
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
F=22KN
d=14mm
The pin-jointed truss framework, with frictionless joints, as presented in Figure 3
is to be modelled using the finite element method. It is assumed each member is
modelled as 2D linear truss element. Points A, C and D are fixed to ground, while a
load F is applied to point B at the angle shown.
All members have a constant
How would I assemble the global stiffness matrix for this?
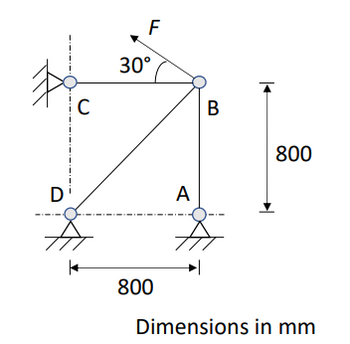
Transcribed Image Text:с
30°
F
A
B
800
800
Dimensions in mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A number of elements along with their crystal structures and atomic radii are listed in the following table. Which pairs might be expected to have complete solid solubility in each other? Crystal Atomic Crystal Structure Atomic Structure radius (nm) radius (nm) Silver Palladium FCC 0.144 Lead FCC 0.175 FCC 0.137 0.137 Tungsten Rhodium ВСС Copper Gold FCC 0.128 FCC 0.134 Platinum Tantalum FCC 0.144 FCC 0.138 Nickel FCC 0.125 ВСС 0.143 Aluminum Sodium FCC 0.143 Potassium ВСС 0.231 ВСС 0.185 Molybdenum ВСС 0.136arrow_forwardAn external load caused tensile stress is imposed along the [001] of a BCC single crystal. The initial yielding of the crystal causes the coordinate motion of atoms along the direction with how many degrees with respect to the direction of the tensile stress.arrow_forwardHi can you please help me with the attached question?arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardQ1/A Prove that the volume of an FCC unit cell, Vc is; Vc = 16R³√2 B) Explain in general terms, why many polymers and some ceramic glasses have an amorphous or semicrystalline structure.arrow_forwardI Review I Constants I Periodic Table Part A The (Figure 1) shows two thin beams joined at right angles. The vertical beam is 17.0 kg and 1.00 m long and the horizontal beam is 29.0 kg and 2.00 m long. Find the center of gravity of the two joined beams. Express your answer in the form x, y, taking the origin at the corner where the beams join. Express your answers in meters. Enter your answers separated by a comma. Neglect the lateral dimensions of the beams. Submit Part B Calculate the gravitational torque on the joined beams about an axis through the corner. Figure 1 of 1 Express your answer with the appropriate units. HÀ ? T = 1.00 m Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 2.00 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY