
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
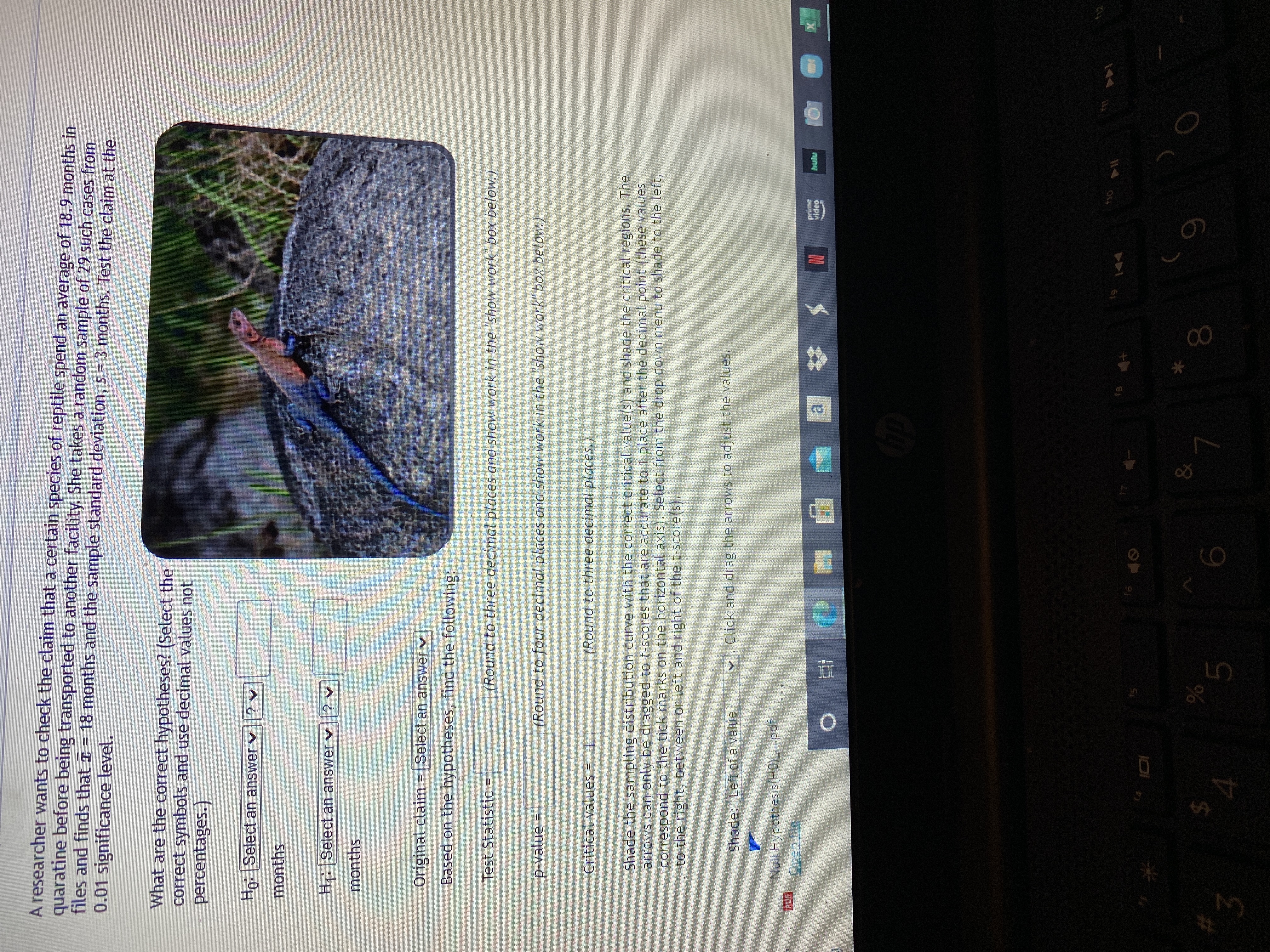
Transcribed Image Text:A researcher wants to check the claim that a certain species of reptile spend an average of 18.9 months in
quaratine before being transported to another facility. She takes a random sample of 29 such cases from
files and finds that I
= 18 months and the sample standard deviation, s = 3 months. Test the claim at the
0.01 significance level.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A manufacturer claims that a certain brand of cold tablets contains an average 600 mg of acetaminophen. To test this claim, a researcher creates a random sample of 32 tablets. The mean of this sample is 631.7 mg, and the standard deviation is 62.3 mg. Test the claim using a level of significance of 1%. What type of test will be used in this problem? What evidence justifies the use of this test? Check all that apply The original population is approximately normal The population standard deviation is not known The sample standard deviation is not known There are two different samples being compared np>5 and nq>5 The sample size is larger than 30 The population standard deviation is known Enter the null hypothesis for this test.H0 Enter the alternative hypothesis for this test.H1: Is the original claim located in the null or alternative hypothesis? What is the test statistic for the given statistics? What is the p-value for this test? What is the decision…arrow_forwardMany cheeses are produced in the shape of a wheel. Because of the differences in consistency between these different types of cheese, the amount of cheese, measured by weight, varies from wheel to wheel. Heidi Cembert wishes to determine whether there is a significant difference, at the 10% level, between the weight per wheel of Gouda and Brie cheese. She randomly samples 18 wheels of Gouda and finds the mean is 1.3 lb with a standard deviation of 0.3 lb; she then randomly samples 10 wheels of Brie and finds a mean of 0.95 lb and a standard deviation of 0.21 lb. What is the df and p-value for Heidi's hypothesis of equality? Assume normality. (Give your answer correct to four decimal places.)arrow_forwardI collected data on levels of anxiety after receiving three types of therapies (CBT, psycho education, and psycho analysis). Below are the anxiety scores for 9 patients. Is there a difference in anxiety based on treatment type ? CBT: 3, 2, 0 Psycho Education: 8, 8, 9 Psycho Analysis: 10, 12, 12 (Look at the table)arrow_forward
- A simple random sample of 37 men from a normally distributed population results in a standard deviation of 11.4 beats per minute. The normal range of pulse rates of adults is typically given as 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the range rule of thumb is applied to that normal range, the result is a standard deviation of 10 beats per minute. Use the sample results with a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that pulse rates of men have a standard deviation equal to 10 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: 0= 10 beats per minute O B. Ho: 0± 10 beats per minute H,: 0+ 10 beats per minute H,: 0= 10 beats per minute O C. Ho: o2 10 beats per minute H1: o< 10 beats per minute O D. Ho: 0 = 10 beats per minute H: o<10 beats per minutearrow_forwardA manufacturer claims that a certain brand of cold tablets contains an average 600 mg of acetaminophen. To test this claim, a researcher creates a random sample of 32 tablets. The mean of this sample is 631.7 mg, and the standard deviation is 62.3 mg. Test the claim using a level of significance of 1%. What type of test will be used in this problem? What evidence justifies the use of this test? Check all that apply The original population is approximately normal The population standard deviation is not known The sample standard deviation is not known There are two different samples being compared np>5 and nq>5 The sample size is larger than 30 The population standard deviation is known Enter the null hypothesis for this test.H0 Enter the alternative hypothesis for this test.H1: Is the original claim located in the null or alternative hypothesis? What is the test statistic for the given statistics? What is the p-value for this test? What is the decision…arrow_forwardIn a study of pulse rates of men, a simple random sample of 150 men results in a standard deviation of 11.4 beats per minute. The normal range of pulse rates of adults is typically given as 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the range rule of thumb is applied to that normal range, the result is a standard deviation of 10 beats per minute. Use the sample results with a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that pulse rates of men have a standard deviation equal to 10 beats per minute; see the accompanying StatCrunch display for this test. What do the results indicate about the effectiveness of using the range rule of thumb with the "normal range" from 60 to 100 beats per minute for estimating o in this case? Assume that the simple random sample is selected from a normally distributed population. Click the icon to view the StatCrunch display. Let o denote population standard deviation of the pulse rates of men (in beats per minute). Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: o H₁:…arrow_forward
- Volunteers who had developed a cold within the previous 24 hours were randomized to take either zinc or placebo lozenges every 2 to 3 hours until their cold symptoms were gone. Twenty-five participants took zinc lozenges, and 23 participants took placebo lozenges. The mean overall duration of symptoms for the zinc lozenge group was 3.5 days, and the standard deviation of overall duration of symptoms was 1.4 days. For the placebo group, the mean overall duration of symptoms was 7.2 days, and the standard deviation was 2 days. (a) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean overall duration of symptoms if everyone in the population were to take the zinc lozenges. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) to days (b) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean overall duration of symptoms if everyone in the population were to take the placebo lozenges. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) to daysarrow_forwardVolunteers who had developed a cold within the previous 24 hours were randomized to take either zinc or placebo lozenges every 2 to 3 hours until their cold symptoms were gone. Twenty-five participants took zinc lozenges, and 23 participants took placebo lozenges. The mean overall duration of symptoms for the zinc lozenge group was 4.5 days, and the standard deviation of overall duration of symptoms was 1.6 days. For the placebo group, the mean overall duration of symptoms was 8 days, and the standard deviation was 1.8 days. (a) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean overall duration of symptoms in a population of individuals like those who used the zinc lozenges. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)to days(b) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean overall duration of symptoms in a population of individuals like those who used the placebo lozenges. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)to days(c) On the basis of the intervals computed in parts (a) and…arrow_forwardA simple random sample of 34 men from a normally distributed population results in a standard deviation of 8.8 beats per minute. The normal range of pulse rates of adults is typically given as 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the range rule of thumb is applied to that normal range, the result is a standard deviation of 10 beats per minute. Use the sample results with a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that pulse rates of men have a standard deviation equal to 10 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. ... a. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. H: 0 10 beats per minute O B. H, o= 10 beats per minute H:o = 10 beats per minute H o<10 beats per minute O D. H, 62 10 beats per minute H o<10 beats per minute O C. H, o= 10 beats per minute H: 0 10 beats per minute b. Compute the test statistic. %3D (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Find the P-value. P-value = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) d. State…arrow_forward
- According to a city's estimate, people on average arrive 1.5 hours early for domestic flights. The population standard deviation is known to be 0.5 hours. A researcher wanted to check if this is true so he took a random sample of 50 people taking domestic flights and found the mean time to be 2.0 hours early. At the 1% significance level, can you conclude that the amount of time people are early for domestic flights is more than what the city claims. Will you reject or not reject the null hypothesis and what is your conclusion in words? O Reject the null hypothesis; the city's claim is true. O Do not reject the null hypothesis; the city's claim is false and people arrive earlier than the city claims. O Reject the null hypothesis; the city's claim is false and people arrive earlier than the city claims. O Do not reject the null hypothesis; the city's claim is true.arrow_forwardA simple random sample of 36 men from a normally distributed population results in a standard deviation of 12.8 beats per minute. The normal range of pulse rates of adults is typically given as 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the range rule of thumb is applied to that normal range, the result is a standard deviation of 10 beats per minute. Use the sample results with a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that pulse rates of men have a standard deviation equal to 10 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.Question content area bottomPart 1a. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below.A.H0: σ=10 beats per minuteH1: σ≠10 beats per minuteB.H0: σ≠10 beats per minuteH1: σ=10 beats per minuteC.H0: σ≥10 beats per minuteH1: σ<10 beats per minuteD.H0: σ=10 beats per minuteH1: σ<10 beats per minutePart 2b. Compute the test statistic.χ2=enter your response here (Round to three decimal places as needed.)Part 3c. Find the…arrow_forwardA simple random sample of 36 men from a normally distributed population results in a standard deviation of 11.8 beats per minute. The normal range of pulse rates of adults is typically given as 60 to 100 beats per minute. If the range rule of thumb is applied to that normal range, the result is a standard deviation of 10 beats per minute. Use the sample results with a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that pulse rates of men have a standard deviation equal to 10 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. H0: σ≥10 beats per minute H1: σ<10 beats per minute B. H0: σ≠10 beats per minute H1: σ=10 beats per minute C. H0: σ=10 beats per minute H1: σ≠10 beats per minute D. H0: σ=10 beats per minute H1: σ<10 beats per minute b. Compute the test statistic. χ2=48.73448.734 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Find…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman