
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the competitive market for dress shirts. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves for a typical firm in the industry.
For each price in the following table, use the graph to determine the number of shirts this firm would produce in order to maximize its profit. Assume that when the price is exactly equal to the average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero shirts and the profit-maximizing quantity. Also, indicate whether the firm will produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. Lastly, determine whether it will make a profit, suffer a loss , or break even at each price.
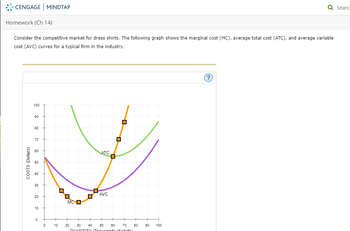
Transcribed Image Text:### Homework (Ch 14)
Consider the competitive market for dress shirts. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves for a typical firm in the industry.
#### Graph Explanation:
- The x-axis represents the **Quantity (Thousands of shirts)** produced, ranging from 0 to 100.
- The y-axis represents the **Costs (Dollars)** associated with production, ranging from 0 to 100.
Three curves are displayed on the graph:
1. **MC (Marginal Cost)**: Illustrated by the orange curve, which initially decreases and then increases, resembling a 'U' shape.
2. **ATC (Average Total Cost)**: Depicted by the green curve, which is generally 'U' shaped but positioned higher than the AVC curve. It also intersects the MC curve at its minimum point.
3. **AVC (Average Variable Cost)**: Shown by the purple curve, also 'U' shaped but lower than the ATC curve. It intersects the MC curve at its minimum point as well.
The points where the MC curve intersects both the ATC and AVC curves represent the cost-output correspondence for the production of dress shirts at the most efficient level.
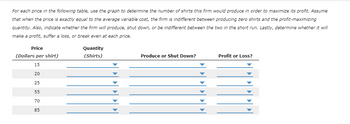
Transcribed Image Text:### Maximizing Profit Analysis Table
#### Instructions:
For each price in the following table, use the graph to determine the number of shirts this firm would produce in order to maximize its profit. Assume that when the price is exactly equal to the average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero shirts and the profit-maximizing quantity. Also, indicate whether the firm will produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. Lastly, determine whether it will make a profit, suffer a loss, or break even at each price.
| Price (Dollars per shirt) | Quantity (Shirts) | Produce or Shut Down? | Profit or Loss? |
|----------------------------|--------------------|-----------------------|-----------------|
| 15 | | | |
| 20 | | | |
| 25 | | | |
| 55 | | | |
| 70 | | | |
| 85 | | | |
#### How to Interpret the Graph:
1. **Price (Dollars per shirt)**: The price at which the shirts are sold.
2. **Quantity (Shirts)**: The number of shirts produced by the firm at the given price.
3. **Produce or Shut Down?**: Determines if the firm should continue producing shirts or cease production.
- **Produce**: The firm should continue producing shirts.
- **Shut Down**: The firm should cease production as it would be more cost-effective.
- **Indifferent**: The firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, typically when the price equals the average variable cost.
4. **Profit or Loss?**: Indicates if the firm will make a profit, suffer a loss, or break even.
- **Profit**: Revenues exceed the costs.
- **Loss**: Costs exceed the revenues.
- **Break Even**: Revenues are equal to costs.
#### Additional Notes:
- When the price is below the average variable cost, the firm should shut down as it would not cover the variable costs.
- If the price is above the average total cost, the firm will make a profit.
- If the price is equal to the average total cost, the firm will break even.
- Detailed graph analysis is necessary to fill in the quantities and make decisions regarding production and profitability at each given price point
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be scored on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. PRICE (Dollars per unit) 100 TOTAL REVENUE (Dollars) 90 80 20 10 0 1250 1125 1000 875 750 625 500 On the previous graph, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, or 50 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. 375 250 125 + 0 0 0 Demand 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Units) + 5 20 10 15 25 30 35 QUANTITY (Number of units) 40 Graph Input Tool Market for Goods 45 50 Quantity Demanded (Units)…arrow_forwardThe following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for demin overalls. Hint: Once you have positioned the rectangle on the graph, select a point to observe its coordinates. PRICE (Dollars per overalls) 50 10 10 5 0 MC 2 ATC 8 18 QUANTITY (Thousands of overallises per day) AVC 10 20 Profit or Loss In the short run, given a market price equal to $15 per overalls, the firm should produce a daily quantity of On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of $15 and the quantity of production from your previous answer. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs a loss. The rectangular area represents a short-run thousand per day for the firm. $ overallses.arrow_forwardSuppose a firm engaged in the illegal copying of DVD’s has a daily short run total cost function given by: STC = (q^2)+25 If pirated DVD’s sell for $20, how many will the firm copy each day? What will its profits be? What is the firm’s short run producer surplus at P=20? Develop a general expression for this firm’s producer surplus as a function of the price of pirated DVD’s.arrow_forward
- 6arrow_forwardDouglas Fur is a small manufacturer of fake-fur boots in San Diego. The following table shows the company’s total cost of production at various production quantities. On the following graph, plot Douglas Fur’s average total cost (ATC) curve using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot its average variable cost (AVC) curve using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot its marginal cost (MC) curve using the orange points (square symbol). (Hint: For ATC and AVC, plot the points on the integer; for example, the ATC of producing one pair of boots is $210, so you should start your ATC curve by placing a green point at (1, 210). For MC, plot the points between the integers: For example, the MC of increasing production from zero to one pair of boots is $90, so you should start your MC curve by placing an orange square at (0.5, 90).) Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.arrow_forwardThe graph shows the Cost curves for a profit maximizing firm in a competitive market. If the market price is $30 and the firm produces at the profit maximum quantity, what is the amount of the total fix costarrow_forward
- For the pizza seller whose marginal, average variable, and average total cost curves are shown in the graph below, what is the profit-maximizing level of output and how much profit will this producer earn if the price of pizza is $1.50 per slice?Instructions: In the graph below, label all three curves by clicking on the dropdown to select the appropriate label. Instructions: Enter your response as a whole number. If you are entering a negative number, be sure to include a negative sign (−). When the price is $1.50 per slice, the profit-maximizing level of output is slices per day. Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places). At the profit-maximizing level of output, the producer's profit is: $ per day.arrow_forward4. Various measures of cost Douglas Fur is a small manufacturer of fake-fur boots in San Francisco. The following table shows the company's total cost of production at various production quantities. Fill in the remaining cells of the following table. Average Variable Cost (Dollars per pair) Average Total Cost (Dollars per pair) Quantity Total Cost Marginal Cost Fixed Cost Variable Cost (Pairs) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 120 1 210 2 270 3 315 4 380 5 475 630arrow_forwardSuppose Mary has the utility function U(x1, x2) = v(xi) +2x2 with v such that v' > 0 and v" < 0. Suppose initially Mary chooses the optimal bundle x = 10 and x2 5. What is the new optimal x if prices for both xj and x2 are cut in half (reduced by 50%)? %3D Ox1 = 5 X1 = 11.7 Ox1 = 20 O None of the other answers are correct Ox1 = 10 %3!arrow_forward
- Consider the perfectly competitive market for titanium. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost ( MCMC ), average total cost ( ATCATC ), and average variable cost ( AVCAVC ) curves shown on the following grapharrow_forwardProblem 2.5 The cost function for Acme Laundry is TC(q) = 10 + 10q + q^2 so its marginal cost function is MC(q) = 10 + 2q where q is tons of laundry cleaned. Derive the firm's average cost and average variable cost curves. What q should the firm choose so as to maximize its profit if the market price is p? How much does it produce if the competitive market price is p = 50?arrow_forwardThe table below presents the average and marginal cost of producing cheeseburgers per hour at a roadside diner. Cheeseburger Production Costs Quantity(burgers per hour) Average Variable Cost (dollars) Average Total Cost (dollars) Marginal Cost (dollars) 0 — — — 10 $1.00 $6.60 $1.00 20 0.70 3.50 0.40 30 0.70 2.57 0.70 40 0.78 2.18 1.00 50 0.88 2.00 1.30 60 1.07 2.00 2.00 70 1.34 2.14 3.00 80 1.74 2.44 4.50 90 2.23 2.86 6.20 100 2.81 3.37 8.00 a. At a quantity of 40 cheeseburgers per hour, the average total cost of production is (Click to select) falling rising at a minimum and the marginal cost of cheeseburger production is (Click to select) falling rising at a minimum . b. At a quantity of 60 cheeseburgers per hour, the average variable cost of production is (Click to select) falling rising at a minimum and the average total cost of cheeseburger production is (Click to select) falling rising at a minimum .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education