
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
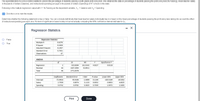
Transcribed Image Text:The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test. She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), mean teacher salary
in thousands of dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in thousands of dollars (Spending) of 47 schools in the state.
Following is the multiple regression output with Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, X, = Salaries and X, = Spending.
E Click the icon to view the results.
Determine whether the following statement is true or false: You can conclude definitively that mean teacher salary individually has no impact on the mean percentage of students passing the proficiency test, taking into account the effect
of instructional spending per pupil, at a 1% level of significance based solely on but not actually computing the 99% confidence interval estimate for B1.
Regression Statistics
O False
Regression Statistics
Multiple R
0.4276
O True
R Square
0.1828
Adjusted R Square
0.1457
Standard Error
5.7351
Observations
47
ANOVA
df
SS
MS
F
Significance F
Regression
2
323.8284
161.9142
4.9227
0.0118
Residual
44
1447.2094
32.8911
Total
46
1771.0378
Coefficients
Standard Error
t Stat
P-value
Lower 95%
Upper 95%
Intercept
-72.9916
45.9106
-1.5899
0.1190
-165.5184
19.5352
Salary
2.7939
0.8974
3.1133
0.0032
0.9853
4.6025
Spending
0.3742
0.9782
0.3825
0.7039
-1.5972
2.3455
Print
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose you are interested in studying regional differences in crime rates. You take a random sample of 100 cities in the South, and find a mean crime rate of 55 with a sample variance of 5.78. A sample of 100 cities in the North has a mean crime rate of 50 with a sample variance of 6.72. Construct a 95% confidence interval around the difference in crime rates between the population of Southern cities and the population of Northern cities. Interpret, in words, the meaning of this interval.arrow_forwardA consumer product testing organization uses a survey of readers to obtain customer satisfaction ratings for the nation's largest supermarkets. Each survey respondent is asked to rate a specified supermarket based on a variety of factors such as: quality of products, selection, value, checkout efficiency, service, and store layout. An overall satisfaction score summarizes the rating for each respondent with 100 meaning the respondent is completely satisfied in terms of all factors. Suppose sample data representative of independent samples of two supermarkets' customers are shown below. Supermarket 1 Supermarket 2 n = 260 n, = 300 = 84 X, = 83 (a) Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether there is a difference between the population mean customer satisfaction scores for the two retailers. (Let u, = the population mean satisfaction score for Supermarket 1's customers, and let u, = the population mean satisfaction score for Supermarket 2's customers. Enter != for as…arrow_forwardA recent article published by the Wall Street Journal said the Cincinnati airport had the most expensive airfares among the largest airports in the US. While they had some statistics to support this statement, a statistician decided to investigate further. A sample of 46 flights originating in Cincinnati was selected, and the round-trip airfare for each flight was recorded. The sample data is summarized in the StatCrunch output below: With 98% confidence, we estimate the mean airfare for flights out of Cincinnati is between $ and $. (Round the limits of your interval to 4 decimal places.) The mean airfare nationwide was reported as $376 for a round-trip ticket. Does the interval found above support the claim that Cincinnati has airfares which are more expensive than other airports in the US? The interval does not support the claim because the entire interval is not above $376. We can't make this conclusion based on a confidence interval. The interval does not support this claim…arrow_forward
- Research published in the Journal of Quantitative Criminology(Mar. 2010) revealed that the risk of burglaries in homes located on cul-de-sacs is lower than from homes on major roads. What size sample would be required to estimate the proportionof cul-de-sac homes in your home city that were burglarized in the past year within3% at the 95% confidence level?arrow_forward(c) What is the 95% confidence interval for the population mean score u based on this one sample? (Enter your answer rounded to one decimal place.) Lower value = Higher value =arrow_forwardA market research firm used a sample of individuals to rate the purchase potential of a particular product before and after the individuals saw a new television commercial about the product. The purchase potential ratings were based on a 0 to 10 scale, with higher values indicating a higher purchase potential. The null hypothesis stated that the mean rating "after" would be less than or equal to the mean rating "before." Rejection of this hypothesis would show that the commercial improved the mean purchase potential rating. Use a = 0.05 and the following data to test the hypothesis and comment on the value of the commercial. Purchase Rating Individual After Before 1 6 5 6 4 3 7 4 4 3 3 8 8 6 State the null and alternative hypotheses. (Use u, = mean rating after - mean rating before.) O Ho: Hs0 H3: H = 0 O Ho: Hd#0 Hai Hq= 0 O Ho: Hg=0 O Ho: Hd> 0 Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) 1.183 Calculate the p-value. (Round your answer to…arrow_forward
- A market research firm used a sample of individuals to rate the purchase potential of a particular product before and after the individuals saw a new television commercial about the product. The purchase potential ratings were based on a 0 to 10 scale, with higher values indicating a higher purchase potential. The null hypothesis stated that the mean rating "after" would be less than or equal to the mean rating "before." Rejection of this hypothesis would show that the commercial improved the mean purchase potential rating. Use a = .05 and the following data to test the hypothesis and comment on the value of the commercial. Purchase Rating Purchase Rating Individual After Before Individual After Before 1 6. 6. 3 2 6. 4 6. 7 8 7 6. 5 4 4 8 6. 6 a. What are the hypotheses? Ho: ld is Select Ha: ld is select b. Compute d (to 3 decimals). Compute sa (to 1 decimal).arrow_forward1. In a test of the effectiveness of garlic for lowering cholesterol, 43 subjects were treated with garlic processed tablet form. Cholesterol levels were measured before and after the treatment. The chang (before-after) in their levels of LDL cholesterol (in mg/dL) have a mean of 4.2 and a standard devia 19.4. Construct a 99% confidence interval estimate of the mean net change in LDL cholesterol after garlic treatment. What does the confidence interval suggest about the effectiveness of garlic in redu LDL cholesterol?arrow_forwardhelp with 12.2arrow_forward
- 8. A confidence interval for estimating the mean An industrial/organizational psychologist wants to improve worker productivity for a client firm, but first he needs to gain a better understanding of the life of the typical white-collar professional. Fortunately, he has access to the 2008 Workplace Productivity Survey, commissioned by LexisNexis and prepared by WorldOne Research, which surveyed a sample of 650 white-collar professionals (250 legal professionals and 400 other professionals). One of the survey questions was, “How many work-related emails do you receive during a typical workday?” For the subsample of legal professionals (n = 250), the mean response was M = 36.7 emails, with a sample standard deviation of s = 23.8 emails. The estimated standard error is sMM? = A-0.085, B-1.341, C-0.095 or D-1.505 (choices to choose from.) . Use the following Distributions tool to develop a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean number of work-related emails legal…arrow_forwardThe following data are the semester tuition charges ($000) for a sample of private colleges in various regions of the United States. At the .05 significance level, can we conclude there is a difference in the mean tuition rates for the various regions? Northeast ($000) Southeast ($000) West ($000) 15 13 12 16 14 13 17 15 11 15 13 12 17 11 What is the F-value? What is the decision rule? The F-value is and Ho isarrow_forward5. A researcher constructed a 95% confidence interval for the true mean number of years students take to earn a bachelor's degree. His results were (4.319, 4.841). a. What is the point estimate for the average number of years to complete a bachelor's degree? b. Does his interval support or contradict the widely held belief that it takes 4 years to complete a bachelor's degree? Why or why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman