
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
based on the chart answer the following:
1. which proteins will be most excluding use gel filtration chromotagrpahy
2. which proteins will migrate closer to the anode using SDS- PAGE
3. which protein will have the most net positive charge at a ph of 7.4
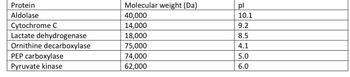
Transcribed Image Text:**Protein Properties Overview**
This table lists a series of proteins along with their respective molecular weights and isoelectric points (pI). The molecular weight is expressed in Daltons (Da).
| Protein | Molecular Weight (Da) | pI |
|---------------------------|-----------------------|-----|
| Aldolase | 40,000 | 10.1|
| Cytochrome C | 14,000 | 9.2 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 18,000 | 8.5 |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | 75,000 | 4.1 |
| PEP carboxylase | 74,000 | 5.0 |
| Pyruvate kinase | 62,000 | 6.0 |
**Explanation:**
- **Molecular Weight (Da):** This indicates the mass of the molecule. Larger values signify heavier proteins.
- **pI (Isoelectric Point):** This is the pH at which the protein carries no net charge. Different proteins have unique pI values, influencing their behavior in various pH environments.
This data is crucial for understanding the biochemical properties and behaviors of these proteins, useful in fields such as biochemistry and molecular biology.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Explain Chromatography, Electrophoresis and pH
Chromatographic techniques:
- These are a diverse group of laboratory methods that are used for the separation and analysis of mixtures of substances.
- These are widely employed in various scientific disciplines such as chemistry, biochemistry, pharmacology and environmental science.
- Thes techniques relies on the differential distribution of components within a sample between a stationary phase and a mobile phase which allows the separation and identification of individual compounds.
- There are different types of chromatographic techniques which include GC, HPLC, LLC, Ion exchange chromatography, SEC, TLC, Paper chromatography, Affinity chromatography, HIC, Chiral chromatography, SPE, etc.,
- The specific chromatographic technique is selected depending on the nature of the sample and the properties of the compounds to be separated.
Electrophoretic techniques:
- These are a group of laboratory methods used to separate and analyze charged molecules i.e., DNA, RNA, proteins, and particles, based on their mobility in an electric field.
- These techniques are essential tools in various scientific disciplines such as molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics and materials science.
- There are different types of electrophoretic techniques which include Gel electrophoresis, PAGE, CE, Proteomics electrophoresis, Agarose Gel electrophoresis, PFGE, IEF, EMSA, Particle electrophoresis, Electrophoresis in Microfluidic Devices, etc.,
pH:
- It is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity) of a solution.
- It quantifies the concentration of H⁺ ions in a solution.
- The scale typically ranges from 0 to 14, by considering 7 as neutral.
- When pH of a solution is below 7, it is considered as acidic solution.
- When pH of a solution is above 7, it is considered as basic or alkaline solution.
- It is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration i.e., pH = -log[H⁺].
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Calculate the GI50 value from the graph showing different concentrations of N3P. Show full working. Explain if cytotoxicity is caused by test agent.arrow_forwarda.Describe what makes thioglycollate medium suitable for culturing anaerobes. What would the growth patterns of Clostridium sporogenes and Micrococcus luteus be in this medium? b. In the Kligler test, why do we inoculate the surface of the agar slope and then stab into the butt of the slope? What does a pink coloured colony indicate when using MAC (MacConkey Agar)?arrow_forwardHi, my question is 6 ml of urine is added to 30 ml of water. 0.1 ml is plated. 109 colonies form. What is the CFU/ml of the urine culture?arrow_forward
- bacterial suspension with a population of 6.3 x 107cells/mL was diluted as follows: 4 mL was removed and added to 16 mL of diluent. This was again diluted 1 in 300. Determine the concentration of cells after EACH dilution. Concentration after the 1st dilution Concentration after the 2nd dilutionarrow_forwardHelicobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers, can grow in medium with a pH above 5. It can survive but not grow in pH 2 medium as long as the medium contains Urea. You inoculate a pH 2 broth with 1,000,000 H. pylori and for 8 hours the organism did not grow. The next morning however, the medium has become quite turbid, suggesting that the organism has grown. Explain how this could happen. What phylum and class does this organism belong?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON