
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
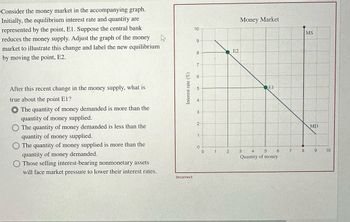
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the money market in the accompanying graph.
Initially, the equilibrium interest rate and quantity are
represented by the point, El. Suppose the central bank
reduces the money supply. Adjust the graph of the money
market to illustrate this change and label the new equilibrium
by moving the point, E2.
After this recent change in the money supply, what is
true about the point E1?
The quantity of money demanded is more than the
quantity of money supplied.
The quantity of money demanded is less than the
quantity of money supplied.
The quantity of money supplied is more than the
quantity of money demanded.
Those selling interest-bearing nonmonetary assets
will face market pressure to lower their interest rates.
Interest rate (%)
Incorrect
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
E2
Money Market
EI
3 4 5 6
Quantity of money
7
8
MS
MD
9
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves. Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level decreases from 150 to 125. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money. ? INTEREST RATE (Percent) 12 10 2 0 0 15 Money Supply Money Demand 30 45 60 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 75 90 Money Demand Money Supplyarrow_forwardMake 1 demand graph and 1 supply graph to plot the data in the table Suppose that the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below: Amount of Real GDP Demanded, Billions Price Level (Price Index) Amount of Real GDP Supplied, Billions $100 300 $450 200 250 400 300 200 300 400 150 200 500 100 100arrow_forwardThe following table shows the quantity of money supplied and the quantity of money demanded for various interest rates. Interest Rate (Percent) Demand for Money (Billions of dollars) Supply of Money (Billions of dollars) 11 50 250 9 150 250 7 250 250 5 350 250 3 450 250 The following graph depicts the money supply curve in orange. On the graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to graph the money demand, and the black point (plus symbol) to signify the initial equilibrium point in the market. Next, shift the money supply curve to show the affects of a $200 billion increase in the money supply. Then, plot the point corresponding to the new equilibrium point using the purple point (diamond symbol). 13 MS 12 11 10 INTEREST RATE (Percent) + 5 M 9 3 2 MS Money Demand Equilibrium Equilibrium,arrow_forward
- Suppose that changes in bank regulations expand the availability of credit cards so that people need to hold less cash. Show how this event affects the demand for money. Value of Money (1/P) Supply Quantity of Money Demand Demand 0 Supplyarrow_forwardCS 21 Economics please answer both a & barrow_forwardSuppose the economy's price level is 2 and real GDP is 30 , 000 for the year. Suppose the money supply is 5 , 000. If the money market is in equilibrium, then how many times per year is the typical dollar bill used to pay for a newly produced good or service? 10 8 12 16arrow_forward
- What happens to the interest rates on bonds during recessions. I am confused becaus During an economic downturn,income and wealth are falling and thus the demand for bonds fall at every price level– the demand curve shifts to the left. Does this decrease the price of bonds meaning higher interest rates? Or an alternartive explanation: In recessions the government tends to cut interest rates in order to stimulate economic activity by creating incentive for banks to lower their rates on loans to consumers and firms, encouraging consumption and investment. This can lead to the interest rates on assets falling. Bonds are often a safe haven during recessionary periods because they offer a fixed income stream in times of uncertainty, and thus they may be favoured to other types of assets invesmtents increasing demand for bonds. The increase in demand Increases price of bonds thus decreases interest rates. or in terms of supply: the supply of bonds may fall because there is less incentive to…arrow_forwardIs it possible that money supply can be more than the money demand (this means that we can have too much money)?arrow_forwardGeneral Equilibrium is a situation in which all market in an economy are simultaneously in equilibrium (both the good market and the money market in equilibrium, as shown below). Now suppose the U.S. economy is now shown at the intersection of the IS and LM curves. Now President Joe Biden passed his Infrastructure bill. Please use graph to explain how such a bill may affect the economy in the long run and short run, in terms of price level, P, output Y and interest rate r. Please also add the AD-AS analysis with your argument.arrow_forward
- (Q#4) Banks have become much less strict about issuing new credit cards. They are issuing far more cards, with lower rates and more generous credit limits. First predict how this will impact the demand for money balances. The expansion of credit cards will end up: [a] increasing the demand for money balances since more items will be purchased and more money will be needed to pay for them [b] reducing the demand for money balances as the delay of payment with them reduces the immediate need for money in a bank checking асcountarrow_forwardTOPIC: A possible break in the Note: everything you need will be in the picturearrow_forwardThe Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. In this case, assume that a = $2 billion. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the expected price level by 1, the quantity of output supplied will exceed the natural level of output by $2 billion. Suppose the natural level of output is $50 billion of real GDP and that people expect a price level of 95. On the following graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to plot this economy's long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. Then use the orange line segments (square symbol) to plot the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve at each of the following price levels: 85, 90, 95, 100, and 105. PRICE LEVEL 125 120 115 110 105 100 95 90 85 80 75 0 + 10 20 ¶¶ 30 40 50 60 70 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) + 80 90 100 -O AS LRAS (?) The short-run quantity of output supplied by firms will rise above the natural level of output when the actual price level falls…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education