
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Johnson Company uses a perpetual inventory system. The January 2018 inventory information is as follows. Assume cash purchases and sales.
DATA
Date
Jan 1
Description
Inventory on hand
Units
Per Unit
1,000 $
4
Jan 3
Purchase
3,000 $
5
Jan 6
Sale
2,750 $
10
Jan 15
Purchase
5,000 $
6
Jan 22
Sale
4,500 $
10
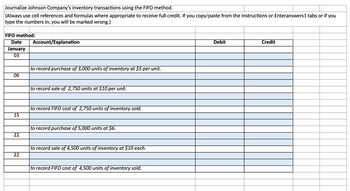
Transcribed Image Text:Journalize Johnson Company's inventory transactions using the FIFO method.
(Always use cell references and formulas where appropriate to receive full credit. If you copy/paste from the Instructions or Enteranswers 1 tabs or if
type the numbers in, you will be marked wrong.)
FIFO method:
Date
January
03
Account/Explanation
Debit
Credit
you
| to record purchase of 3,000 units of inventory at $5 per unit.
06
to record sale of 2,750 units at $10 per unit.
to record FIFO cost of 2,750 units of inventory sold.
15
22
| to record purchase of 5,000 units at $6.
|to record sale of 4,500 units of inventory at $10 each.
22
to record FIFO cost of 4,500 units of inventory sold.
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost 80 units @ $50.60 per unit 215 units @ $55.60 per unit Units Sold at Retail March 1 March 5 March 9 March 18 Beginning inventory Purchase Sales Purchase 240 units @ s85.60 per unit 75 units @ $60.60 per unit 130 units @ $62.60 per unit March 25 Purchase March 29 Sales 110 units @ $95.60 per unit Totals 500 units 350 units ok Problem 5-1A (Algo) Part 4 it 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, units sold include 55 units from beginning inventory, 185 units from the March 5 purchase, 35 units from the March 18 purchase, and 75 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) nces Weighted Average Gross Margin FIFO LIFO Specific ID Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross…arrow_forwardCo.'s purchases and sales of a particular product during the year are shown below: Jan. 1 Beginning Inventory Jan. 18 Purchase 1,500 units @ $ 10 1,250 units @ $ 12 1,500 units @ $ 20 1,750 units @ $ 14 1,750 units @ $ 25 500 units @ $ 15 Jan 20 Sold Jan. 25 Purchase Jan. 27 Sold Jan. 29 Purchase Assuming that company uses perpetual inventory system, determine the cost of goods sold and compute the ending inventory as of Jan. 31 and make the journal entry for Jan. 27 transaction inventory subsidiary ledger for LIF0 cost flow assumption. by using DATE IN OUT BALANCE Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Jan 1 Jan 18 Jan 20 Jan 25 Jan 27 Jan 29arrow_forwardWilliam & Company uses a perpetual inventory system. The following information is available for November: Nov. 1 4 7 10 Balance Purchase Purchase Sale 12 Sale Units 20 40 40 (20) (50) Purchase Price $5.00 $5.50 $9.00 Assume all sales and purchases are on credit. Sales Price $8.00 $8.00arrow_forward
- Knowledge Check Crane Works' uses a periodic inventory system. Its accounting records show the following as of December 31, 2025. Inventory, Dec. 31, 2025 Purchase Returns and Allowances Inventory, Jan. 1, 2025 Cost of goods purchased Cost of goods sold $ $4,050 $ 730 5,550 Compute cost of goods purchased and cost of goods sold. Freight-In Purchases Purchase Discounts $1,800 95,100 1,480 Sused Submit Answerarrow_forwardThe following inventory transactions apply to Green Company for Year 2. January 1 Purchased 240 units @ $10 April 1 Sold 120 units @ $19 August 1 Purchased 420 units @ $11 December 1 Sold 525 units @ $20 The beginning inventory consisted of 165 units at $11 per unit. All transactions are cash transactions. Required Record these transactions in general journal format assuming Green uses the FIFO cost flow assumption and keeps perpetual records. Compute cost of goods sold for Year 2.arrow_forwardces Montoure Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. Date Activities January 1 Beginning inventory February 10 Purchase March 13 Purchase March 15 Sales August 21 Purchase September 5 Purchase September 10 Sales Totals Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail 685 units @$45.00 per unit 570 units @ $42.00 per unit 285 units @ $27.00 per unit 1,140 units @ $75.00 per unit 185 units 585 units @ $50.00 per unit @ $46.00 per unit 2,310 units 770 units @ $75.00 per unit 1,910 units Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Cost of goods available for sale Number of units available for sale 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory. Ending inventory units unitsarrow_forward
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 24 units @ $15 5 Sale 15 units 17 Purchase 25 units @ $18 30 Sale 16 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the last-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for the September 30 sale. b. Determine the inventory on September 30.arrow_forwardBins Incorporated uses the periodic inventory system. The following table shows beginning inventory and inventory purchases for 2020: Month Beginning Inventory January February March Totals Sales Units Units 2,240 2,880 1,960 3,000 2,080 2,800 2,720 8,680 9,000 Purchases Cost per unit $5.00 $7.00 $5.00 $7.00 Totals $11,200 $13,720 $10,400 $19,040 $54,360 Relative to March, the company projects a 5 percent increase in cost of goods sold during April. The desired ending inventory balance for April is $2,400. Romaguera Inc pays cash to settle 60 percent of its purchases on account during the month of purchase and pays the remaining 40 percent in the month following the purchase. The accounts payable balance as of March 31 was $6,800. Required: Based on the FIFO inventory valuation methods answer the following questions. You may round your final answer to the nearest dollar. What is the ending inventory balance at the end of March? $ What is the total cost of goods sold at the end of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education