
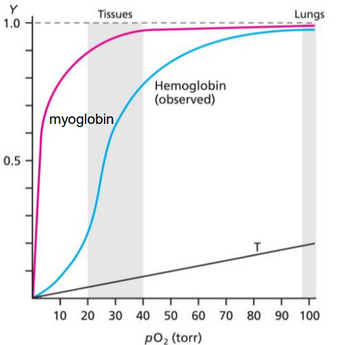
From the figure of O2 binding to myoglobin and hemoglobin (ignore the line
marked as T) as described in lecture (shown below) answer the following questions.
a) Estimate the P50 for myoglobin from the plot. Show how this estimation is
determined from the binding curve above. ( The first ghraph)
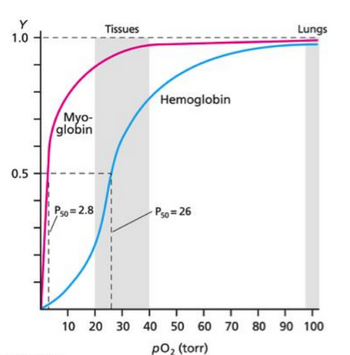
b)Using YO2 = PO2/P50 + PO2 , calculate the fraction of O2 bound for myoglobin at 1 torr. (2nd graph)
c)Using the binding curve on the previous page, show how you can estimate what
fraction of hemoglobin is bound near tissues at a pO2 of 30 torr and provide this value.
If the pH were lowered, will the amount of O2 bound to hemoglobin at 30 torr increase
or decrease? Explain why this is so based on how this changes hemoglobin structure.
If 2,3-BPG were added to the solution, will the amount of O2 bound to hemoglobin at
30 torr increase or decrease? Explain why this is so based on how this changes hemoglobin
structure.
The body receives nutrition, oxygen, and waste removal from the blood, which is a fluid that circulates continuously. Blood is "thicker" than pure water because it is mostly liquid and contains many suspended cells and proteins. More than a gallon of blood is present in the average person.
The majority of blood is made up of a liquid called plasma. Plasma contains proteins that carry substances through the blood, aid in blood clotting, and carry out other tasks. Additionally, glucose and other dissolved nutrients are present in blood plasma.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Based on the following data, is the p50 higher or lower than normal in (a) hemoglobin Yakima and (b) hemoglobin Kansas? Explain. Name Yakima Kansas Mutation Asp G1 (99) ẞ → His Asn G4 (102) ß → Thr Effect Disrupts a hydrogen bond that stabilizes the T conformation Disrupts a hydrogen bond that stabilizes the R conformationarrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about hemoglobin. The number of high affinity binding sites in the R form of hemoglobin is .The number of low affinity binding sites in the R form of hemoglobin is .The number of O2 molecules that need to bind to convert hemoglobin from the T to R form is .The number of high affinity binding sites in the T form of hemoglobin is .The number of low affinity binding sites in the T form of hemoglobin isarrow_forwardWhich statement is true for the heme group present myoglobin: a. Oxygen binding to heme group is influenced by serine residues within proteins’ sequences. b. Oxygen binding to heme can become irreversible as a result of interaction with certain protein residues. c. Oxygen reversibly binds to the heme prostetic group and this binding is influenced by histidine residues within the myoglobin sequence. d. The heme group dissociates from Mb after oxygen is released.arrow_forward
- 46arrow_forwardThe doctor also mentioned a new treatment for Sickle Cell Disease to JJ called Voxelotor (Oxbryta). Voxelotor binds to the a-globin chain and alters the structure of HbS stabilizing it in the R-state (relaxed state). Q7: In the presence of Voxelotor would you expect the affinity of HbS for O2 to increase or decrease? Q8: How would you classify the mechanism of action for Voxelotor?arrow_forwardWhat would the order of elution be (first to last to come out of a size-exclusion chromatography column) for the mixture of myoglobin (17.7 kDa), hemoglobin (64.5 kDa), lysozyme (14.3 kDa) & albumin (67 kDa)? a. Albumin, hemoglobin, lysozyme, myoglobin Ob. Hemoglobin, myoglobin, lysozyme, albumin Oc. Lysozyme, myoglobin, albumin, hemoglobin Od. Albumin, hemoglobin, myoglobin, lysozymearrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forward(e) Two ADP agonists (drugs) were also found to bind to platelets: 2-methylthio-ADP bound with a Kp of 7 µM and 2-(3-aminopropylthio)-ADP bound with a Kp of 200 µM. Can these drugs effectively compete with ADP for binding to platelets? Explain your answer.arrow_forwarda. How many subunits does hemoglobin have? What are their conventional names? b. Identify the oxygen binding sites on hemoglobin. How many oxygens can one molecule of hemoglobin bind? How many oxygens can one subunit of hemoglobin bind? c. Identify the central cavity of hemoglobin. Is it the same or different than the oxygen binding site of hemoglobin?arrow_forward
- Normal Hgb is referred to as HbA and contains 4 subunits, 2 a-globin chains and 2 B-globin chains, arranged as two dimers of aß. In Sickle Cell Disease, both B-globin chains are altered in the dimers (aßS/aßS). Q3: Which level of structure does the aß/aß and aßS/aßS in HbA and HbS describe?arrow_forwardWhy is the decreased affinity of fetal hemoglobin for BPG advantageous? With fewer BPG molecules bound to heme, there are more heme residues available for O2 binding. O A. B. Decreased BPG binding biases the fetal hemoglobin toward the R state. C. More free BPG is available to bind to adult hemoglobin, resulting in a shift to the R state. BPG is more available to bind to fetal myoglobin. helping to release O2 in fetal muscle tissue. D. 47arrow_forwardAbsorbed from the intestines into the blood, nitrites (NO2-) interact with the hemoglobin of the blood and block its respiratory function, turning part of the hemoglobin (HbFe2+) into methemoglobin (HbFe3+), unable to transfer oxygen from the lungs to tissues. With the formation of a large amount of methemoglobin, oxygen starvation of tissues occurs, which can cause damage to the central nervous system.10 to 20 % - of methemoglobin (HbFe3+) - asymptomatic cyanosis,20 to 50% of methemoglobin (HbFe3+) - hypoxia develop,> 50% of methemoglobin (HbFe3+) - the person will die.The body weight of the average person is 60 kg. Blood mass averages 8% of a person’s body weight; blood density ρ = 1,050 g/cm3, the hemoglobin (Hb) content in it is 14 g per 100 ml.molecular weight of hemoglobin 65-68 kg/mol (use 68 kg/mol for calculation). Assume that 1 mole of hemoglobin reacts with one mole of nitrite ion to form 1 NO molecule:HbFe2+ + NO2- → HbFe3+ + NOwill a 290 mg dose of sodium nitrite be…arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





