
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In the image below, the blue squiggly line represents a folded protein. There are two particular amino acids that are colored red and black in the protein. The structure of each of these two specific amino acids is shown in the indicated box.
A mutation occurs in the gene that encodes the protein illustrated above. The result of this mutation is that one of the amino acids above is substituted with another. Specifically, the amino acid whose structure is shaded red above (the one on the left in the illustration) is replaced by the amino acid shown below. Use this information to answer the two questions that follow.
Please answer these questions.
 1. Based on this description, indicate which type of mutation occurred: missense, nonsense, silent, or indel
2. How would this mutation affect this protein's structure and function? Explain in 2-4 sentences. Be specific, and be sure to include details of these specific amino acids in your response. (I'm giving you the structures of these specific amino acids for a reason...). You may refer to them as the "red," "black" and "yellow" amino acid if that makes life easier.
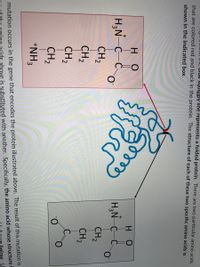
Transcribed Image Text:The image contains a diagram illustrating the impact of a genetic mutation on a protein's structure. The diagram shows a folded protein with an arrow pointing from its structure to two specific amino acids framed within boxes.
**Top Box:**
The chemical structure of the amino acid shown includes:
- An amino group: \( \text{H}_3\text{N}^+ \)
- A central carbon: \( \text{C} \)
- A hydrogen: \( \text{H} \)
- A carboxylate group: \( \text{C} \)
- Two oxygen atoms, one forming a double bond with carbon (one with a negative charge: \( \text{O}^-\))
- A side chain consisting of four methylene groups (\( \text{CH}_2 \)) and an amine group (\( \text{NH}_3^+\))
**Bottom Box:**
The chemical structure includes:
- An amino group: \( \text{H}_3\text{N}^+ \)
- A central carbon: \( \text{C} \)
- A hydrogen: \( \text{H} \)
- A carboxylate group: \( \text{C} \)
- Two oxygen atoms, one of which has a negative charge (\( \text{O}^-\))
- A side chain consisting of two methylene groups (\( \text{CH}_2 \)) connected to a carboxylate group (\( \text{C} \)), which is double-bonded to an oxygen and single-bonded to a negatively charged oxygen (\( \text{O}^-\))
**Explanation:**
The folded structure represents a protein, and the highlighted amino acids indicate a mutation where one amino acid (top structure) is replaced by another (bottom structure) in the protein sequence. The illustration highlights how a small change in the amino acid sequence might affect the overall protein structure and function.
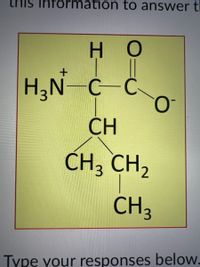
Transcribed Image Text:This image displays the structural formula of an amino acid, specifically the ionized form of leucine. The diagram can be broken down as follows:
- The central carbon atom (C) is bonded to four groups:
- An amino group (\( \text{H}_3\text{N}^+ \))
- A hydrogen atom (H)
- A carboxylate group (\( \text{COO}^- \))
- A side chain with a branched alkyl group
- The side chain consists of the following:
- A methylene group (\( \text{CH} \)), which is bonded to two additional groups:
- One methyl group (\( \text{CH}_3 \))
- A second carbon atom (\( \text{CH}_2 \)) that is part of a methyl group (\( \text{CH}_3 \))
Overall, the structure demonstrates the basic features of an amino acid with a specific emphasis on the branched-chain structure typical of leucine. This structural representation is significant in studying how the structure of amino acids influences protein structure and function.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Introduction
Protein is a nitrogenous organic macromolecule that is crucial to human health. It is responsible for the creation of enzymes, hormones, and antibodies in the human body.
Proteins are built up of amino acids, which are made up of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen, as well as the side chain or R group. Differences in the sidechains or R groups of amino acids can be used to distinguish them.
Mutation is a term used to describe a change in the sequence of DNA. Mutagens, viruses, a mistake during cell division, or radiation exposure can all cause it.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a short peptide that forms an alpha-helix within a larger protein structure. Suppose that one glutamate residue at some specific position in the helix were mutated to a leucine residue. The mutation could either make the helix more stable, or less stable. i) Describe two situations in which a Glu-to-Leu mutation could make the helix more stable. ii) Describe two situations in which the Glu-to-Leu mutation could make the helix less stable. Explain briefly the basis for the stabilizing and destabilizing effect in all cases.arrow_forwardA sample of a peptide of unknown sequence was treated with trypsin; another sample of the same peptide was treated with chymotrypsin. The sequences (N-terminal to C-terminal) of the smaller peptides produced by trypsin digestion were as follows: Trp-Arg-Thr-Gin Ser-Trp-Arg-His-Trp-Ala-Lys Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg The sequences of the smaller peptides produced by chymotrypsin digestion were as follows: Arg-His-Trp Arg-Thr-Gin Ala-Lys-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Trp Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys-Ser-Trp The original peptide sequence was: Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys-Ser-Trp-Ala-Lys-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Trp-Arg-His-Trp-Arg-Thr-Gin Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Trp-Arg-Thr-Gin-Ser-Trp-Arg-His-Trp-Ala-Lys Trp-Arg-Thr-Gin-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Ser-Trp-Arg-His-Trp-Ala-Lys-Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys Arg-His-Trp-Arg-Thr-Gln-Ala-Lys-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Trp-Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys-Ser-Trp Asp-Val-Ala-Ala-Lys-Ser-Trp-Arg-His-Trp-Ala-Lys-Asn-Ser-Asn-Val-Ile-Arg-Trp-Arg-Thr-Gin…arrow_forwardA gene contains 141 codons. How many nucleotides are present in the gene’s coding sequence? How many amino acids are expected to be present in the polypeptide encoded by this gene?arrow_forward
- You have discovered a novel protein that has a pI = 5.5. To study the functional properties of this new protein, your research group has made a mutant that contains two amino acid changes—namely, a surface Phe residue in the normal protein has been replaced by His (side chain pKa = 6.1) and asurface Gln has been replaced by Glu (side chain pKa = 6.0). Is the pI of themutant protein predicted to be greater than, less than, or the same as the pIof the normal protein? Support your answer with the appropriate calculationarrow_forwardCystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disorder caused by different types of mutations, many of which prevent ions from moving across cell membranes. Normally there are channel proteins that allow passage of the ions, but in patients with one kind of CF these proteins seem odd. Closer examination shows that these proteins display the correct amino acid sequence. However, they fail to do their job. A) Given that the primary structure of the protein is correct, what can you infer about the DNA sequence for the gene coding this protein on this patient, is there a mutation? Explain. B) Why is the primary structure insufficient to guarantee the proper function of the protein?arrow_forwardTo visualize the spatial arrangement of amino acid residues in an a-helix, it is helpful to imagine you are looking down the long axis of the helix, just as you would look down a soda straw. Viewed in this orientation, the residues form a circle, with each residue offset from its neighbor by 100 degrees. This representation is called a helical wheel. Use the circle below to indicate the position of each residue around the helix of the enzyme lysozyme. NH ...Arg - Cys - Glu- Leu - Ala Ala - Ala Met-Lys COO- The first two amino acids, Arg-1 and Cys-2, are shown as an example. Arg-1 O Glu-3 Which amino acid in the polypeptide is the first to pass the origin (i.e., which amino acid passes Arg- 1 first, completing one full circle)? Select the best answer. O Leu-4 O Ala-5 O Ala-6 O Ala-7 Met-8 O Lys-9 100° O none of the above Cys-2arrow_forward
- 1) You are studying the toxic protein called ectatomin, a major component of ant venom (specifically from the species Ectatomma tuberculatum), that embeds into cell membranes and creates pores that cause cells to lyse. Ectatomin is a small dimer, meaning the protein is comprised of two polypeptides; the sequences of the two polypeptides are given in the table with single-letter abbreviations. polypeptide sequences of ectatomin monomers polypeptide |protein sequence polypeptide 1 GVIPKKIWETVCPTVEPWAKKCSGDIATYIKRECGKL polypeptide 2 WSTIVKLTICPTLKSMAKKCEGSIATMIKKKCDK You could use absorbance at 280nm or colorimetric assays like the Bradford assay or bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA) assay to quantify the amount of ectatomin you have for your experiment. Why might you choose to use a colorimetric method instead of absorbance at 280nm? Select the best answer. a) Measuring absorbance at higher wavelengths, like 595nm or 562nm, is more accurate than measuring absorbance at 280nm. b) The Bradford…arrow_forwardYou have discovered a novel protein that has a pl = 5.5. To study the functional properties of this new protein your research group has made a mutant that contains two amino acid changes-namely, a surface Phe residue in the normal protein has been replace by His (side chain pk = 6.1), and a surface Gln has been replace by Glu (side chain pk. = 6.0). The pl of the mutant protein is predicted to be: A. Greater than the pl of the normal protein. B. Less than the pl of the normal protein. C. The same as the pl of the normal protein.arrow_forwardBased on the alignment of these protein sequences below, which [pairs] of the genes appear to be most similar to each other? [at least mention 2 points]; Why? [at least mention 2 points] Image of the protein sequences :arrow_forward
- A recent genome sequencing project for the bacterium Burkholderia mallei has identified a new protein with high similarity to the lysylphosphatidylglycerol flippase enzyme. A short section of the new protein sequence is shown below. TVEVNAPGDVQKALSELQQINDGRLDIRI (a) Are any reverse turns likely to be present? Explain your answer. (b) Are any beta-strands likely to be present? Explain your answer. (c) Are any alpha helices likely to be present? Explain your answer. (d) Is any supersecondary structure likely to be present? Explain your answer. (e) Identify two residues that are likely to be buried in the core of the folded protein. Explain your answer. (f) Identify two residues that are likely to be hydrogen bonded to each other. Explain your answer.arrow_forwardProteins called molecular chaperones assist in the process of protein folding. One class of chaperones found in organisms from bacteria to mammals is heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). All Hsp90 chaperones contain a 10 amino acid signature sequence that readily allows identification of these proteins in sequence databases. Two representations of the Hsp90 signature sequence are shown here. Y-x-[NQHD]-[KHR]-[DE]-[IVA]-F-[LM]-R-[ED]. 4 YSNKE/FLRE 3. 7. 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 C Bitsarrow_forwardA particular amino acid contains a -CH2NH3+ group. Is this amino acid more likely to be found on the inside or outside of the folded protein? Briefly explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON