
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
6. The following graph shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost
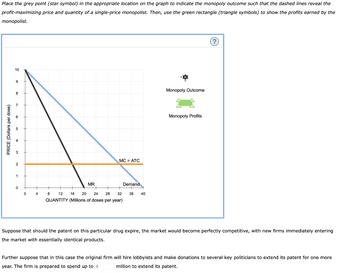
Transcribed Image Text:Place the grey point (star symbol) in the appropriate location on the graph to indicate the monopoly outcome such that the dashed lines reveal the
profit-maximizing price and quantity of a single-price monopolist. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to show the profits earned by the
monopolist.
PRICE (Dollars per dose)
10
9
8
7
2
1
0
0
4
MR
8
MC = ATC
32
12 16 20 24 28
QUANTITY (Millions of doses per year)
Demand
36 40
Monopoly Outcome
Monopoly Profits
(?)
Suppose that should the patent on this particular drug expire, the market would become perfectly competitive, with new firms immediately entering
the market with essentially identical products.
Further suppose that in this case the original firm will hire lobbyists and make donations to several key politicians to extend its patent for one more
year. The firm is prepared to spend up to $ million to extend its patent.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7.arrow_forwardSuppose that Karina is running a tattoo parlor with two types of customers. The first type is willing to pay $80 for a tattoo, while the second type is willing to pay just $40 for a tattoo. The ink for a tattoo costs $10. Customers will only buy one tattoo each. If Karina can only set a single price, what price will she set? a. 80 b. 40 c. 70 d. 30arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- 2. In the following table are demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. Complete the table by filling in the columns for total revenue, marginal revenue, and marginal cost. Answer these three questions: (a) What output will the monopolist produce? (b) What price will the monopolist charge? (c) What total profit will the monopolist receive at the profit-maximizing level of output? Quantity Price revenue 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 O 9 10 $34 $ 32 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 Total Marginal Total revenue cost มี $ 20 36 46 50 54 56 64 80 100 128 160 Marginal cost $arrow_forwardI'm not sure if I am doing this correctly, also not sure where the profit and loss go on the graphs.arrow_forward3 You are the manager of a monopoly. Your analytics department estimates that a typical consumer’s inverse demand function for your firm’s product is P = 350 −20Q, and your cost function is C(Q) = 70Q. a. Determine the optimal two-part pricing strategy. Per-unit fee: $ 70 Fixed fee: $ b. How much additional profit do you earn using a two-part pricing strategy compared with charging this consumer a per-unit price? $arrow_forward
- 8. Natural monopoly analysis The following graph shows the demand (D) for gas services in the imaginary town of Utilityburg. The graph also shows the marginal revenue (MR) curve, the marginal cost (MC) curve, and the average total cost (ATC) curve for the local gas company, a natural monopolist. On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for this natural monopolist. PRICE (Dollars per hundred cubic feet) 20 18 16 14 0 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 QUANTITY (Hundreds of cubic feet) MR 4 ATC MC 9 10 D Monopoly Outcome (? Which of the following statements are true about this natural monopoly? Check all that apply. In order for a monopoly to exist in this case, the government must have intervened and created it.arrow_forwardPlease refer to th graph attached. The graph shows the Demand, Marginal Revenue, Average Total Cost, Average variable Costs and Marginal Cost curves for a monopolist. (a) What is the profit maximizing/ loss minimizing quantity of output and what is the maximum price the monopolist can charge? (b) Is this monopolist making economic profit or economic loss? How do you know? Explain please. (c) Calculate the firms profit or loss and show the economic profit/loss on the graph.arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forward
- 5arrow_forward£/unit 100 90 SRMC 80 70 60 50 40 30 SRAC 20 D= AR 10 MR 20 60 80 100 Units 10 30 40 50 70 90 Figure 12 Demand and cost curves for a firm in monopolistic competition Figure 12 shows the demand curve, D, marginal revenue curve, MR, and short run marginal cost (SRMC) and average cost (SRAC) curves for a firm in monopolistic competition. Using Figure 12, determine the maximum level of profit the firm can make £arrow_forward23arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education