
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
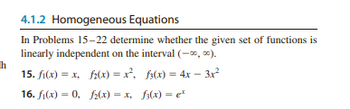
Transcribed Image Text:h
4.1.2 Homogeneous Equations
In Problems 15-22 determine whether the given set of functions is
linearly independent on the interval (-∞, ∞).
15. f(x)=x, f(x) = x², f(x)=4x-3x²
16. f(x) = 0, f(x) = x, f(x) = ex
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve all parts !arrow_forwardQ1 / Reduce the block diagram to the simple form R(s) S 13 S 0. S 1 S C(s)arrow_forwardPoints for stress vs strain (in image) Assume the compressive concrete strength (f’c) is 3,000 lb/in2 (psi)Calculate a cubic function (3rd order polynomial – Ax3+Bx2+Cx+Constant)Use this function to create a function that describes the slope of the cubic function (the derivative of thecubic function). This new function allows you to calculate the tangent to any point along the curve. Thetangent is the modulus of elasticity (E). The concrete code provides a formula to calculate E for concrete. That formula is:E = 57,000√??′, where f’c is in units of psi, and E is in units of psi.Use the derivative function you calculated to locate the point on the curve where the slope of the curvematches E using the concrete code formula. Express that stress point on the curve as a percentage ofthe compressive strength of the concrete. Now, calculate the secant modulus for the test case using 1,500 psi (50% f’c) as the arbitrary point onthe curve.Assume fracture occurs at the last point…arrow_forward
- please answer question 3 , 5, 7 in full detail explanationarrow_forwardThe natural exponential function can be expressed by . Determine e2by calculating the sum of the series for:(a) n = 5, (b) n = 15, (c) n = 25For each part create a vector n in which the first element is 0, the incrementis 1, and the last term is 5, 15, or 25. Then use element-by-element calculations to create a vector in which the elements are . Finally, use the MATLAB built-in function sum to add the terms of the series. Compare thevalues obtained in parts (a), (b), and (c) with the value of e2calculated byMATLAB.arrow_forwardhere is the pronblem with the solution but i dont know how the steps to solve it . pleasde helparrow_forward
- Example -4s F(s) = = (s²+4)² As + B Cs+D + (s²+4) (s²+4)² (s²+4) (H.W)arrow_forwardQuestion number 1arrow_forwardIn Problem 3 use Euler’s method to obtain a four-decimalapproximation of the indicated value. First use h= 0.1 and then useh =0.05. Find an explicit solution for each initial-value problem andthen construct tables similar to Tables 2.6.3 and 2.6.4. 3) y'=y, y(0)=1; y(0)arrow_forward
- 0.8 m wo B D E 0.8 m 1.0 m Bar AB rotates about the fixed point A with constant angular velocity wo. The system starts with bar AB horizontal. 1) Use the relative velocity equation to find the velocity of C in terms of the angles 0 and > and their derivatives. 2) Determine the lengths of bars AB and BC so that as bar AB rotates, the collar C moves back and forth between the positions D and E. A design constraint is that bar BC must be longer than bar AB (as shown in sketch). 3) You are given the design constraint that the magnitude of the acceleration of collar C must not exceed 200 m/s². What is the maximum allowable value of wo? 4) Create the following plots for a complete revolution of bar AB using the values for lengths and angular velocity determined above: о о e and > versus time as 2 sub-plots. Position, velocity, and acceleration of C versus time as 3 sub-plots. Velocity and acceleration of C versus its position as 2 sub-plots. - 5) Use your plotted results to describe the…arrow_forwardSolve the following without the use of AI. Show all steps. Thank You!arrow_forward3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY