
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
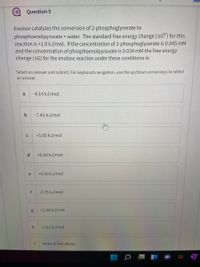
Transcribed Image Text:Question 5
Enolase catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to
phosphoenolpyruvate + water. The standard free energy change (AGO) for this
reaction is +1.8 kJ/mol. If the concentration of 2-phosphoglycerate is 0.045 mM
and the concentration of phosphoenolpyruvate is 0.034 mM the free energy
change (AG) for the enolase reaction under these conditions is:
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select
an answer.
a
-4.14 kJ/mol
b
-7.43 kJ/mol
+5.05 kJ/mol
d.
+6.60 kJ/mol
e
+0.50 kJ/mol
f
-0.75 kJ/mol
+1.08 kJ/mol
-2.52 kJ/mol
None of the above
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5) A certain aerobic organism is able to metabolize the following glycolipid: "CH,OH H OH но OH A. Draw the 2 resulting structures that would occur upon initial hydrolysis of the 0-glycosidic bond. B. Calculate how much ATP is formed upon complete aerobic oxidation of one mole of the compound. Assume that no ATP is produced when one mole of the glycosidic bond in the above compound is hydrolyzed. Show calculation below.arrow_forwardGive correct explanationarrow_forwardGR Methanol and ethanol bind to the same active site on the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) to undergo oxidation, as shown in the equations below. In methanol poisoning, ethanol is given intravenously to prevent the formation of formaldehyde that has toxic effects. In this scenario, what type of inhibitor is ethanol with regard to alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzing the oxidation of methanol? budy CH3-OH + NAD+ HCHO+NADH + H+ CH3-CH2-OH + NAD+ CH3-CHO + NADH + H* O a competitive inhibitor ADH O an irreversible inhibitor ADH O a noncompetitive inhibitor O both a noncompetitive and an irreversible inhibitor O Sea hparrow_forward
- Given the following information on reduction potentials, calculate the standard free energy in kJ/mol based on your understanding of electron transfer through the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Round to nearest whole number. Lipoamide + 2H+ + 2e- → dihydrolipoamide ∆εο = -0.29 FAD + 2H+ + 2e- → FADH2 ∆εο = −0.01arrow_forwardAlthough the ATP-ADP reaction is the principle energy shuttle in metabolic pathways, many other examples of coupled reactions exist. glutamic acid + NH3 glutamine + H2O, ΔGo = 14 kJ. Can be coupled with the acetyl phosphate reaction shown CH3COOPO3H2 + H2O CH3COOH + H3PO4, ΔGo = -46.9 kJ a. Calculate ΔGo for the overall process.arrow_forward1. Identify the most likely additional substrates, products, and coen- zymes for each reaction in the following imaginary pathway. COO Н—с—NH— сно CoO COO CH, Н—с—NH—сно H-C-NH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 H-C-CH3 H-C-CH3 H-C-NH, H-C-NH3 H-C-NH3 COO COO || C-NH2 || C-NH2 C- NH2 H-C-NH3 H-C-NH3 H-C-NH-CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 H-C-CH3 H-C-CH3 H-C-CH3 H-C- NH3 C=0 C=0 CoO CoO COO -0- O=0- -arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY