
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
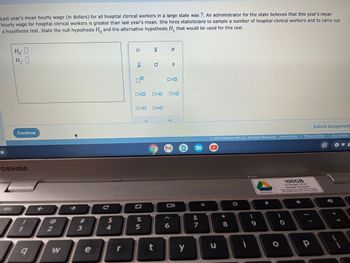
Transcribed Image Text:Last year's mean hourly wage (in dollars) for all hospital clerical workers in a large state was 7. An administrator for the state believes that this year's mean
hourly wage for hospital clerical workers is greater than last year's mean. She hires statisticians to sample a number of hospital clerical workers and to carry out
a hypothesis test. State the null hypothesis Ho and the alternative hypothesis H₁ that would be used for this test.
Ho: O
H₁: 0
esc
Continue
TOSHIBA
1
9
2
M
# 3
e
C
54
r
U
ô
09
OSO
0=0
%
5
t
a XI
>
p
(6
S
<D
NE
Oll
0
Y
&
7
2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
u
* 00
8
i
9
GMAE05733011
O
Submit Assignment
100GB
of Google Drive
storage included
"Offer subject to change without notice-
see Google Drive terms for more details
0
p
2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A facilities manager at a university reads in a research report that the mean amount of time spent in the shower by an adult is 5 minutes. He decides to collect data to see if the mean amount of time that college students spend in the shower is significantly different from 5 minutes. In a sample of 15 students, he found the average time was 4.61 minutes and the standard deviation was 0.75 minutes. Using this sample information, conduct the appropriate hypothesis test at the 0.05 level of significance. Assume normality. a) What are the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses? Но: х = 5 versus Ha: x # 5 5 versus Ha: H 5 Но: и Но: и 5 versus Ha: l # 5 b) What is the test statistic? Give your answer to four decimal places. -2.0140 c) What is the P-value for the test? Give your answer to four decimal places. 1.9560 X d) What is the appropriate conclusion? Fail to reject the claim that the mean time is 5 minutes because the P-value is larger than 0.05 Fail to reject the claim that the…arrow_forwardA magazine reported that at the top 50 business schools in a region, students studied an average of 12.5 hours. Set up a hypothesis test to try to prove that the mean number of hours studied at your school is different from the reported 12.5 hour benchmark. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Question content area bottom Part 1 a. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. H0: α=12.5 H1: β≠12.5 B. H0: α≠12.5 H1: α=12.5 C. H0: α=12.5 H1: α≠12.5 D. H0: μ=12.5 H1: X≠12.5 E. H0: μ≠12.5 H1: X=12.5 F. H0: β≠12.5 H1: β=12.5 G. H0: μ=12.5 H1: μ≠12.5 H. H0: X=12.5 H1: X≠12.5 I. H0: α≠12.5 H1: β=12.5 J. H0: X≠12.5 H1: X=12.5 K. H0: μ≠12.5 H1: μ=12.5 L. H0: β=12.5 H1: β≠arrow_forwardState the null and alternative hypotheses. John, a restaurant owner, suspects that prices of tomatoes in Bury are higher than the rest of Manchester. He finds that the city average price of a certain type of premium tomatoes is £20.9 with standard deviation £0.95. He takes a sample of this type of tomato from 5 local Bury stores and obtains an average price of £22.46.arrow_forward
- You are a researcher verifying the claim that the average adult consumes 1.7 cups of coffee per day. The population standard deviation is 0.5 cups per day. You sample 30 adults and find the average is 1.85 cups per day. Test the claim above at the alpha = 0.05 significance level. What do you conclude about the number of cups of coffee that adults consume each day? Group of answer choices - You cannot reject the null hypothesis. Even though your sample indicated 1.85 cups, there still is not sufficient evidence to overturn the claim that adults consume 1.7 cups per day. - This is a borderline case where the test statistic and the critical values are the same. We can neither accept nor reject the null hypothesis in this case. - You reject the null hypothesis. With thirty people consuming 1.85 cups on average , there is sufficient evidence to overturn the claim that adults consume 1.7 cups per day.arrow_forwardYou wish to test the claim that the average IQ score is less than 100 at the .01 significance level. You determine the hypotheses are: Ho: μ=100 H1:μ<100H You take a simple random sample of 79 individuals and find the mean IQ score is 98.3, with a standard deviation of 15.3. Let's consider testing this hypothesis two ways: once with assuming the population standard deviation is not known and once with assuming that it is known. Round to three decimal places where appropriate. Assume Population Standard Deviation is NOT known Assume Population Standard Deviation is 15 Test Statistic: t = Test Statistic: z = Critical Value: t = Critical Value: z = p-value: p-value: Conclusion About the Null: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesis Conclusion About the Null: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesis Conclusion About the Claim: There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the average IQ score is less…arrow_forwardProf. Gersch does a statistical test and finds his p-value to be 0.038. If he had set his significance level to 0.05 prior to the test, then what should he decide? a. He should reject the null hypothesis with reservations about the test methods. b. He should decide to conduct another test with a greater sample size. c. He should decide to conduct another test with a greater significance level. d. He should not reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. e. He should reject the alternative hypothesis in favor of the null hypothesis. f. He should reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.arrow_forward
- In 1990, the average duration of long-distance telephone calls originating in one town was 9.4 minutes. A long-distance telephone company wants to perform a significance test to determine whether the average duration of long-distance phone calls has changed from the 1990 mean of 9.4 minutes. The hypotheses are: H0: μ = 9.4 minutes HA: μ ≠ 9.4 minutesSuppose that the results of the sample lead to non-rejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion as a Type I error, a Type II error, or a correct decision, if in fact the mean duration of long-distance phone calls has changed from the 1990 mean of 9.4 minutes. Choose the best asnwer below: A. Neither B. Type I error C. Type II error D.No errorarrow_forwardOnly 15% of registered voters voted in the last election. Will voter participation increase for the upcoming election? Of the 347 randomly selected registered voters surveyed, 56 of them will vote in the upcoming election. What can be concluded at the a = 0.01 level of significance? a. For this study, we should use z-test for a population proportion b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Họ: ? Select an answer (please enter a decimal) H.: ?vSelect an answer v (Please enter a decimal) c. The test statistic ?v (please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) d. The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) e. The p-value is v f. Based on this, we should fail to reject g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly higher than 15% at a = 0.01, so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the percentage of registered voters who will vote in the upcoming election will be equal to 15%. a…arrow_forwardAccording to a large oil company, the average cost per barrel of oil last year was $47. You believe that due to the current oil crisis in Russia and Iran that the cost of a barrel of oil has decreased. You collect a simple random sample of 60 barrels of oil and find an average price of $42 and a standard deviation of $12. Use this information to answer the following questions and conduct the hypothesis test with a level of significance of a = .01. You may use Statcrunch or a calculator. Write all non-calculation answers in complete sentences. a. Which test would you use and why? b. Write the null and alternative hypothesis in complete sentences. (Make sure you mark which is the null and which is the alternative.) c. Write the null and alternative hypothesis as symbols. d. State the requirements that have been met to run the test. e. What is the test statistic and the p-value? (Make sure you use the right notation.) f. Should you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? g. State…arrow_forward
- Suppose the national average dollar amount for an automobile insurance claim is $670.543. You work for an agency in Michigan and you are interested in whether or not the state average is different from the national average. The hypotheses for this scenario are as follows: Null Hypothesis: μ = 670.543, Alternative Hypothesis: μ ≠ 670.543. A random sample of 27 claims shows an average amount of $668.645 with a standard deviation of $68.6867. What is the test statistic and p-value for this test? Question 8 options: 1) Test Statistic: -0.144, P-Value: 0.44345 2) Test Statistic: -0.144, P-Value: 0.5566 3) Test Statistic: -0.144, P-Value: 1.5566 4) Test Statistic: 0.144, P-Value: 0.8869 5) Test Statistic: -0.144, P-Value: 0.8869arrow_forwardThe U.S. Postal Service (USPS) is faced with the issue of a large portion of mail (letters and packages) that cannot be delivered because of an illegible or non-existent address. USPS would like to find out if there is any evidence that the proportion of undeliverable mail has significantly decreased since last year when it was 6%. Which of the following are the correct null and alternative hypotheses for this test? Select one: a. Ho: p = 0.06 versus Ha:p> 0.06 b. Ho: p 0.06 ge Next page Moodle Accessibility Specification Coastal Carolina University (CCU) does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, genc national origin, age, genetic information, mental or physical disability, or status as a disabled or Vietnam-era veteran in it programs, activities or employment practices. For more information related to discrimination, please contact Title IX, Titl office phone 843-349-2382: FEN email eenarnastal adur or thel Dent of Education office for…arrow_forwardThe College Board reports that the scores on the math SAT were normally distributed with a mean of 525. A random sample of 15 students at your high school had a mean of 550 and a sample standard deviation of 105. What values of the sample mean would lead to rejection of the null hypothesis at the 0.01 level of significance?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman