
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Obtain the following basic equations modeling natural convection in the two-dimensional plane at steady conditions in terms of the given dimensionless quantities.
Note: The buoyancy term in the y-momentum equation will be obtained based on dimensionless numbers.
Note: second photo gives you what you need
![u[a?v a²v]
əy²
pay ' plax² ' dy²
dv
dv
1 ƏP
-+v-
+ gßr(T – Tc)
и
-
-
-- -
|
ax
ду
рду р](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/a5c88977-0b28-4158-beef-1ad154d2cc54/23694439-e647-444a-8ecf-cba228f553ee/fzqagm_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:u[a?v a²v]
əy²
pay ' plax² ' dy²
dv
dv
1 ƏP
-+v-
+ gßr(T – Tc)
и
-
-
-- -
|
ax
ду
рду р
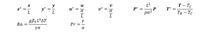
Transcribed Image Text:y
y':
L2
T- Tc
T* = -
и
x* =
L
u* =
a
P* =
P
pa?
TH - Tc
Ra =
Pr
= -
ya
a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A vertical pipe 90 mm diameter and 2.5 m height is maintained at a constant temperature of 125 o The pipe is surrounded by still atmospheric air at 25 oC. Find heat loss by natural convection. Properties of water at 75 oC: Density = 1.0145 kg/m3 Kinematic viscosity = 20.55 x10-6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.693 Thermal conductivity (k) = 30.06 x 10–3 W/m Karrow_forwardbetween two concentric spherical sheets there is air. The inner spherical sheet has a radius of 10 cm and is filled with ice at 0 ° C, the outer spherical sheet has a radius of 10.05 cm and is at a temperature of 15 ° C. What amount of heat will be transmitted from one sheet to another by conductivity ends in 1/4 hour ?. Considering that the air is pressurized, it is considered to be 15 N / m ^ 2 and at a temperature of 2 ° C. The diameter of the air molecules is taken equal to 3 x 10 ^ -10 m. the molar mass of air is taken equal to 29 g / mol; Boltzman's constant k = 1.38 x 10 ^ -23 J / Karrow_forwardfluid mechanicsarrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardHeat transfer. Show all steps for solutionarrow_forward..P15 A horizontal cylinder 10 cm in diameter contains helium gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. A piston keeps the gas inside a region of the cylinder 20 cm long. (a) If you quickly pull the piston outward a distance of 12 cm, what is the approximate temperature of the helium immediately afterward? What approximations did you make? (b) How much work did you do, including sign? (Note that you need to consider the outside air as well as the inside helium in calculating the amount of work you do.) (c) Immediately after the pull, what force must you exert on the piston to hold it in position (with the helium enclosed in a volume that is 20 + 12 = 32 cm long)? (d) You wait while the helium slowly returns to room temperature, maintaining the piston at its current location. After this wait, what force must you exert to hold the piston in position? (e) Next, you very slowly allow the piston to move back into the cylinder, stopping when the region of helium gas is 25 cm long.…arrow_forward
- Heat transferarrow_forwardAt 25oC, one block was blown by wind at 65oC as shown in Figure 1. The block has dimension of 9m-long, 4m-wide and 2m-thick in its size. Considering that time is 1 atm and a velocity of 60 km/h, calculate the force drag on the wall surface. Also, find the solution (force drag) if the velocity has partially blown on the wall.arrow_forwardTopic: Heat transfer Completely solve and box the final answer. 1. A 20degC water flows to 50cmx60cm flat plate with velocity of 5.2m/s . The flat plate surface temperature is maintained at 40deg C. The air flows parallel to the 50cm side of the plate. If the kinematic viscosity of water is 78x10-8 m2/s, at what length the flow become turbulent?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY