
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
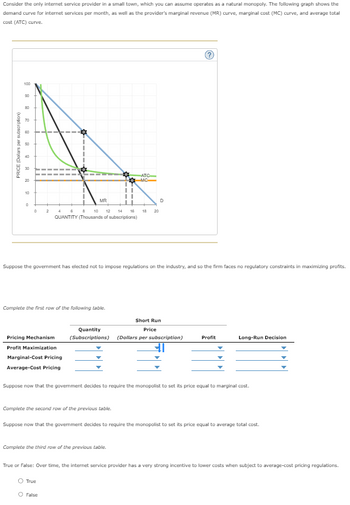
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the only internet service provider in a small town, which you can assume operates as a natural monopoly. The following graph shows the
demand curve for internet services per month, as well as the provider's marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total
cost (ATC) curve.
PRICE (Dollars per subscription)
100
90
80
70
40
20
10
0
0
2
||
Pricing Mechanism
Profit Maximization
4
Complete the first row of the following table.
MR
8 10 12 14
QUANTITY (Thousands of subscriptions)
Marginal-Cost Pricing
Average-Cost Pricing
O True
Suppose the government has elected not to impose regulations on the industry, and so the firm faces no regulatory constraints in maximizing profits.
O False
16
ATC
-MC
Complete the third row of the previous table.
18 20
D
Short Run
Price
Quantity
(Subscriptions) (Dollars per subscription)
Suppose now that the government decides to require the monopolist to set its price equal to marginal cost.
Profit
Complete the second row of the previous table.
Suppose now that the government decides to require the monopolist to set its price equal to average total cost.
Long-Run Decision
True or False: Over time, the internet service provider has a very strong incentive to lower costs when subject to average-cost pricing regulations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a cable company provides cable service to a small town. The total revenue, marginal revenue, total cost, and marginal cost of providing various quantities of cable subscriptions (units in thousands per month) are presented in the table below. Quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Price 202 200 198 196 194 192 190 Total Revenue $0 200 396 588 776 960 1140 Assume the local cable company is a monopoly. To maximize profits, the monopoly should produce At that level of output, the cable company will earn economic profits of $ (thousand per month). Marginal Revenue 200 196 192 188 184 180 Total Cost 0 180 270 330 420 660 960 Marginal Cost 180 90 60 90 240 300 (thousand) units. (Enter a numeric response using an integer.)arrow_forwardJuan's demand for ice cream from the Ice Cream Monopoly Company is illustrated in the figure below. $ per cone 3.00 2.75 2.50 2.25 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0 1 Juan's Demand for Ice Cream 2 3 4 5 6 8 Ice Cream Cones 9 Demand 10 11 12arrow_forwardThe following graph depicts the demand (D), marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and average total cost (ATC) curves for a firm operating as a natural monopoly. Costs and Revenues (dollars) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Market for a Natural Monopoly MC Quantity and ATC MR 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 D B ↑ Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. If the firm is operating as a natural monopoly, what is the profit-maximizing level of output and price charged to consumers? $ units will be sold b. At what price would the firm earn a normal profit? c. Suppose the government regulated the monopoly such that it were required to charge the perfectly competitive price. What is the regulated price?arrow_forward
- 3. Natural monopoly analysis The following graph gives the demand (D) curve for 5G LTE services in the fictional town of Streamship Springs. The graph also shows the marginal revenue (MR) curve, the marginal cost (MC) curve, and the average total cost (ATC) curve for the local 5G LTE company, a natural monopolist. On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for this natural monopolist. 18 16 2006 ± 14 12 1 PRICE (Dollars per gigabyte of data) ° 00 2 Monopoly Outcome ATC MC D MR 0 + + 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 QUANTITY (Gigabytes of data)arrow_forward8. Natural monopoly analysis The following graph shows the demand (D) for gas services in the imaginary town of Utilityburg. The graph also shows the marginal-revenue (MR) curve, the marginal-cost (MC) curve, and the average-total-cost (ATC) curve for the local gas company, a natural monopolist. On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for this natural monopolist. PRICE (Dollars per hundred cubic metres) 2 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 MR ATC MC 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 QUANTITY (Hundreds of cubic metres) D + Monopoly Outcome (? Which of the following statements are true about this natural monopoly? Check all that apply. It is more efficient on the cost side for one producer to exist in this market rather than a large number of producers. The gas company is experiencing economies of scale. The gas company is experiencing diseconomies of scale. The gas company must own a scarce resource. True or False: Without government…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education