
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
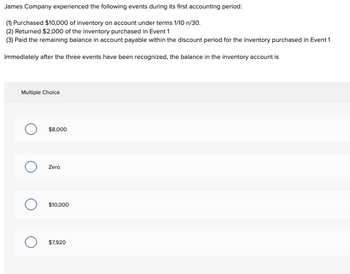
Transcribed Image Text:James Company experienced the following events during its first accounting period:
(1) Purchased $10,000 of inventory on account under terms 1/10 n/30.
(2) Returned $2,000 of the inventory purchased in Event 1
(3) Paid the remaining balance in account payable within the discount period for the inventory purchased in Event 1
Immediately after the three events have been recognized, the balance in the inventory account is
Multiple Choice
$8,000
Zero
$10,000
$7,920
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The accounting records of Skysong Electronics show the following data. Beginning inventory 1.000 units at $5 Purchases 9,000 units at $7 9.500 units at $10 Sales (a) Determine cost of goods sold during the period under a periodic inventory system using the FIFO method. (Round answer to O decimal places, e.g. 1,250.) Cost of goods sold during the period FIFOarrow_forwardFisher Corporation uses the perpetual FIFO inventory method and has the following information regarding its inventory: Date Inventory Events Amount June 1 Beginning balance 60 units at $6 $360 June 3 Purchased 510 units at $10.00 5,100 June 25 Purchased 370 units at $12.00 4,440 If the company sold 350 units of inventory for $12 each what would be the effect of the sale? Record the effect on the following accounts: Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Revenues and Expenses (Income Statement) Net Income Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3500 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Increase $4200 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Increase $3500 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - No Change; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - Increase $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - No Changearrow_forwardAccounting You have the following information for Sheffield Inc. Sheffield Inc. uses the periodic method of accounting for its inventory transactions. March 1 Beginning inventory 2,000 liters at a cost of 60¢ per liter. March 3 Purchased 2,500 liters at a cost of 62¢ per liter. March 5 Sold 2,300 liters for $1.05 per liter. March 10 Purchased 4,000 liters at a cost of 69¢ per liter. March 20 Purchased 2,300 liters at a cost of 77¢ per liter. March 30 Sold 5,200 liters for $1.25 per liter. Prepare partial income statements for 2022 through gross profit, under each of the following cost flow assumptions. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 125.25.) (1) Specific identification method assuming: (i) The March 5 sale consisted of 1,000 liters from the March 1 beginning inventory and 1,300 liters from the March 3 purchase; and The March 30 sale consisted of the following number of units sold from beginning inventory and each purchase: 450 liters from March 1; 550 liters from March 3;…arrow_forward
- Please read and asnwer question using table provided.arrow_forwardJames Company experienced the following events during its first accounting period: (1) Purchased $10,000 of inventory on account under terms 1/10 n/30. (2) Returned $2,000 of the inventory purchased in Event 1. (3) Paid the remaining balance in account payable for the inventory purchased in Event 1. Based on this information, which of the following shows how paying off the account payable (Event 3) will affect the Company's financial statements? Balance Sheet Income Statement Assets = Liabilities + A. (8,000) B. (7,900) C. (8,000) D. (7,920) Multiple Choice Option A Option D Option C Option B (8,000) (7,900) (8,000) (7,920) Stockholders' Equity n/a n/a n/a n/a Revenue n/a n/a n/a n/a Expense n/a 7,900 8,000 n/a Net Income n/a (7,900) (8,000) n/a Statement of Cash Flows (8,000) Operating Activity (7,900) Operating Activity (8,000) Operating Activity (7,920) Operating Activityarrow_forwardA company using the perpetual inventory system purchased inventory worth $25,000 on account with terms of 2/10, n/30. Defective inventory of $2,000 was returned 2 days later and the accounts were appropriately adjusted. If the invoice is paid within 10 days, the amount of the purchase discount that would be available to the company is OA. $500 OB. $460 OC. $540 OD. $490arrow_forward
- A company has beginning inventory for the year of $14,500. During the year, the company purchases inventory for $190,000 and ends the year with $21,000 of inventory. The company will report cost of goods sold equal to: Multiple Choice $211,000. $190,000. $196,500. $183,500.arrow_forwardConey Island Inc. had the following operating transactions during January 2020, its first month of operations. Date Transaction 1/1 Purchased 2 units of inventory costing $4 each on credit 1/3 Purchased 3 units of inventory costing $5 each on credit 1/10 Purchased 4 units of inventory costing $6 each on credit 1/21 Paid for the January 1 purchase 1/23 Paid for the January 3 purchase 1/30 Sold 7 units of inventory at $10 each on credit 1/30 Matched the inventory cost to January 30 on a FIFO basis 1/31 Estimated that 10% of credit sales will not be realized in cash Record the above transactions in Coney Island’s journal Present Coney’s income statement through gross profit for January 2020arrow_forwardKirtland Corporation uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, the accounting records for the most popular item in inventory showed the following: Assessment Tool iFrame Transactions Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase, January 30 b. Purchase, May 1 c. Sale ($5 each) d. Sale ($5 each) Units 400 Unit Cost $ 3.00 300 460 3.40 4.00 (160) (700) Required: a. Compute the amount of goods available for sale. b. & c. Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31, under Average cost, First-in, first-out, Last-in, first-out and Specific identification inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected two- fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second sale was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. Complete this…arrow_forward
- During the year, TRC Corporation has the following inventory transactions. Date Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Apr. 7 Purchase Jul.16 Purchase Oct. 6 Purchase Weighted Average Cost Total Beginning Inventory Purchases: Apr 07 Jul 16 Oct 06 Transaction Sales revenue Gross profit For the entire year, the company sells 450 units of inventory for $70 each. 3. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit. (Round "Average Cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and all other answers to the nearest whole number.) Number of Units 60 140 210 120 530 Cost of Goods Available for Sale # of units 60 140 210 120 530 Average Cost per unit Cost of Goods Available for Sale $ $ Unit Cost 3,120 $ 52 54 57 58 7,560 11,970 6.960 29,610 Total Cost $ 3,120 7,560 11,970 6,960 $29,610 Cost of Goods Sold - Weighted Average Cost of units Sold Average Cost of Cost per Unit Goods Sold Ending Inventory - Weighted Average Cost # of units in Ending Inventory…arrow_forwardTariq Fisher Company uses a perpetual inventory system. On January 1, its inventory account had a beginning balance of Rs 450,000. Tariq engaged in the following transactions during the year:Prepare all necessary transaction as General Entries and answer given below option. Purchased merchandise inventory for Rs 500,000. Generated net sales of Rs 600,000. Recorded inventory shrinkage of Rs 10,000 after taking a physical inventory at year-end. Reported gross profit for the year of Rs 180,000 in its income statement. At what amount was Cost of Goods Sold reported in the company’s year-end income statement? At what amount was Merchandise Inventory reported in the company’s year-end balance sheet? Immediately prior to recording inventory shrinkage at the end of the year, what was the balance of the Cost of Goods Sold account? What was the balance of the Merchandise Inventory account? d- Calculate the Gross profit margin ratioarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education