
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
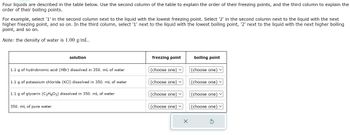
Transcribed Image Text:Four liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the
order of their boiling points.
For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next
higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling
point, and so on.
Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL.
solution
1.1 g of hydrobromic acid (HBr) dissolved in 350. mL of water
1.1 g of potassium chloride (KCI) dissolved in 350. mL of water
1.1 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) dissolved in 350. mL of water
350. mL of pure water
freezing point
(choose one)
(choose one)
(choose one)
(choose one) ✓
X
boiling point
(choose one)
(choose one)
(choose one)
(choose one)
S
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Colligative properties :
Colligative properties are the properties that are depends on the number of molecules present in the solution instead of nature of molecules present in solution.
Elevation in the boiling point :
Due to the number of molecules present in the solution, the boiling point of the solution increases.
Lowering in the freezing point :
Due to the number of molecules present in the solution, the freezing point of the solution decreases.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.3 atm. کارا pressure (atm) solid ]°C 200 liquid gas temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. X 400arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 2.7 g of potassium sulfate (K2SO4) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 2.7 g of nitric acid (HNO3) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) |(choose one) - 2.7 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) v 100. mL of pure water (choose one) |(choose one) v ?arrow_forwardREFER TO IMAGEarrow_forward
- Four liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 7.7 g of hydroiodic acid (HI) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) O (choose one) 7.7 g of potassium hydroxide (KOH) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) C (choose one) O 7.7 g of calcium chloride (CaCl2) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) C (choose one) O 500. mL of pure water (choose one) (choose one)arrow_forwardDetermine the chemical formulas for the two compounds. Based on their structures, which compound will have the higher boiling point?arrow_forwardList the substances BaCl₂, H₂, CO, HF, and Ne in order of increasing normal boiling point. Solution (a) BaCl₂-IONIC substance: strongest intermolecular force. High normal b.p. H₂ - Has ONLY LDF intermolecular forces. Its MM = 2.016 g/mol. CO - Has BOTH LDF and dipole-dipole interactions, thus dipolar forces are more predominant. HF - Has BOTH LDF and H-Bonding. Will have quite a high normal b.p. Ne - Has ONLY LDF available. Its AM = 20.180 g/mol. Thus: BaCl₂ has the highest comparative b.p. since it is ionic. When a substance has LDF only, then it is necessary to compare other factors, principally MM, AM, and/or shape. For these small molecules, mass will suffice. Lowest normal b.p. Highest normal b.p. H₂ < Ne HF < BaCl, IDF only (MM decides) < dipole-dipole < H-bondarrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point (choose onel Ⓒ boiling point (choose one) > 8.1 g of sodium bromide (NaBr) dissolved in 100. mL of water 8.1 g of glycerin (CyHyO₂) dissolved in 400. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) B 8.1 g of hydrolodic acid (HI) dissolved in 400. mL of water Ichoose onel (choose one) 400. mL of pure water [choose one) (choose one)arrow_forwardBased on the graph which describes two liquids, A and B, select ALL of the FALSE statements. XA OA The substance with the higher pure vapor pressure (P") is B OB. The substance with the higher pure vapor pressure (P°) is A OC. For any mixture of A and B (any ratio of A and B), the mole fraction of B in the vapor phase will be larger than the mole fraction of B in the liquid phase. OD. An equimolar mixture of liquids A and B are placed in a closed container (25 °C). At equilibrium, the vapor above the mixture will contain more moles of B than A OE Substance B has greater intermolecular forces than A MacBook Pro esc %23 & 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9. delete Q E R T. Y tab A D F G J K os lock > V B N M control option command command option vapor pressurearrow_forwardLabelling a typical simple phase diagram.arrow_forwardEnter your answer in the provided box. The vapor pressure of a liquid doubles when the temperature is raised from 75°C to 85°C. At what temperature will the vapor pressure be five times the value at 75°C?arrow_forwardThe organic compound trans-anethole is found in many oils/flavorings. This compound has a melting point of 50. ∘F. On Tuesday (this is a true story), a friend left a small vial of this compound in her back seat of her car outside for an hour and it solidified. At what temperature in ∘C does this compound freeze? We used this flavoring to make a holidy candy flavored with anise.arrow_forwardIn addition to filling in the blanks below, show all of your work for this problem on paper for later upload. The heat of vaporization of isopropanol is 44.0 kJ/mol. The vapor pressure of isopropanol at 400 torr is 67.8 °C. Calculate the normal boiling point of isopropanol. Enter your value in the first box and an appropriate unit of measure in the second box.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY