inventories. A subset of the transactions it recorded during a recent month is shown below. a. Purchased $75,700 in raw materials for cash. b. $71,700 in raw materials were used in production. Of this amount, $65,200 was direct materials and the remainder was indirect materials. c. Paid employees $152,700 cash. Of this amount, $133,700 was direct labor and the remainder was indirect labor. d. Paid $126,000 for additional manufacturing overhead costs. e. Applied manufacturing overhead of $130,500 to production using the company's predetermined overhead rate. f. All of the jobs in process at the end of the month were completed. g. All of the completed jobs were shipped to customers. h. Any underapplied or overapplied overhead was closed to Cost of Goods Sold. Required: 1. Post the above transactions to T-accounts. 2. Calculate the adjusted cost of goods sold for the period.arrow_forwardA consumer electronics company was formed to develop cell phones that run on or are recharged by fuel cells. The company purchased a warehouse and converted it into a manufacturing plant for $8,000,000. It completed installation of assembly equipment worth $1,700,000 on December 31st. The plant began operation on January 1st. The company had a gross income of $8,600,000 for the calendar year. Manufacturing costs and all operating expenses, excluding the capital expenditures, were $2,170,000. The depreciation expenses for capital expenditures amounted to $465,000. The corporate tax rate is 21%. (a) Compute the taxable income of this company. The taxable income of this company is $ 5965000. (Round to the nearest dollar.) (b) How much will the company pay in federal income taxes for the year? The federal income taxes for the year will be $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forward
- The Juarez Corporation incurred the following transactions during its first year of operations. (Assume all transactions involve cash). 1) Acquired $1,800 of capital from the owners. 2) Purchased $380 of direct raw materials. 3) Used $280 of these direct raw materials in the production process. 4) Paid production workers $480 cash. 5) Paid $280 for manufacturing overhead (applied and actual overhead are the same). 6) Started and completed 260 units of inventory. 7) Sold 130 units at a price of $6 each. 8) Paid $120 for selling and administrative expenses. The amount of cost of goods manufactured would be:arrow_forwardSpacely Sprockets, Inc. invested $4,995,000 for new manufacturing equipment for its plant in Jetson, NY. The equipment was anticipated to have a useful life of 11 years, or 29,800 machine hours and a residual value of $507,000. In its first year in operation the equipment was used for 2,180 hours and an additional 2,700 hours in its second year of usage.The Income Statement for years 1 and 2 of Spacely Sprockets, Inc. are shown below.All items rounded to nearest whole dollar. Spacely Sprockets, Inc. Year 1 Year 2 Net Sales $35,590,000 $36,164,000 COGS $23,120,000 $22,978,000 Gross Profit $12,470,000 $13,186,000 Operating Expenses(before adding in Depreciation) $7,650,000 $8,152,000 Income from Operations $4,820,000 $5,034,000 Income Tax Expense (at 30%) $1,446,000 $1,510,200 Net Income $3,374,000 $3,523,800 Round all items to the nearest whole dollar and use rounded values for all future calculations.1. Calculate the depreciation expense for year 1 and 2 using…arrow_forwardHarshman Company constructed a building for its own use. The company incurred costs of $45,000 for materials and supplies, $64,000 for direct labor, and $5,000 for a supervisor's overtime that was caused by the construction. Harshman uses a factory overhead rate of 50% of direct labor cost. Before construction, the company had received a bid of $159,000 from an outside contractor. 1. Assuming common practice is followed, at what value should Harshman capitalize the building? 2. The cost of the constructed asset will more closely approximate the cost of an equivalent purchased asset when the approach is used.arrow_forward
- A consumer electronics company was formed to develop cell phones that run on or are recharged by fuel cells. The company purchased a warehouse and converted it into a manufacturing plant for $8,000,000. It completed installation of assembly equipment worth $1,700,000 on December 31st. The plant began operation on January 1st. The company had a gross income of $8,600,000 for the calendar year. Manufacturing costs and all operating expenses, excluding the capital expenditures, were $2,170,000. The depreciation expenses for capital expenditures amounted to $465,000. The corporate tax rate is 21%. (a) Compute the taxable income of this company. The taxable income of this company is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardJurvin Enterprises is a manufacturing company with no beginning inventories. A subset of the transactions it recorded during a recent month is shown below. a. Purchased $75,700 in raw materials for cash. b. $71,200 in raw materials were used in production. Of this amount, $66,600 was direct materials and the remainder was indirect materials. c. Paid employees $152,900 cash. Of this amount, $134,500 was direct labor and the remainder was indirect labor. d. Paid $126,000 for additional manufacturing overhead costs. e. Applied manufacturing overhead of $128,000 to production using the company's predetermined overhead rate. f. All of the jobs in process at the end of the month were completed. g. All of the completed jobs were shipped to customers. h. Any underapplied or overapplied overhead was closed to Cost of Goods Sold. Required: 1. Post the above transactions to T-accounts. 2. Calculate the adjusted cost of goods sold for the period. Complete this question by entering your answers in…arrow_forwardJurvin Enterprises is a manufacturing company with no beginning inventories. A subset of the transactions it recorded during a recent month is shown below. a. Purchased $76,500 in raw materials for cash. b. $71,500 in raw materials were used in production. Of this amount, $65,500 was direct materials and the remainder was indirect materials. c. Paid employees $150,800 cash. Of this amount, $134,200 was direct labor and the remainder was indirect labor. d. Paid $126,300 for additional manufacturing overhead costs. e. Applied manufacturing overhead of $127,900 to production using the company's predetermined overhead rate. f. All of the jobs in process at the end of the month were completed. g. All of the completed jobs were shipped to customers. h. Any underapplied or overapplied overhead was closed to Cost of Goods Sold. Required: 1. Post the above transactions to T-accounts. 2. Calculate the adjusted cost of goods sold for the period.arrow_forward
- Solomon Company started year 1 with $270,000 in its cash and common stock accounts. During year 1, Solomon paid $202,500 cash for employee compensation and $62,100 cash for materials. Required Determine the total amount of assets and the amount of expense shown on the year 1 financial statements assuming Solomon used the labor and materials to make 1,500 chairs. Further, assume that Solomon sold 1,200 of the chairs it made. State the name(s) of the expense account(s) shown on the income statement. Determine the total amount of assets and the amount of expense shown on the year 1 financial statements assuming Solomon used the labor and materials to provide dental cleaning services to 500 patients. State the name(s) of the expense account(s) shown on the income statementarrow_forwardA construction company entered into a fixed-price contract to build an office building for $36 million. Construction costs incurred during the first year were $9 million, and estimated costs to complete at the end of the year were $21 million. The company recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. During the first year the company billed its customer $9 million, of which $6 million was collected before year-end. What would appear in the year-end balance sheet related to this contract? Note: Enter your answers in whole dollars and not in millions (i.e., $4 million should be entered as $4,000,000). > Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Balance Sheet (Partial) Assets: Accounts receivable Costs plus profit in excess of billings $ 3,000,000 $ 9,429,600 Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education