
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
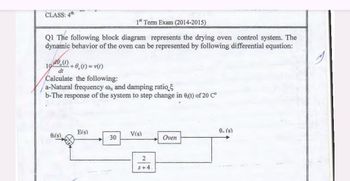
Transcribed Image Text:CLASS: 4th
1st Term Exam (2014-2015)
Q1 The following block diagram represents the drying oven control system. The
dynamic behavior of the oven can be represented by following differential equation:
100.(1)
dt
+0₁(t) = v(t)
Calculate the following:
a-Natural frequency on and damping ratio
b-The response of the system to step change in 0,(t) of 20 C°
E(s)
On (s)
0:(s)
V(s)
30
Oven
2
+
S+4.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A) Assuming that no inputs are present to a first-order and a second-order systems, mention two fundamental differences between the two systems. B) Determine the damping ratio and natural frequency of the single-loop RLC electrical circuit system shown below. d²1 dI I + R + = dt² dt с L E(t). C) State two distinctions between odd and even functions, and name and sketch a function that's neither odd nor even. D) What is the frequency in Hertz and the amplitude of the 5th term (i.e. the 4th harmonics) of the following signal? 4 2π 10π == - sin TT 4 бп y(t) (² t) + 37 sin (17) 4 + sin 5π (10+) +. 10 10arrow_forwardVibrationsarrow_forwardPlease code in Pythonarrow_forward
- 1. Verify Eqs. 1 through 5. Figure 1: mass spring damper In class, we have studied mechanical systems of this type. Here, the main results of our in-class analysis are reviewed. The dynamic behavior of this system is deter- mined from the linear second-order ordinary differential equation: where (1) where r(t) is the displacement of the mass, m is the mass, b is the damping coefficient, and k is the spring stiffness. Equations like Eq. 1 are often written in the "standard form" ď²x dt2 r(t) = = tan-1 d²r dt2 m. M +25wn +wn²x = 0 (2) The variable wn is the natural frequency of the system and is the damping ratio. If the system is underdamped, i.e. < < 1, and it has initial conditions (0) = zot-o = 0, then the solution to Eq. 2 is given by: IO √1 x(1) T₁ = +b+kr = 0 dt 2π dr. dt ل لها -(wat sin (wat +) and is the damped natural frequency. In Figure 2, the normalized plot of the response of this system reveals some useful information. Note that the amount of time Ta between peaks is…arrow_forwardSolve the following question by hand and without the use of AI. Use detailed mathematical expressions to solve the problem and please do not use AI. Thank You!arrow_forwardA thermocouple is connected to a data acquisition system which is used to measure temperature of air in a duct. For a step-input, the system measures the temperature accurately at steady state. Assume the dynamics of the sensor(thermocouple) limit the system's speed of response. The sensor has a time constant of 0.5 sec. In a given situation, the duct's air temperature varies with time as a sinusoid of frequency 2 rad/s with amplitude of 10°C. In this case, the measured temperature by the system is a sinusoid as wellI, as a function of time. The amplitude of this (measured) sinusoid, at steady-state, is closest to: Select one: а. 10°C b. 5°C С. 3°C O d. 7°Carrow_forward
- Hello Sir,Good Morning I have a question in my home work related mechatronics lesson. The following below is my question. Please advise thank you.arrow_forwardPlease solve the following by hand and without the use of AI. I am working to understand the step by step procedure of solving this problem so pleaase give a detailed step by step procedure, explaining each part as you go. Thank you!arrow_forwardQ5. For a point at distance 50 m and angle 450 to the axis which of the following statements are correct? Consider an infinite baffled piston of radius 5 cm driven at 2 kHz in air with velocity 10 m/s. You may choose multiple options. a. The constant term is given by 515.03 b. The distance dependent term is given by e-jk50/50 c. The directivity term is given by j1(Ka sin 450)/sin 450 d. There is no time dependent term.arrow_forward
- T'sec In helical spring experiment a student plotted the graph of T2 versus the oscillating mass (M), and Used the slope to find the spring :constant, the value of k is 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 O. O a. 13.3 N/m O b. 6.8N/m O c. 5 N/m O d. 3.3 N/m O e. 24 N/m 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 M (9) 70 75 80arrow_forward3. Figure 5 shows a linear graph of a motor driving a heavy rotor. The electric circuit of the motor consists of a voltage source Vs(t) and a resistor with resistance R. The rotor has mass moment of inertia J. The motor is modeled as an ideal transformer with T = kai and V = ka, where i and V are the current and voltage of the motor and T and 2 are the torque and angular velocity of the rotor. Answer the following questions. (a) Determine the driving point impedance Z(s). 2 (b) In an impedance test, the voltage is varied sinusoidally, i.e., Vs(t) = vo coswt, to measure impedance Z(jw) along the pure imaginary axis. Roughly sketch the magnitude of Z (jw) with respect to frequency w. T(t) + R V₁(t) 2 Figure 5: Linear graph of a motor driving a heavy rotorarrow_forwardVibrations please helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY