
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
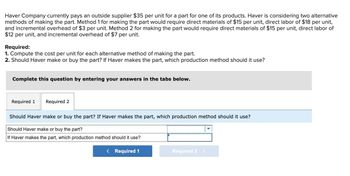
Transcribed Image Text:Haver Company currently pays an outside supplier $35 per unit for a part for one of its products. Haver is considering two alternative
methods of making the part. Method 1 for making the part would require direct materials of $15 per unit, direct labor of $18 per unit,
and incremental overhead of $3 per unit. Method 2 for making the part would require direct materials of $15 per unit, direct labor of
$12 per unit, and incremental overhead of $7 per unit.
Required:
1. Compute the cost per unit for each alternative method of making the part.
2. Should Haver make or buy the part? If Haver makes the part, which production method should it use?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
Should Haver make or buy the part? If Haver makes the part, which production method should it use?
Should Haver make or buy the part?
If Haver makes the part, which production method should it use?
< Required 1
Required 2 >
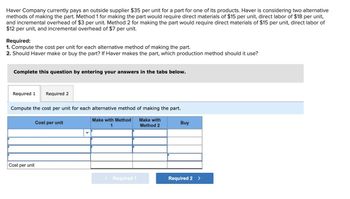
Transcribed Image Text:Haver Company currently pays an outside supplier $35 per unit for a part for one of its products. Haver is considering two alternative
methods of making the part. Method 1 for making the part would require direct materials of $15 per unit, direct labor of $18 per unit,
and incremental overhead of $3 per unit. Method 2 for making the part would require direct materials of $15 per unit, direct labor of
$12 per unit, and incremental overhead of $7 per unit.
Required:
1. Compute the cost per unit for each alternative method of making the part.
2. Should Haver make or buy the part? If Haver makes the part, which production method should it use?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
Compute the cost per unit for each alternative method of making the part.
Make with Method
1
Make with
Method 2
Cost per unit
Cost per unit
< Required 1
Buy
Required 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- what is the correct answer?arrow_forwardTool Time manufactures carpenter-grade screwdrivers. The company is trying to decide whether to continue to make the case in which the screwdrivers are sold, or to outsource the case to another company. The direct material and direct labor cost to produce the cases total $2.40 per case. The overhead cost is $1.00 per case which consists of $0.40 in variable overhead that would be eliminated if the cases are bought from the outside supplier. The $0.60 of fixed overhead is based on expected production of 400,000 cases per year and consists of the salary of the case production manager of $80,000 per year, along with the remainder consisting of rent, insurance, and depreciation on equipment that will have no resale value. The manager will be laid off if the cases were bought externally. The outside supplier has offered to supply the cases for $3.40 each. How much will Tool Time save or lose if the cases are bought externally? Save $0.40 per case Lose $0.20 per case…arrow_forwardLloyd Gettys, a client of Kevin Lomax, is considering two different processes to make his product—process 1 and process 2. Process 1 requires Lloyd to manufacture subcomponents of the product in-house. As a result, materials are less expensive, but fixed overhead is higher. Process 2 involves purchasing all subcomponents from outside suppliers. The direct materials costs are higher, but fixed factory overhead is considerably lower. Relevant data for a sales level of 30,000 units follow: Process 1 Process 2 Sales $8,010,000 $8,010,000 Variable expenses 2,700,000 4,200,000 Contribution margin $5,310,000 $3,810,000 Less total fixed expenses 3,650,625 1,428,750 Operating income $1,659,375 $2,381,250 Unit selling price $267 $267 Unit variable cost $90 $140 Unit contribution margin $177 $127 a. Compute the degree of operating leverage for each process. b. Suppose that sales are 20 percent higher than budgeted. By what percentage will operating income increase for each process? What will be…arrow_forward
- The volume of the raw material required for a certain machine part is 2.02 cu. cm. The finished volume is 1.05 cu. cm. The time for machining each piece is 45 seconds for steel and 30 seconds for brass. The costs of steel is P32.50 per kg and the value of steel scrap is negligible. The cost the brass is P60 per kg and the value of brass scrap is P25 per kg. The wage of the operator is P40 per hr and the overhead cost of the machine is P50 per hour. The weight of steel and brass are 0.0081 and 0.0088 kg per cu. cm, respectively. How much is the total cost per piece of steel and brass. Which material will you recommend? Upload Choose a Filearrow_forwardCarlise Corp., which manufactures ceiling fans, currently has two product lines, the Indoor and the Outdoor. Carlise has to overhead of $132,720. Carlise has identified the following information about its overhead activity cost pools and the two product lines: Quantity/Amount Consumed by Indoor Line Quantity/Amount Consumed by Outdoor Line Activity Cost Pools Cost Driver Materials handling Number of moves Quality control Number of inspections Machine maintenance Number of machine hours Required: 1. Suppose Carlise used a traditional costing system with machine hours as the cost driver. Determine the amount of overhead assigned to each product line. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Indoor Model Outdoor Model Total Cost Assigned to Pool $21, 120 $71,760 4,600 inspections $39,840 29,000 machine hours 19,000 machine hours 600 moves 500 moves 5,800 inspections Overhead Assignedarrow_forwardCantrall Company is trying to decide which product to manufacture. Expected direct materials costs are $4.00 per unit for each product. The expected direct labor costs are $2.00 per unit for one product and $4.00 per unit for another product. In choosing between the two products, the direct materials costs are A) relevant; irrelevant B) irrelevant; relevant C) relevant; relevant D) irrelevant; irrelevant and the direct labor costs arearrow_forward
- Waterway Engine Incorporated produces engines for the watercraft industry. An outside manufacturer has offered to supply several component parts used in the engine assemblies, which are currently being produced by Waterway. The supplier will charge Waterway $315 per engine for the set of parts. Waterway's current costs for those part sets are direct materials, $140; direct labor, $80; and manufacturing overhead applied at 100% of direct labor. Variable manufacturing overhead is considered to be 20% of the total, and fixed overhead will not change if the part sets are acquired from the outside supplier. Required: a. What would be the net cost advantage or disadvantage if Waterway decided to purchase the parts? b. Should Waterway Engine continue to make the part sets or accept the offer to purchase them for $315? a. b. Waterway Engine Incorporated shouldarrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Performance Products Corporation makes two products, titanium Rims and Posts. Data regarding the two products follow: DirectLabor-Hoursper unit AnnualProduction Rims 0.40 18,000 units Posts 0.70 77,000 units Additional information about the company follows: Rims require $14 in direct materials per unit, and Posts require $11. The direct labor wage rate is $15 per hour. Rims are more complex to manufacture than Posts and they require special equipment. The ABC system has the following activity cost pools: Estimated Activity Activity Cost Pool Activity Measure EstimatedOverheadCost Rims Posts Total Machine setups Number of setups $ 30,030 120 80 200 Special processing Machine-hours $ 147,840 2,000 0 2,000 General factory Direct labor-hours $ 576,000 7,000 29,000 36,000 Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your answers to 2…arrow_forwardThe Grouper Company manufactures 1,478 units of a part that could be purchased from an outside supplier for $14 each. Grouper’s costs to manufacture each part are as follows: Direct materials $2 Direct labor 4 Variable manufacturing overhead 3 Fixed manufacturing overhead 8 Total $17 All fixed overhead is unavoidable and is allocated based on direct labor. The facilities that are used to manufacture the part have no alternative uses. (a) Calculate relevant cost to make. Relevent cost to make $ ___ per unit (c) Calculate net cost to buy if Grouper leases the manufacturing facilities to another company for $9,260 per year. Net cost to buy $ ______arrow_forward
- In its production process, Purple Tree Inc uses a specialized part in the manufacturing of their fancy widget. The costs to make a part are: direct material, $15; direct labor, $27; variable overhead, $15; and applied fixed overhead, $32. Purple Tree has received a quote of $60 from a potential supplier for this part. If Purple Tree buys the part, 75 percent of the applied fixed overhead would continue. They need 12,000 units of the specialized part. Purple Tree Company would be better off by Group of answer choices $60,000 to buy the part. $348,000 to buy the part. $30,000 to manufacture the part. $216,000 to manufacture the part.arrow_forwardHaver Company currently pays an outside supplier $15 per unit for a part for one of its products. Haver is considering two alternative methods of making the part. Method 1 for making the part would require direct materials of $5 per unit, direct labor of $8 per unit, and ncremental overhead of $3 per unit. Method 2 for making the part would require direct materials of $5 per unit, direct labor of $2 per unit, and incremental overhead of $7 per unit. Required: 1. Compute the cost per unit for each alternative method of making the part. 2. Should Haver make or buy the part? If Haver makes the part, which production method should it use? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the cost per unit for each alternative method of making the part. Make with Method Make with 1 Method 2 Cost per unit Cost per unit Required t Buy Required 2 >arrow_forwardStan Fawcett's company currently purchases a gear assembly from Salt Lake Supply, Inc., at $3.80 per unit with a minimum order of 3,000 units. Stan is considering instead producing the gear assembly himself. He estimates that producing it himself will cost $12,000 to set up the process and then $1.82 per unit for labor and materials. a) Using the line drawing tool, add the total cost graph for Stan to produce the assembly instead of purchasing from Salt Lake Supply. Total cost for the purchase option is already plotted. Properly label your line. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. Cost 40,000- ¡Minimum Order 36,000 32,000- 28,000- 24,000 20,000- 16,000 12,000 - 8,000- 4,000- 0+ 0 2,000 4,000 Quantity 6,000 8,000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education