
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
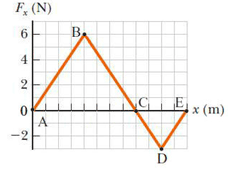
The force acting on a particle varies as in the figure below. (The x axis is marked in increments of 1.50 m.)
Find the work done by the force as the particle moves across the following distances.
(a) from
(b) from
(c) from
x = 0 m to x = 12.0 m
(b) from
x = 12.0 m to x=18.0m
(c) from
x = 0 m to x=18.0m
Transcribed Image Text:F, (N)
B.
G E,
x (m)
-2
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A shopper in a supermarket pushes a cart with a force of 33.0 N directed at an angle of 25.0° below the horizontal. The force is just sufficient to balance various friction forces, so the cart moves at constant speed. Find the work done by the shopper on the cart as she moves down a 54.2-m-long aisle. The shopper goes down the next aisle, pushing horizontally and maintaining the same speed as before. If the work done by frictional forces doesn't change, would the shopper's applied force be larger, smaller, or the same? What about the work done on the cart by the shopper? Is the work larger in part a, or is the work larger in part b; or is the work the same in both parts?arrow_forwardShow work! Thanksarrow_forwardA block of mass 2.50 kg is pushed to 2.20 m long along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant force 15.1579 N directed 1.011450944 radians below the horizontal. Determine the work done on the block by the applied force.arrow_forward
- You are loading a refrigerator weighing 2135 N onto a truck, using a wheeled cart. The refrigerator is raised 1.06 m to the truck bed when it is rolled up a ramp. (Assume that there is no frictional force between the refrigerator and the ramp.) (a) Calculate the minimum work that must be done by the force you apply and the magnitude of the force if the ramp is at an angle with the horizontal of 45.0 degrees. minimum work = force = (b) Calculate the minimum work that must be done by the force you apply and the magnitude of the force if the ramp is at an angle with the horizontal of 10.2 degrees. minimum work = force=arrow_forwardPlease include formulas and show all work thanksarrow_forwarda crate with mass m = 23.9 kg being pushed up an incline that makes an angle φ = 19.2 degrees with horizontal. The pushing force is horizontal, with magnitude P, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the incline is μ = 0.337. Consider the work done on the crate as it moves a distance d = 4.34 m at constant speed. Part (a) What is work done by the pushing force, in joules? Part (b) What is the work done by friction, in joules? Part (c) What is the work done by gravity, in joules? Part (d) What is the net work, in joules?arrow_forward
- You have two vectors: A = 7.27î + 3ĵ and B = 4î - 0.95ĵ + 12k. If vector A represents a force vector and vector B is a displacement vector, what is the magnitude of work done by this force?arrow_forwardAn object is subject to a nonconstant force F = (5x3 − 4x) such that the force is in newtons when x is in meters. Determine the work done on the object as a result of this force as the object moves from x = 0 to x = 1.30 ✕ 102 m.arrow_forwardA person pulls a 75-kg box 20 m along a horizontal floor by a constant force Fp = 125 N, which acts at a 42 degree angle. The floor is not smooth and exerts a friction force of Ff = 65 N. Determine the following: The work done by each force acting on the crate (Don’t forget any!) The net work done on the cratearrow_forward
- A single conservative force acts on the a 5.0 kg object. The equation Fx = 2x + 4 describes the force, where x is in meters. As the object moves along the x axis from x = 1.0 m to x = 5.0 m calculate the work done by this force.arrow_forwardThe force acting on a particle varies as in the figure below. (The x axis is marked in increments of 2.50 m.) F (N) x (m) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves across the following distances. (a) from x = 0 m to x = 20.0 m (b) from x = 20.0 m to x = 30.0 m (c) from x = 0 m to x = 30.0 marrow_forwardWe know that the work (W) done by a force vector F applied to an object over a displacement ?x is given byW = F(cos?) ?x,where F is the magnitude of the force, and ? is the angle between the applied force and the direction of the displacement. This expression assumes that the force is constant over the displacement ?x. If F is not constant, it can be shown that the work done is equal to the area under the curve force versus position.Based on what above said, calculate the work done by the force versus position represented in each graph (a), (b), and (c) in the figure below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON