
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
in the first picture Consider the
in the second picture, graph the supply curves when there are 20, 30, and 40 firms in the market
If there were 20 firms in this market, the short-run
per pound. At that price, firms in this industry would ____________ . Therefore, in the long run, firms would __________ the copper market.
Because you know that perfectly competitive firms earn _____________ economic profit in the long run, you know the long-run equilibrium price must be ____________
per pound. From the graph, you can see that this means there will be ____________ firms operating in the copper industry in long-run equilibrium.
True or False: Each of the firms operating in this industry in the long run earns negative accounting profit.
True
False
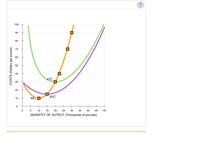
Transcribed Image Text:100
90
80
70
60
50
40
АТС
30
20
AVC
10
MC
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of pounds)
COSTS (Dollars per pound)
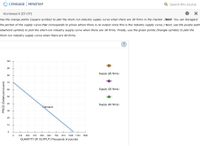
Transcribed Image Text:CENGAGE MINDTAP
Q Search this course
Homework (Ch 07)
Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard
the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple point
(diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 30 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the
short-run industry supply curve when there are 40 firms.
100
90
Supply (20 firms)
80
70
60
Supply (30 firms)
50
40
Supply (40 firms)
Demand
30
10
123
250
373
500
623
750
873
1000 1123 1250
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of pounds)
PRICE (Dollars per pound)
20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the market for tilapia. Ripple Rock Fish Farms, a small family fishery in Ohio, and The Fishin’ Company, a large corporate supplier, are both producers of tilapia. The marginal cost curves for both firms are shown in the accompanying graph. a. Suppose the market price of tilapia is $2.50 per pound. Move point A to Ripple Rock’s quantity sold. Move point B to The Fishin’ Company’s quantity sold. b. How many pounds of tilapia do they collectively supply?________thousand pounds c. To achieve efficient production, The Fishin’ Company should supply _____ ("more", or "less", or "the same") it is currently producing, and Ripple Rock should supply __________ ("more", or "less", or "the same") it is currently producing.arrow_forwardthen, plot the supply curve and equilibrium on the second photoarrow_forwardIn competitive markets, there are many small firms with each firm unable to influence the market price. Suppose company ABX operates in the wheat market. The company produces and markets wheats at a Price = $20 per container. The firm’s total costs are given as: TC = 50 +2Q + 3Q2 What level of output should the firm produce? Hint: Set P = MC and solve for Q. Use a graph to show your answers as wellarrow_forward
- Consider the competitive market for steel. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves shown on the following graph. V AVC COSTS (Dollars per ton) 100 882 889 80 20 0 MC 5 25 30 35 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons) 15 20 10 45 40 50 The following diagram shows the market demand for steel.arrow_forward7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the competitive market for rhenium. Assume that no matter how many firms operate in the industry, every firm is identical and faces the same marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves plotted in the following graph. COSTS (Dollars per pound) 100 90 80 70 60 40 20 10 + 0 + 0 MC + 5 ATC AVC D 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds) 40 + 45 50 ?arrow_forwardConsider the perfectly competitive market for titanium. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost ( MCMC ), average total cost ( ATCATC ), and average variable cost ( AVCAVC ) curves shown on the following grapharrow_forward
- Initially, all firms in a perfectly competitive market are in long-run equilibrium. Assume that the market demand for the product produced by the firms in the market suddenly rises. Suppose the following graph shows the marginal revenue (MR) and marginal cost (MC) curves of a firm in this market at its initial long-run equilibrium, with an equilibrium price of P₁ and a profit-maximizing quantity of output of Q₁. Show the short-run effect of the increase in market demand on this firm by shifting the marginal revenue curve, the marginal cost curve, or both on the following graph. PRICE AND COST 2 MC Q₂ QUANTITY In the short run, the firm will respond by producing In the long run, some firms will respond by PRICE MR QUANTITY Supply MR Demand O Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate both the short-run effects and the new long-run equilibrium after firms finish adjusting to the increase in market demand. MC the industry. Demand goods and…arrow_forward6. Deriving the short-run supply curve The following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for sun lamps. COSTS (Dollars) 100 20 80 TO 0 □ 5 D MC-D Price (Dollars per lamp) 10 20 32 40 50 60 ATC AVC Quantity (Lamps) DO 15 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) 50 For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero lamps and the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. ? Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss?arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the daily market for small cardboard boxes in San Diego. PRICE (Dollars per small box 10 9 Demand 0 161 6 QUANTITY (Millions of small boxes) 2 Supply 19 10 Suppose that Talero is one of more than a hundred competitive firms in San Diego that produce such cardboard boxes. Based on the preceding graph showing the daily market demand and supply curves, the price Talero must take as given isarrow_forward
- Avocados have been proven to bring many health benefits if consumed regularly. Many others including Gavin are huge fans of avocados and have plans to start a new business selling avocados. Assume the market for avocados to be perfectly competitive. Answer the following questions: a. If these firms are able to continue entering the market for avocados, it is likely that they are earning an economic profit. In order to earn an economic profit, firms must ensure that the price is above its Type ATC for Average Total Cost, AVC for Average Variable Cost, TC for Total Cost or VC for Variable Cost. b. Gavin decided to build an avocado farm in Brisbane. It is estimated that Gavin will need to spend $14.55 thousand on farming equipment costs. Gavin will also need to spend $20.95 thousand on labour and overhead costs. However, it is expected that Gavin will be able to sell 5 tonnes of avocados and gain revenue of $47.66 thousand from selling these avocados. Calculate the thousand. Answer to the…arrow_forwardSuppose Madison operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells rompers. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for rompers with a market price equal to $20 per romper. The following graph shows Madison's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for rompers for quantities zero through seven (including zero and seven) that Madison produces. TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 200 175 150 125 100 75 0 -25 □ 0 ☐ 1 2 3 5 QUANTITY (Rompers) 4 6 Total Cost 7 8 o Total Revenue Profitarrow_forwardConsider the perfectly competitive market for steel, which is in long-run equilibrium. Now the demand for cars, for which steel is an essential input, decreases. As a result, we would expect that in the market for steel Profits will increase in the long-run Firms will enter the market in the short-run The quantity produced by the individual firm will increase in the short-run. Profits will decrease in the short-runarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education