
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
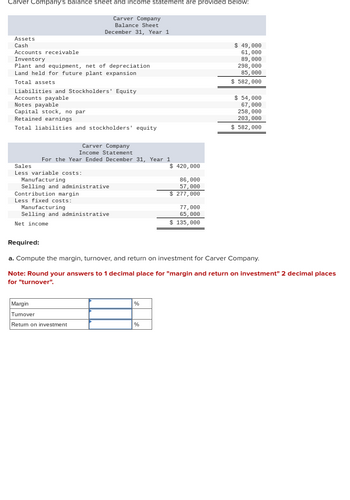
Transcribed Image Text:Carver Company's balance sheet and income statement are provided below:
Assets
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventory
Plant and equipment, net of depreciation
Land held for future plant expansion
Total assets
Carver Company
Balance Sheet
December 31, Year 1
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
Accounts payable
Notes payable
Capital stock, no par
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity
Carver Company
Income Statement
For the Year Ended December 31, Year 1
Sales
Less variable costs:
Manufacturing
Selling and administrative
Contribution margin.
Less fixed costs:
Manufacturing
Selling and administrative
Net income
Margin
Turnover
Return on investment
$ 420,000
%
86,000
57,000
$ 277,000
77,000
65,000
$ 135,000
$ 49,000
61,000
89,000
298,000
85,000
$ 582,000
Required:
a. Compute the margin, turnover, and return on investment for Carver Company.
Note: Round your answers to 1 decimal place for "margin and return on investment" 2 decimal places
for "turnover".
$ 54,000
67,000
258,000
203,000
$ 582,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Provide answer pleasearrow_forward! Required information Problem 13-58 & 13-59 (Static) (LO 13-4, 5) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following information is available for Fairmount Industries from year 1 operations: Sales revenue (45,000 units) Manufacturing costs Materials Variable cash costs. Fixed cash costs Depreciation (fixed) Marketing and administrative costs Marketing (variable, cash) Marketing depreciation Administrative (fixed, cash) Administrative depreciation Total costs Operating profits (losses) All depreciation charges are fixed. Old manufacturing equipment with an annual depreciation charge of $22,000 will be fully depreciated by the end of year 1 and will not be replaced with new equipment because it is still operating to specification. Sales volume is expected to decrease by 2 percent. Sales price is expected to increase by 8 percent. On a per-unit basis, expectations are that materials costs will decrease by 5 percent and variable manufacturing cash costs…arrow_forwardSales Variable manufacturing and selling expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses: Advertising, traceable Depreciation of special equipment Salaries of product-line managers Allocated common fixed expenses* Total fixed expenses Net operating income (loss) Total $ 930,000 472,000 458,000 69,000 43,300 116,000 186,000 414,300 $ 43,700 Dirt Bikes $ 265,000 115,000 150,000 8,200 20,300 40,700 53,000 122, 200 $ 27,800 Mountain Bikes $ 410,000 204,000 206,000 40,400 7,600 38,300 82,000 168,300 $ 37,700 Answer is not complete. Required: 1. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) per quarter of discontinuing the Racing Bikes? 2. Should the production and sale of racing bikes be discontinued? Racing Bikes $ 255,000 153,000 102,000 20,400 15,400 *Allocated on the basis of sales dollars. Management is concerned about the continued losses shown by the racing bikes and wants a recommendation as to whether or not the line should be discontinued. The special equipment used to produce racing…arrow_forward
- Financial information for BDS Enterprises for the year-ended December 31, 20xx, was gathered from an accounting intern, who has asked for your guidance on how to prepare an income statement format that will be distributed to management. Subtotals and totals are included in the information, but you will need to calculate the values. Pretax income ? Gross profit ? Allocated costs (uncontrollable) $2,040 Labor expense 41,580 Sales 190,000 Research and development (uncontrollable) 310 Depreciation expense 17,000 Net income/(loss) ? Cost of goods sold 119,700 Selling expense 1,260 Total expenses ? Marketing costs (uncontrollable) 790 Administrative expense 690 Income tax expense (21% of pretax income) ? Other expenses 330 A. Prepare the income statement to include all costs, but separate out uncontrollable costs using the above information. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. BDS Enterprises Income Statement For the Year Ended December…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following information is available for Fairmount Industries from year 1 operations: Sales revenue (55,000 units) Manufacturing costs Materials Variable cash costs Fixed cash costs Depreciation (fixed) Marketing and administrative costs Marketing (variable, cash) Marketing depreciation Administrative (fixed, cash) Administrative depreciation Total cost Operating profits (losses) $ 1,670,000 $ 250,000 555,000 337,000 170,000 181,000 51,000 172,000 20,000 $ 1,735,000 $ (66,000) All depreciation charges are fixed. Old manufacturing equipment with an annual depreciation charge of $32,000 will be fully depreciated by the end of year 1 and will not be replaced with new equipment because it is still operating to specification Sales volume is expected to decrease by 2 percent. Sales price is expected to increase by 8 percent. On a per-unit basis, expectations are that materials costs will decrease by…arrow_forwardPresented below is information related to the Southern Division of Lumber Ltd. Contribution margin Controllable margin $1,222,800 $1,018,975 Average operating assets $4,075,900 Minimum rate of return 17 % Calculate the Southern Division's return on investment and residual income. Return on investment Residual income $ %arrow_forward
- Determining missing items in return and residual income computations Data for Uberto Company are presented in the following table of rates of return on investment and residual incomes: Invested Assets Income from Operations Return on Investment Minimum Return Minimum Acceptable Income from Operations Residual Income $950,000 $228,000 (a) 13% (b) (c) $550,000 (d) (e) (f) $60,500 $27,500 $350,000 (g) 14% (h) $38,500 (i) $260,000 $52,000 (j) 12% (k) (l) Determine the missing values, identified by the letters above. For all amounts, round to the nearest whole number. a. fill in the blank 1% b. $fill in the blank 2 c. $fill in the blank 3 d. $fill in the blank 4 e. fill in the blank 5% f. fill in the blank 6% g. $fill in the blank 7 h. fill in the blank 8% i. $fill in the blank 9 j. fill in the blank 10% k. $fill in the…arrow_forward(1)Garcon Company | Pepper Company (2) Finished goods inventory, beginning $ 13,200 / $ 16, 750 Work in process inventory, beginning 18,000/ 22,650 Raw materials inventory, beginning 9, 800/12, 750 Rental cost on factory equipment 30, 250/26, 350 Direct labor 19, 400 / 39,400 Finished goods inventory, ending 17,300 / 16, 400 Work in process inventory, ending 26, 200/20, 400 Raw materials inventory, ending 8, 000/ 9,200 Factory utilities 14, 100/13, 750 General and administrative expenses 27, 500/53, 500 Indirect labor 12, 150 / 12, 260 Repairs-Factory equipment 4, 820/2, 350 Raw materials purchases 47,000/67,500 Selling expenses 62, 400 / 54,400 Sales 295, 320/394, 170 Cash 29, 000/24, 200 Accounts receivable, net 15,800 / 23,450arrow_forwardgo.3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education