
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 1
In our original lab, the plan was to collect cheek cells from everyone and test for the ability to detect the bitter compound PTC. We would do this by
extracting the DNA from your cells, amplifying it, cutting it with a restriction enzyme, and then separating out the fragments by electrophoresis. The
taster allele (dominant) is cut by the restriction enzyme BstNI, which the allele for not tasting is not. Therefore, individuals who have a single band in
their digested enzyme are non-tasters (homozygous). Individuals like Jennifer who are homozygous dominant will have two bands (one tends to be
much brighter than the other). If there are 3 bands, the individual has one allele that was cut and the other was not. Therefore, they are heterozygotes
and can still taste (though maybe not as strongly).
IT taster
U D
It taster
U D
MARKER
100 bp
ladder
MARKER t nontaster
PBR322/
U D
BstNI
1857 bp
1058 bp
929 bp
383 bp
221 bp
177 bp
121 bp
44 bp
primer dimer
lif present)
Examine the gel below. Fill in the blanks with the genotype and phenotype of each individual.
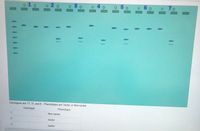
Transcribed Image Text:4 D
5 D
U 6 D
U 7D
Genotypes are TT, Tt, and tt. Phenotypes are Taster or Non-taster.
Genotype
Phenotype
1
Non taster
taster
taster
131
%3D
2.
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are studying a genome that has 42% G:C content and the remaining 58% of the genome is As and Ts. Assuming a random distribution of these bases what is the expected distance (ie there will be a cut once in every XX base pairs) between cut-sites for restriction enzyme that cuts at the sequence GAATTC? 256 3207 4168 4096arrow_forwardDraw a diagram showing what pGEM will look like after it has been digested with BamHI. Be sure to show both strands (with enzyme sequence) and include the origin of replication, the ampicillin resistance gene, 3’ and 5’, and the DNA sequence at the restriction site. It will probably be easiest to simply draw it as an open circle, not a line. Now show what pGEM will look like after it has been digested with EcoRI instead of BamHI. Again, be sure to show both strands and include the origin of replication, the ampicillin resistance gene, 3’ and 5’, and the DNA sequence at the restriction site.arrow_forwardCompared to the normal A allele, the disease-causing allele in sickle cell anemia (S allele) is missing an MstII restriction site. On a Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with MstII and hybridized with the probe shown on the diagram below, a person with sickle anemia, carrying two S alleles, will show Choose an answer below: a single band at 1.1 kb. a single band at 1.3 kb. a single band at 0.2 kb. one band at 0.2 and one at 1.3 kb. one band at 1.1 and one at 1.3 kb.arrow_forward
- Which of the following sequences, in the double-stranded form, can probably be recognized by a restriction enzyme? Choose an answer from below? TTCCTT CGACGA GTCGAC GGTTGG GAGGACarrow_forwardExplain the process of how X-gal screening works with pUC19, you may build a model with boxes and arrows. 2. You are utilizing BamHI (GGATCC) restriction site and HindIII (AAGCTT) restriction site. Within pUC19, BamHI is at position 263, while HindIII is at position 233. (Hint: position is like coordinate on a map). If you manage to insert GTF2H5 in pUC19 vector, what are the sizes of fragments if you digest the pUC19-GTF2H5 (this is after insertion) with the following restriction enzyme combination after gel electrophoresis: BamHI and HindIII There is an NdeI site right in the middle of the GTF2H5 that has been inserted in pUC19, what would be the fragment sizes, if you digest with BamHI and NdeI. HindIII and NdeI BamHI, HindIII, and NdeI. 3. Design an experiment to confirm the presence of insert GTF2H5 in pUC19 vector using the following method (besides restriction analysis above), assuming that you know the sequence of GTF2H5: Southern Blot Polymerase Chain Reactionarrow_forwardIn the following "gene library" cloning experiment Digested genomic DNA AmpR gene TCR gene TCR is tetracycline resistant marker, AmpR is ampicillin resistant marker and BamHI is the unique restriction enzyme on plasmid. A PhD student digests/cuts the plasmids with BamHI restriction enzyme and the genomic DNA with EcoRI restriction enzyme. After performing the cloning experiment and obtaining colonies on a selection plate, the obtained cells will be ..... (Hint: this question is even more challenging; the PhD student was later demoted to an MSc student). a) resistant to ampicillin and tetracycline b) sensitive to tetracycline and ampicillin c) resistant to tetracycline and sensitive to ampicillin d) resistant to ampicillin and sensitive to tetracycline e) sensitive to ampicillin and tetracycline BamHIarrow_forward
- Genomic DNA from a family where sickle-cell disease is known to be hereditary, is digested with the restriction enzyme MstII and run in a Southern Blot. The blot is hybridised with two different 0.6 kb probes, both probes (indicated in red in the diagram below) are specific for the β-globin gene (indicated as grey arrow on the diagram below). The normal wild-type βA allele contains an MstII restriction site indicated with the asterisk (*) in the diagram below; in the mutated sickle-cell βS allele this restriction site has been lost. What size bands would you expect to see on the Southern blots using probe 1 and probe 2 for an individual with sickle cell disease (have 2 βS alleles)? Probe 1 Probe 2 (a) 0.6kb 0.6kb and 1.2kb (b) 0.6kb and 1.8kb 0.6kb, 1.2kb and 1.8kb (c) 1.2kb 0.6kb (d) 1.8kb 1.8kb a. (a) b. (b) c. (c) d. (d)arrow_forwardA more modern molecular technique to RFLP fingerprinting is called Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphisms (AFLPs). In AFLP analysis, restriction enzymes are again used to digest genomic DNA into multiple fragments. Next, adapters complementary to restriction site overhangs are ligated to the fragments using an enzyme called DNA ligase. These adapters are complementary to primers used to amplify the fragments using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Can you think of any potential benefits of AFLP analysis over RFLP? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardResearchers are manipulating the gene cxx2 for their experiments, and they have inserted a smallnumber of base pairs randomly somewhere into the gene. They isolate several versions (with differentinsertions) of this modified gene and carry out an RT-PCR using a primer that recognizes thetranscriptional start site area (eg. from +1 to +20), and a primer that binds to the polyA tail.For the first modified gene sample, they observe that the intron is no longer being spliced out.Which of the lettered arrowheads indicates a location where this insertion could be? (Therecould be one answer or several. Give all answers that apply)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education