
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337406659
Author: WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:d
CE
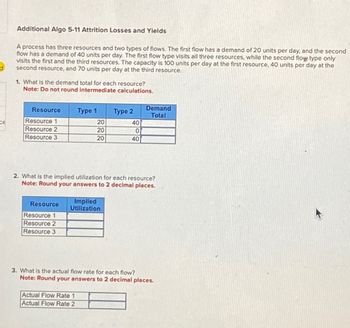
Additional Algo 5-11 Attrition Losses and Yields
A process has three resources and two types of flows. The first flow has a demand of 20 units per day, and the second
flow has a demand of 40 units per day. The first flow type visits all three resources, while the second flow type only
visits the first and the third resources. The capacity is 100 units per day at the first resource, 40 units per day at the
second resource, and 70 units per day at the third resource.
1. What is the demand total for each resource?
Note: Do not round intermediate calculations.
Resource
Resource 1
Resource 2
Resource 3
Resource
Resource 1
Resource 2
Resource 3
Type 1
20
20
20
Implied
Utilization
Actual Flow Rate 1
Actual Flow Rate 2
Type 2
2. What is the implied utilization for each resource?
Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
40
TO
40
Demand
Total
3. What is the actual flow rate for each flow?
Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- JB Bunt's fleet repair facility has the capacity to repair 800 trucks per month. However, due to scheduled maintenance of their equipment, management feels that they can repair no more than 600 trucks per month. Last month, two of the employees were absent several days each, and only 400 trucks were repaired. What is the utilization of the repair shop?arrow_forward3. A bread-manufacturing line typically produces 150 loaves of bread during an 8-hour shift. On average, there are 30 loaves under processing in the line at any given time. What is the value and what is the L value? What is the average time it takes to produce a loaf of bread from the raw ingredients?arrow_forwardChairs are made in a process with a single resource. There are two types of chairs. The resource's processing time for the first type is 30 minutes and demand for this type is 2.3 chairs per hour. The resource's processing time for the second type is 23 minutes and demand for this type is 2.8 chairs per hour. There is 1 worker at this resource. Instruction: Round your answer to one decimal place. What is the implied utilization (%) of this resource?arrow_forward
- A recurring maintenance job in a factory is being done by a three-man crew. Due to the nature of the job and space limitations, it was observed that two of the men were idle 37% of the time; one of the men was also idle an additional of the time, and at any given time only one man was required. The men were each paid P24.00 per hour. Each time the job was performed a set of tools and equipment with a value equivalent to P36.00 per hour was used. If the three-men crew could complete the work in 5 hours, which crew size would be the most economicalarrow_forwardA toy firm produces drums sequentially on three machines- A, B, and C- with cycle times of three, four, and six minutes, respectively. a) Determine the optimum efficiency and output rates for adding one, two... six more machines b) Assume now that two identical lines are operating, each with machines A, B, and C. If new machines can be shared between the lines, how should one, two, and then three new machines be added? What are the resulting efficiencies and outputs of the two lines? Is it always best to equally share extra machines between the two lines?arrow_forwardIn a multi-station serial process system, the capacity of the system is the equal to the capacity of the station that has the highest capacity among all stations. True Falsearrow_forward
- Prevost Chemicals manufactures an industrial solvent at its only processing plant. A liquid chemical and labor are the two primary inputs. All other resources are included in manufacturing overhead. The plant never has any work-in-process or finished goods inventories. Information from the previous four periods of production follows: Chemical input (gallons) Labor input (hours) Solvent sales (gallons) Average price of chemical per gallon Average wage rate per hour Average sales price per gallon Manufacturing overhead (total) Required A Required B Required C Required: a. Compute the partial productivity measures for chemical for the four periods. b. Compute the partial productivity measures for labor for the four periods. c. Compute the total factor productivity for the four periods. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Period Period 1 125,000 12,500 110,000 Period 1 $ 2.00 28.00 10.26 236,000 Compute the partial productivity measures for chemical for the…arrow_forwardSniparrow_forwardDeja Brew, Inc., produces and sells 1,000 pallets of tea. Selling price per pallet: $700 Variable cost per pallet: $100 Annual fixed costs: $20,000 How many units would Deja Brew, Inc., need to sell to make $10,000? Round to the nearest whole pallet.arrow_forward
- The MacJunkin Company manufactures transmission parts. The current process uses 20 workers and produces 400 units per hour. You are considering changing the process with new manufacturing methods that increase output to 470 units per hour but will require 22 workers. Workers are paid at a rate of $15 per hour, and overhead is charged at 140% (or 1.4 times) labor costs. Finished switches sell for $80/unit. The details are as follows: Current Process New Process Output (Units/Hour) 400 470 Number of Workers 20 22 Material (Cost/Hour) $120 $150 These are the correct answers can you show me how to get these answers? A. What is the multifactor productivity ratio for the current process? 38.10 B. What is the multifactor productivity ratio for the new process? 39.92 Your answer is correct.arrow_forwardWhich one of the following is a variable to be considered when calculatingproduction lot size? a forecasted demandb customer orderc the lower of customer orders and forecasted demandd the higher of customer orders and forecasted demandarrow_forwardA loan processing operation at a local bank processes an average of 7 loans per day. The operation has a design capacity of 10 loans per day and an effective capacity of 8 loans per day. What is the utilization of the processing operation? Select one: a. 100.0% b. 87.5% c. 70.0% d. 80.0% Warranty expense, the cost that a business incurs for the repair or replacement of goods that has sold, is an example of which of the following? Select one: a. Internal failure cost b. Appraisal cost c. Prevention cost d. External failure costarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259667473
Author:William J Stevenson
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259666100
Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781285869681
Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781478623069
Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:Waveland Press, Inc.