
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
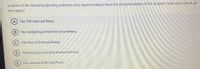
Transcribed Image Text:In which of the following signaling pathways does ligand binding induce the phosphorylation of the receptor molecules? (Check all
that apply.)
A The TGF-beta pathway.
B The Hedgehog/smoothened pathway.
The Notch/Delta pathway.
D) The Receptor-tyrosine kinase pathway.
E) The canonical Wnt pathway.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2 of 16 Compound Binds to Elicits biological receptor response A Yes Yes B Yes No C No No Refer to the table above. Compound X is the natural ligand that binds to a receptor and stimulates a signal transduction pathway associated with the receptor. Based on the information given in the table, what are the roles of compounds A, B, and C? O A is an antagonist, B is an agonist, and C is a ligand. A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C has no role. A is a ligand, B has no role, and C is an antagonist. A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C is an agonist. A has no role, B is an agonist, and C is an antagonist.arrow_forwardBinding EGF to the EGF receptor causes phosphorylation of tyrosines on the cytoplasmic tail of the receptor. Which of the following best describes the mechanism by which this phosphorylation activates downstream signaling complexes? Select one A. Causes degradation of receptor by proteasome pathway B. Causes EGF receptor to be internalized so it can interact directly with downstream signaling molecules C. Tyrosine phosphorylation alters 3D structure of downstream signaling proteins causing them to change from an inactive to active conformation D. Causes release of EGF from receptor E. Alters the localization of downstream signaling partners in the cytoplasmarrow_forwardWhen a signal binds to the Tyrosine kinase receptor (RTK), you have studied that a list of events occur sequentially. Map the events in the correct order from 1st to the last step.arrow_forward
- A biochemist is designing a new drug that will mimic the shape and function of a particular intercellular signaling molecule. Therefore she must produce a molecule that will bind to the receptor protein and... A. produce a cellular response by altering the Na+/K+ pump located near the receptor site. B. induce a change in the receptor molecule shape, which will ultimately prevent a cellular response. C. induce a change in the receptor molecule shape, which will ultimately produce a cellular response. D. induce a change in the phospholipid bilayer that causes a polar reversal allowing the molecules to be endocytose (engulfed).arrow_forwardxytocin stimulates contraction of smooth muscles in the breast and uterine wall. The key step in muscle contraction is release of calcium from internal cell stores. With which type of receptor does oxytocin interact to cause muscle contraction? A. Gαi-coupled receptor B. Tyrosine kinase coupled receptor C. Cytokine type 1 receptor D. Ser/Thr kinase receptor E. Gαq-coupled receptorarrow_forwardSame question but two different sectionsarrow_forward
- Arrange following the boxed information in sequence regarding the dissociation and reassociation of G proteins following the activation of a G protein coupled receptor. GTP-bound Ga, dissociates from B and y cuhunits Gas exchanges GTP for GDP Gas reassociates with By subunits and the rorentor reforms Binding of the ligand to a G-protein rounled recentor GTP-bound Gas binds and activates adenvlul rurlase GTP is hydrolyzed and GDP bound Gas suhunit dissoriates Conformational change Increased synthesis of CAMP from ATParrow_forwardYou decide to investigate cell signaling of a pair of newly identified GPCRs, GPCR-W and GPCR-Z. Each binds the same ligand, but activates different downstream heterotrimeric G-proteins that act on adenylyl cyclase. You discover that ligand binding has opposite effects on adenylyl cyclase activity for each receptor. GPCR-W causes an increase in adenylyl cyclase activity, while GPCR-Z causes a decrease in adenylyl cyclase activity. You obtain a cell line expressing GPCR-W, GPCR-Z, the relevant G-proteins, and adenylyl cyclase. There is baseline adenylyl cyclase activity producing a baseline amount of cAMP. You embark on a research project to characterize the following mutations in the components of the signaling pathway. 2. Will each of the following mutations increase or decrease the levels of cAMP inside the cell upon adding the ligand to the cell culture? A mutation in GPCR-W that prevents G-protein activation? A mutation in GPCR-Z that prevents G-protein activation? A mutation in…arrow_forwardWhich of the following would inhibit the activity of TGF-Beta receptor? multiple answers A. Deletion of Extracellular domain B. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor C. Mutation that prevents homodimerization of Type II Receptor D. Mutation of phosphorylation site on Type I receptor E. Inhibition Type II receptor binding to Type I receptorarrow_forward
- How could we promote rapid or slow signaling for medical purposes? So there are many examples of slow and rapid signaling via coupled receptors. For an example, salivary gland secretion is rapid signaling and cell growth is slow signaling. These pathways could be twisted and used to resolve medical issues in a more natural and less damaging way. Are there any experiments that have or could be done to test out promoting rapid signaling to speed up slow processes such as cell growth in a severe wound? What experiments have or could be done to test out slowing down signaling that is fast like cells responding to their environment negatively (over-active allergies)? Thank you.arrow_forwardTAS2R38 codes for a G-protein coupled receptor which contributes to the tasting of PTC. What does this tell you about PTC as a type of ligand? a It is a protein-based ligand that can cross the CM into the cell b It is a lipid based ligand that can cross the CM into the cell c It is a protein-based ligand that requires a second messenger d It is a lipid-based ligand that requires a second messengerarrow_forwardOutside of cell not GTP Activated G protein Inside of cell 7.In the figure above, part of the signal transduction mechanism common to G protein- linked receptors is shown. Of the steps in this pathway, select the step that will occur next. a. Extracellular signal binds to the receptor. b. Signal binding to receptor causes a change in shape in the receptor. c. GTP bound to the G protein is exchanged for GDP. d. Activated G protein subunit binds to effector protein. e. Activated cellular enzymes catalyze the formation of products, effectively amplifying the signal inside the cell.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON