
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
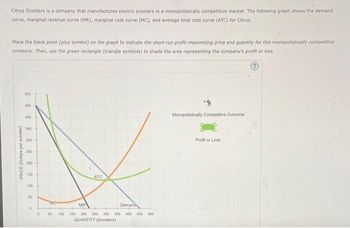
Transcribed Image Text:Citrus Scooters is a company that manufactures electric scooters in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows the demand
curve, marginal revenue curve (MR), marginal cost curve (MC), and average total cost curve (ATC) for Citrus.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolistically competitive
company. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the company's profit or loss.
PRICE (Dollars per scooter)
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
Co
0
0
"MC
50
100
ATC
MR
Demand
150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
QUANTITY (Scooters)
Monopolistically Competitive Outcome
Profit or Loss
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- MelCo’s Xamoff The global pharmaceuticals giant, MelCo, has had great success with Xamoff, and over-thecounter medicine that reduces exam-related anxiety. A patent currently protects Xamoff from competition, although rumors persist that similar products are in development. Two years ago, MelCo sold 25 million units for a price of $10 for a package of ten. Last year it raised the price to $11, and sales fell to 22 million units. Finally, a financial analyst estimates the cost of production at $2 per package. (a) Estimate the elasticity of demand for this product at $10. Is this price too high or too low? (b) Estimate the elasticity of demand for this product at $11. Is this price too high or too low? (c) Based on your answers to (a) and (b), what can we say about MelCo’s profit-maximizing price?arrow_forwardIn the long run, the positive economic profits earned by the monopolistic competitor will attract a response either from existing firms in the industry or firms outside. As those firms capture the original firm’s profit, what will happen to the original firm’s profit-maximizing price and output levels? Show on a grapharrow_forwardIn long run equilibrium, economic profits tend to zero in a perfectly competitive market and also in a monopolistically competitive market. This is true because both market structures share a crucial characteristic. What is the characteristic that causes economic profits to get pushed towards zero in both perfect competition and monopolistic competition?arrow_forward
- What are the characteristics of monopolistically competitive markets? If the price of the product in a monopolistically competitive market increases what happens to the number of individual firms in the market and to the level of profit in the long run? Fully explain your answer.arrow_forwardSuppose that a company operates in the monopolistically competitive market for denim jackets. The following graph shows the demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve for the firm. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. ? 100 PRICE (Dollars per jacket) 8 20 60 50 X ATC 20 MC MR 2 2 2 2 10 0 0 30 40 50 60 70 QUANTITY (Thousands of jackets) 10 20 80 Demand 90 100 Mon Comp Outcome Min Unit Costarrow_forwardDiscuss the long-term effects in a monopolistically competitive market if an existing firm is making profits or losses. Use graphs to help your explanations.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a firm produces wooden train engines in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve: Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm, Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost.arrow_forwardexplain the relationship between the market price and a monopolistically competitive firm’s marginal revenue, be able to find the profit-maximizing output and pricearrow_forwardPlace the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolistically competitive company. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the company's profit or loss. Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes. Select and drag the rectangles from the palette to the graph. To resize, select one of the points on the rectangle and move to the desired position. PRICE (Dollars per bike) 500 450 400 350 PRICE (Dollars per bike) 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 MC + 50 100 AC MR 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Bikes) Demand Enjano Given the profit-maximizing choice of output and price, the shop is earning shops in the industry than in long-run equilibrium. + Monopolistically Competitive Outcome Now consider the long run in which bike manufacturers are free to enter and exit the market. QUANTITY (Bikes) Show the possible effect of free entry and exit by shifting the…arrow_forward
- Suppose you manage a firm in a monopolistically competitive market Suppose you manage a firm in a monopolistically competitive market. Which of the following strategies will do a better job of helping you maintain economic profits: obtaining a celebrity endorsement for your product or supporting the entry of firms that will compete directly with your biggest rival? Explain your answer. Suppose you manage a firm in a monopolistically competitive marketarrow_forwardThe table below shows the total cost (TC) and marginal cost (MC) for Choco Lovers, a monopolistic firm producing different quantities of chocolate gift boxes. Fill in the blanks in the table. Quantity 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Price $22 20 16 14 12 10 Profit Profit-maximizing quantity Profit-maximizing price 18 Total Revenue 50 100 180 240 280 300 300 Total Cost $50 55 57.5 62.5 72.5 122.5 Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue $1 0.5 2 4 6 1 10 12 8 Instructions: Enter your answers as whole numbers. For profit, round your answer to 2 decimal places. 0 20arrow_forwarda) Using the following graph state the price and quantity the firm will be at if the monopolistic competition market is in long run equilibrium. Explain why the firm will be at that price and quantity. Price P1 MC ATC B P 2 P3 P4 P5 MR D Q2 Q3 Quantity b) State the conditions that establish the market structure monopolistic competition, and state how the market adjusts to long run equilibrium and what is different about long run equilibrium for this market structure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education