
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
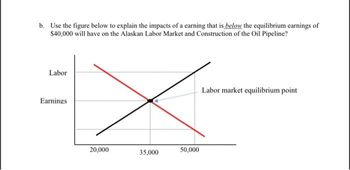
Transcribed Image Text:b. Use the figure below to explain the impacts of a earning that is below the equilibrium earnings of
$40,000 will have on the Alaskan Labor Market and Construction of the Oil Pipeline?
Labor
Earnings
20,000
35,000
50,000
Labor market equilibrium point
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. Minimum wage legislation The following graph gives the labor market for the fast-food industry of the imaginary city of Combopolis. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. WAGE (Dollars per hour) 20 18 Graph Input Tool Market for Labor in the Fast Food Industry Wage 6 (Dollars per hour) 16 Supply 14 Labor Demanded (Hundreds of workers) 630 Labor Supplied (Hundreds of workers) 0 12 10 2 2 0 10 0 ° Demand 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 810 900 LABOR (Hundreds of workers) In this market, the equilibrium wage is $ per hour, and the equilibrium quantity of labor is Suppose the mayor of Combopolis introduces a legal minimum wage of $6 per hour. This type of price control is called a hundred workers. For each of the wages listed in the following table, determine the…arrow_forward14. The figure shows the supply and demand for labor in the textile industry. In each of the following scenarios, identify the direction of the shift in either the supply or demand curve and state whether the resulting equilibrium wage and quantity increase or decrease. What are the original equilibrium wage and quantity? Immigration and layoffs from other jobs increase the population of textile workers. A new technology for making self-printed T-shirts reduces the marginal product of labor for textile workers.arrow_forwardThe height of the supply curve (S) measures D the cost to taxpayers of drafting a worker. the value to the maitary of drafting a worker. the difference between the cost to the taxpyer and the cost to the military of drafting a worker. the opportunity coss of a potential draftee.arrow_forward
- 5. Consider the market for labor. When you draw a supply and demand curve, what group of people represent “supply”? Explain.arrow_forwardIn Akron, 150 people are willing to spend an hour working as yoga instructors for an hourly wage of $10. For each additional $5 that the wage increases above $10, an additional 50 people are willing to spend an hour working. For hourly wages of $10, $15, $20, $25, and $30, plot the daily labor supply curve for yoga instructors on the following graph. 50 45 40 35 & WAGE (Dollars per hour) 20 15 10 5 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 LABOR (Number of workers) 400 450 500 Supply What is one explanation for why this labor supply curve is upward sloping? Wages have to increase to accommodate union pressure. Unemployment benefits are steadily declining. The opportunity cost of leisure decreases as wages decrease. People prefer to spend time doing leisure activities rather than working. ?arrow_forward11. Describe what happens to quantity of labor supplied when wages are at the equilibrium level, above equilibrium, and below equilibrium.arrow_forward
- to finance a new health insurance program, the government of Millonia imposes a new $2-per-hour payroll tax to be paid by employers. What do you expect to happen to wages and the size of the workforce? Explain How will this answer change in markets where labor is inelastically demanded? Explainarrow_forward(c) Let us now turn to the labor market for grocery store workers in Little town. Recently one of the last two grocery stores in Little town closed leaving only one employer for grocery store workers in this area. This labor market is not very competitive. What type of market structure is this? (d) Draw a typical supply curve (i.e. average expenditure), marginal expenditure, and demand for the grocery store in Little Town. Label the equilibrium wage and number of grocery store workers. (e) Suppose that some time has passed and the population has grown in Little Town and there are now many grocery stores. Now suppose that the grocery store workers unionize. Draw a graph to depict the equilibrium wage and number of workers in this new market.arrow_forwardA firm's resource input, total output of labor, and product price schedules are given in the table. If labor is the only variable input, how much labor should the firm employ if the wage rate is $15 per day? Units of Labor Total Output/Day 20 30 2 3 4 5 6 7 * 3 units *4 units *5 units *6 units 38 46 54 62 Price of Good ($) $10 9 8 7 6 5arrow_forward
- ↓ The graph illustrates a labor market in which there is a minimum wage of $5 an hour Draw shapes that represent the following 1) firms' surplus Label it FS 2) workers' surplus. Label it WS 3) deadweight loss. Label it DWL 4) the potential loss from job search Label it Loss >>> A label can be repositioned by clicking on the edge of the label box and dragging it onto the shape Wage rate (dollars per hour) FS 3- 0+ 18 19 (18,2) Minimum wage D 24 25 21 22 23 20 Quantity (millions of hours per year) a Garrow_forward13. Identify which way the labor supply curve would shift under the following scenarios. A country experiences a huge influx of immigrants who are skilled in the textile industry. Wages increase in an industry that requires similar job skills. New machines require additional maintenance over time, so that the marginal productivity of labor rises.arrow_forwardlabor Q per day MPP MRP 0 0 ---- ---- 1 40 2 68 3 89 4 108 5 123 A) calculate table. The price of the product price is $6. B) Refer to table above. If the wage is $120 per day, this firm should hire __ and produce ____ per day.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education