
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
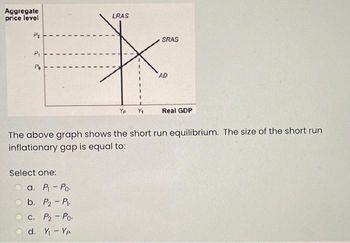
Transcribed Image Text:Aggregate
price level
P₂
P₁
Po
Select one:
LRAS
a. P₁ - Po.
b. P₂ - P.
C. P₂ - Po.
d. Y₁ - Yp
Yp Y₁
SRAS
AD
The above graph shows the short run equilibrium. The size of the short run
inflationary gap is equal to:
Real GDP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A decrease in the nominal wage will cause the aggregate supply curve to a. become steeper. . b. shift inward. c. shift outward. . d. become flatterarrow_forwardPrice Level 0 A B Real GDP Comparing points A and B on this graph, which of the following is true? O At point B, there would be less employment and higher unemployment than at point A. O At point B, there would be a lower wage than at point A. O At point B, there is a higher price level that increases the quantity of real GDP supplied. O At point A, there is greater pressure on the price level and inflation than at point B. O At point A, with a lower wage rate, aggregate supply has decreased compared to point B.arrow_forwardPlease help solve.arrow_forward
- Answer both please otherwise we will give dounvotearrow_forwardPrice Level AS AD Yu YY Real National Income 4. Referring to the above diagram, which of the following is a true statement? A. Macroeconomic policy will be needed to address rising inflation. B. There is sufficient aggregate demand to cause inflationary pressures. C. The equilibrium in the economy is at a level of output above full employment. D. There is insufficient aggregate demand to reach full employment.arrow_forwardChanges in all of the following shift the LM curve except a. income. b. the money supply. c. the price level. d. money demand.arrow_forward
- GNen the following aggregate demand (aD) and aggregatesupply šchedult.() Price level Real Gpp Deman ded Real GDP Supplied Short-RuN 70 80 90 00 450 400 350 300 కం 40 450 500 250 550 4 the potential RGDP is 45o unets of us¢. Draw and Show the short-run economiC equilibrium and evaluate the situation comparing with the long run aggeegate suppy by ygregate (Lias) explain tHhiis sifuation. explaintis sifutión. 6)if aggregate demand increases by us$ 100. Araw and show the aew equilibrium vacues on tthe Same graph and find the Rew equilibrium po'ssible es lucrease In e bemand. GrRre te One suplancution for thus Aggregatarrow_forwardNeed in Less than 20 minsarrow_forwardReal GDP is $20 trillion, the quantity of money is $10 trillion, and the velocity of circulation is 4. What is the price level? The price level is ___ thank sss !!arrow_forward
- give me answer with details explaintion....arrow_forwardWhen the economy goes into a recession. real GOP---- and unemployment ___ .a. rises, risesb. rises, fallsc falls. risesd. falls, fallsarrow_forward2. Explaining short-run economic fluctuations A majority of economists believe that in the long run, real economic variables and nominal economic variables behave independently of one another. For example, an increase in the money supply, a no long-run effect on the quantity of goods and services the economy can produce, a and nominal variables is known as variable, will cause the price level, a AL AXIS However, in the short run, most economists believe that real and nominal variables are intertwined. Economists use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to examine the economy's short-run fluctuations around the long-run output level. The following graph shows an incomplete short-run aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) diagram-it needs appropriate labels for the axes and curves. In the questions that follow you will identify some of the missing labels. AS variable, to increase but will have variable. The distinction between real variables ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education