
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
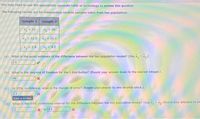
Transcribed Image Text:You may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question.
The following results are for independent random samples taken from two populations.
Sample 1 Sample 2
n = 20
n2 = 30
X,22.5
X = 20.1
S1 = 2.9
S2 = 4.2
(a) What is the point estimate of the difference between the two population means? (Use x, - x.)
2.4
(b) What is the degrees of freedom for the t distribution? (Round your answer down to the nearest integer.)
46
(c) At 95% confidence, what is the margin of error? (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
22
Enter a number.
(d) What is the 95% confidence interval for the difference between the two population means? (Use x, - Xg. Round your answers to on
| to (46
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 9:56 AM Sat Dec 19 * 67% +: 0 3) For the sample below, find the range, quartiles, interquartile range, and 5-number summary. 27, 28, 30, 31, 31, 32, 34, 36, 39, 41, 44, 45 2 19 >arrow_forwardThe average American gets a haircut every 43 days. Is the average different for college students? The data below shows the results of a survey of 11 college students asking them how many days elapse between haircuts. Assume that the distribution of the population is normal. 32, 46, 49, 45, 50, 49, 43, 45, 38, 46, 42 What can be concluded at the the a =0.01 level of significance level of significance? a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Họ: ? Select an answer v H. Select an answer Y C. The test statistic ? (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) d. The p-value - (Please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) e. The p-value is 2 f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis, g. Thus, the final conclusion is that, The data suggest the populaton mean is significantly different from 43 ata = 0.01, so there is fficient evidence tr conrlide that -he nonulation.arrow_forwardAt the distribution hub of a major grocery store chain, a large shipment of honeydew melons has arrived. A worker chooses a random sample of 8 of the melons and records their weights (in kg) as shown below. 1.5, 2.8, 2.2, 3.5, 0.9, 2.5, 4.2, 3.2 Send data to Excel (a) Graph the normal quantile plot for the data. To help get the points on this plot, enter the data into the table in the correct order for a normal quantile plot. Then select "Compute" to see the corresponding area and z-score for each data value. Send data to calculator Index Data value Area 2-score 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ D D Compute 田arrow_forward
- Suppose you needed to test the claim that the two samples described below come from populations with the same mean. Assume that the samples are independent simple random samples. Sample 1: n1 13, a1 = 24, 81 = 7.55 Sample 2: n2 = 3, x2 = 21.9, 82 = 8.92 Find: (a) The estimated degree of freedom is (b) The standardized test statistic is (use Sample 1 - Sample 2)arrow_forwardA physical therapist wanted to know whether the mean step pulse of men was less than the mean step pulse of women. She randomly selected 54 men and 70 women to participate in the study. Each subject was required to step up and down a 6-inch platform. The pulse of each subject was then recorded. The following results were obtained. Two sample T for Men vs Women N Mean StDev SE Mean Men Women 98% CI for mu Men - mu Women (- 12.20, - 1.00) T-Test mu Men = mu Women (vs H2 O C. Ho: H1 = H2; Ha: H1 #H2 (b) Identify the P-value and state the researcher's conclusion if the level of significance was a = 0.01. What is the P-value? P-value =arrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.10 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. Identify the test statistic and p-value. Right arm Left arm 144 167 OA.T-3.07, p-value = 0.037 OB. T = -2.32, p-value = 0.081 OC. T = -1.93, p-value = 0.127 OD. T = -4.01, p-value = 0.016 133 161 132 179 138 145 136 144arrow_forward
- From the data please state the intervals and what this tells us about the silver content between coins 1 and 2arrow_forwardAssume the samples are random and independent, the populations are nomally distributed, and the population variances are equal. The table available below shows the prices (in dollars) for a sample of automobile batteries. The prices are classified according to battery type. At a = 0.10, is there enough evidence conclude that at least one mean battery price is different from the others? Complete parts (a) through (e) below. E Click the icon to view the battery cost data. (a) Let u1. P2. H3 represent the mean prices for the group size 35, 65, and 24/24F respectively. Identify the claim and state Ho and H. H Cost of batteries by type The claim is the V hypothesis. Group size 35 Group size 65 Group size 24/24F 101 111 121 124 D 146 173 182 278 124 140 141 89 (b) Find the critical value, Fo, and identify the rejection region. 90 79 84 The rejection region is F Fo, where Fo = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) (c) Find the test statistic F. Print Done F= (Round to two decimal places as…arrow_forwardGot stuck, and wasn’t sure what to do.arrow_forward
- can you please provide explanationsarrow_forwardHow to find the simple variance & standard Deviation. Show the work for the simple variance mean: 52.1 range: 64 mode: 41.0 & 49.0arrow_forwardThe mean and standard deviation of Carbon concentration is 5 mg/L and 2 mg/L based on 25 samples from a river. The mean and standard deviation of Nitrogen concentration is 7 mg/L and 3 mg/L based on 35 samples from the same river. The experimenter wants to answer the question if the Nitrogen concentration is higher than the Carbon concentration. Which of the following methods do you use? Z-test, Default Procedure Z-test, Pooled Variance Procedure T-test, Pooled Variance Procedure T-test, Default Procedurearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman