
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
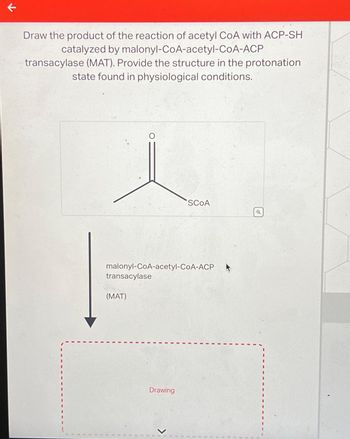
Transcribed Image Text:K
Draw the product of the reaction of acetyl CoA with ACP-SHI
catalyzed by malonyl-CoA-acetyl-CoA-ACP
transacylase (MAT). Provide the structure in the protonation
state found in physiological conditions.
malonyl-CoA-acetyl-CoA-ACP
transacylase
(MAT)
SCOA
Drawing
Q
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Name one reaction of glycolysis, one anaplerotic reaction, and one reaction of TCA cycle that acetyl-COA allostericqally regulates ( and declare whether it is an activator or inhibitor.)arrow_forwardFill in the blanks below (input numbers only!) about the metabolism of hexanoic acid, a fatty acid that is one of the components of vanilla, and whose formula is CH3(CH2)4COOH: First, the fatty acid is activated by attaching CoA, which costs ATP molecules. The fatty acid is then broken down through a beta-oxidation spiral, to make acetyl CoA molecules. This will require "turns" of the beta-oxidation process. Since each turn of the cycle yields ATP molecules, and each acetyl COA will yield ATP molecules by going through the rest of its metabolism, the net ATP molecules produced from one molecule of this fatty acid will bearrow_forward2-Bromopalmitoyl-CoA inhibits the oxidation of palmitoyl-CoA by isolatedmitochondria but has no effect on the oxidation of palmitoylcarnitine. What is the most likely site of inhibition by 2-bromopalmitoyl-CoA?arrow_forward
- The mitochondrial Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC) is a very large enzyme complex which catalyses the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Describe the enzyme components that make up the PDC, indicating the contribution each makes to the pyruvate to acetyl-CoA process, as well as how the PDC itself is regulated by intermediates?arrow_forward(b) number of moles of ATP produced under aerobic glycolysis whereby pyruvate enters the mitochondrion for oxidative decarboxylation to generate acetyl-CoA that enters the citric acid cycle. Write the reac- tions for each step using words. They need not be balanced with respect to charge, protons released or consumed, and stoichiometry. Consider 2.5 ATP/NADH oxidized and 1.5 ATP/FADH2 oxidized. Enzymes need not be named. Compare the number of moles of ATP that are produced under anaerobic glycolysis to the Of the reactions producing ATP in the mitochondrion listed in part (b) above, which are not (c) influenced by the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane?arrow_forwardIn the first step of the TCA cycle the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is transferred to oxaloacetate to produce citrate. Where will the carbonyl carbon of that acetyl group be after the first CO2 is expelled? Group of answer choices The first carbon of α-ketoglutarate The last carbon of α-ketoglutarate The fourth carbon of α-ketoglutarate The third carbon of α-ketoglutaratearrow_forward
- The TCA cycle entails eight enzymatically catalyzed steps starting with the entry of acetyl-CoA into the cycle. (a) Name the enzymes catalyzing each of the steps in the order in which they operate. Indicate the production of reducing power (NADHFADH.), CO, and high energy phosphate at the steps which produce them (b) Which TCA cycle intermediates yield amino acids upon direct transamination, and name those amino acids. You need not draw any structures at all to answer this question.arrow_forwardPlease explain and give the correct answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON