
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following program listing and assume it is run as a module.
1
def main() -> None:
2
х3D 110
3
print(a(b(x)))
4
5
6
def a(x: int) -> int:
х +3 1
8.
return x
10
11
def b(x: int) -> int:
12
x += c(x)
13
return x
14
15
16
def c(x: int) -> int:
17
return x + 1
18
19
20
if -_name__ == "_main__":
21
main()
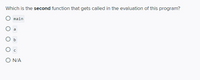
Transcribed Image Text:Which is the second function that gets called in the evaluation of this program?
main
a
O N/A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Build a C program that performs the following operations: Declares three pointer variables called iPtr of type int, cPtr of type char, and fFloat of type float Declares three new variables called iNumber of int type, fNumber of float type, and cCharacter of char type Assigns the address of each non-pointer variable to the matching pointer variable Prints the value of each non-pointer variable Prints the value of each pointer variable Printer the address of each non-pointer variable Prints the address of each pointer variablearrow_forwardC++ and pseudocodearrow_forwardPlease help me with this Principles of programming language homework questionarrow_forward
- Example: The Problem Input File Using C programming language write a program that simulates a variant of the Tiny Machine Architecture. In this implementation memory (RAM) is split into Instruction Memory (IM) and Data Memory (DM). Your code must implement the basic instruction set architecture (ISA) of the Tiny Machine Architecture: //IN 5 //OUT 7 //STORE O //IN 5 //OUT 7 //STORE 1 //LOAD O //SUB 1 55 67 30 55 67 1 LOAD 2- ADD 3> STORE 4> SUB 5> IN 6> OUT 7> END 8> JMP 9> SKIPZ 31 10 41 30 //STORE O 67 //OUT 7 11 /LOAD 1 //OUT 7 //END 67 70 Output Specifications Each piece of the architecture must be accurately represented in your code (Instruction Register, Program Counter, Memory Address Registers, Instruction Memory, Data Memory, Memory Data Registers, and Accumulator). Data Memory will be represented by an integer array. Your Program Counter will begin pointing to the first instruction of the program. Your simulator should provide output according to the input file. Along with…arrow_forwardConsider the following skeletal C program: void fun1(void); /* prototype */void fun2(void); /* prototype */void fun3(void); /* prototype */void main() { int a, b, c; . . .}void fun1(void) { int b, c, d; . . .}void fun2(void) { int c, d, e; . . .}void fun3(void) { int d, e, f; . . .}Given the following calling sequences and assuming that dynamic scoping is used, whatvariables are visible during the execution of the last function? Include with each visible variablethe name of the function in which it was defined.a. main calls fun1; fun1 calls fun2; fun2 calls fun3.b. main calls fun1; fun1 calls fun3.c. main calls fun2; fun2 calls fun3; fun3 calls fun1.d. main calls fun3; fun3 calls fun1.e. main calls fun1; fun1 calls fun3; fun3 calls fun2. Consider the following program, written in JavaScript-like syntax: // main programvar x, y, z;function sub1() {var a, y, z;. . .}function sub2() { var a, b, z; . . .}function sub3() { var a, x, w; . . .}Given the following calling sequences and…arrow_forwardYou can use any C# compiler or the method you already know. The following table contains quarterly sales figures for five (5) departments: Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Total Department 1 750 660 910 800 Department 2 800 700 950 900 Department 3 700 600 750 600 Department 4 850 800 1000 950 Department 5 900 800 960 980 Total Design and write a Windows program/module named SalesAnalysis that will: Declare a two-dimensional integer array named sales – (Note: you have 6 rows and 5 columns) - that will hold the 4 quarterly sales for 5 departments Populate the first four columns for the 5 departments using the data in the preceding table. Contain a loop to compute and populate the total column. Store each department’s total in the array as it is being computed. Contain a loop to compute and populate the total row. Store each quarter’s total in the array as it is being computed.…arrow_forward
- The code box below defines a variable route as a list of directions to navigate a maze. Each instruction is one of the following four basic commands: higher move one step in the positive y direction • lower. move one step in the negative y direction • left: move one step in the negative x direction • right: move one step in the positive x direction Define a function step that takes two arguments, a location (as a tuple of x and y coordinates) and an instruction (higher, lower, left, right) as a string. Given the provided location, it should return the new location (as a tuple of x and y coordinates) when following the specified instruction. If the instruction is invalid, the old location should be returned. Use the function step to determine the final position when starting from the point (0, -4) and following all instructions in the list route. Assign this final position to the variable final_point.arrow_forwardplease modify the c language program into a pep 9 assembly language #include <stdio.h> int num, answer; int divide ( int numer, int denom ) { int quotient, remain; remain = numer; quotient = 0; while ( remain >= denom ) { remain -= denom; quotient++; } // end for return quotient; } // end of divide( ) int modulus ( int n, int d ) { int quot, rem; rem = n; quot = 0; while ( rem >= d ) { rem -= d; quot++; } // end for return rem; } // end of modulus( ) int main() { printf("? "); scanf("%d", &num); answer = divide(num, 20); printf("%d / 20 = %d\n", num, answer); answer = modulus(num, 20); printf("%d mod 20 = %d\n", num, answer); answer = divide(num, 35); printf("%d / 35 = %d\n", num, answer); answer = modulus(num, 35); printf("%d mod 35 = %d\n", num, answer); return 0; } // end of mainarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education