
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
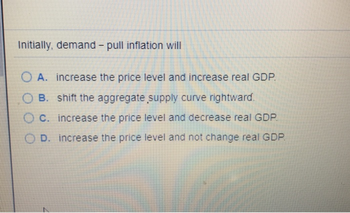
Transcribed Image Text:Initially, demand - pull inflation will
OA. increase the price level and increase real GDP.
B. shift the aggregate supply curve rightward.
C. increase the price level and decrease real GDP.
D. increase the price level and not change real GDP.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Explaining short-run economic fluctuations A majority of economists believe that in the long run, real economic variables and nominal economic variables behave independently of one another. For example, an increase in the money supply, a no long-run effect on the quantity of goods and services the economy can produce, a and nominal variables is known as variable, will cause the price level, a AL AXIS However, in the short run, most economists believe that real and nominal variables are intertwined. Economists use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to examine the economy's short-run fluctuations around the long-run output level. The following graph shows an incomplete short-run aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) diagram-it needs appropriate labels for the axes and curves. In the questions that follow you will identify some of the missing labels. AS variable, to increase but will have variable. The distinction between real variables ?arrow_forwardSince 1970, the United States has experienced 5 periods and 2 periods. O stagflationary, deflationary O inflationary; expansionary O recessionary; inflationary O recessionary; expansionaryarrow_forwardChoose the statement that about deflation that is incorrect. A. The price level falls if aggregate supply increases at a persistently slower rate than aggregate demand. B. An economy experiences deflation when it has a persistently falling price level. OC. A one-time fall in the price level is not deflation. O D. During a period of deflation, the inflation rate is negative.arrow_forward
- Negative supply shocks cause OA. falling unemployment. OB. expansion. OC. increases in GDP. OD. cost-push inflation.arrow_forwardPRICE LEVEL a a" a" LRAS Y, Y₂ QUANTITY OF OUTPUT 8 a. rising price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point A. b. falling price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point C. c. falling price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point A O d. rising price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point C. SRAS, SRAS Refer to Figure 34-3. Starting from point B and assuming that aggregate demand is held constant, in the long run the economy is likely to experience a ADarrow_forwardPrice Level Long-run AS Y, Y₁ Short-run AS Quantity of Real Output Suppose the economy is operating in a recession such as point B in the graph. If policymakers allow the economy to adjust to the long-run natural level on its own O a people will reduce their price expectations and aggregate demand will shift right O b. people will reduce their price expectations and the short-run aggregate supply will shift right Opeople will raise their price expectations and the short-run aggregate supply will shift left O d. people will raise their price expectations and aggregate demand will shift leftarrow_forward
- Price Level Juous 17-18. Long-run AS Y₂Y₁ Short-run AS AD Quantity of Real Output Suppose the economy is operating in a recession such as point B in the graph. If policymakers allow the economy to adjust to the long-run natural level on its own, a. people will raise their price expectations and the short-run aggregate supply will shift left b. people will reduce their price expectations and aggregate demand will shift right c. people will raise their price expectations and aggregate demand will shift left d. people will reduce their price expectations and the short-run aggregate supply will shift rightarrow_forwardIf aggregate demand shifts left, then in the short run a. the price level and real GDP both rise. b. the price and real GDP both fall. c. the price level falls and real GDP rises. d. the price level rises and real GDP falls.arrow_forwardSuppose the price of crude oil increases and we produce just enough crude oil for our own consumption. Increasing the interest rate will the existing recessionary gap. If the central bank does not change the interest rate, will adjust and bring the economy back to Yp. Worsen; wages O b. Improve; wages O c. Improve; tax rates O d. Worsen; tax ratesarrow_forward
- QUESTION 34 If Mexico lowers its inflation target from 3 percent to 2 percent, the initial response to this will be OA that the AD will shift right. B. None of these answers is correct. OC.che MP curve will shift down. OD.that the AD will shift left. OE. that the AS will shift left. 12arrow_forward12. If _____ is rising, it likely means that the economy is shrinking. A. consumer spending B. nominal GDP C. the Consumer Price Index D. the unemployment ratearrow_forwardThe real balance effect is the impact on real GDP caused by the ______ relationship between the price level and the real value of financial assets. A. Independent B. Direct C. Inverse D. Lineararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education