
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
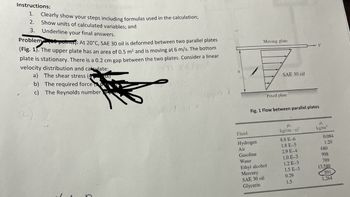
Transcribed Image Text:Instructions:
1.
2.
3.
Clearly show your steps including formulas used in the calculation;
Show units of calculated variables; and
Underline your final answers.
Problem the points): At 20°C, SAE 30 oil is deformed between two parallel plates
(Fig. 1). The upper plate has an area of 0.5 m² and is moving at 6 m/s. The bottom
plate is stationary. There is a 0.2 cm gap between the two plates. Consider a linear
velocity distribution and calculate:
a) The shear stress (US)
b)
The required force
c)
The Reynolds number
(upper)
h
Moving plate
SAE 30 oil
Fluid
Hydrogen
Air
Gasoline
Water
Ethyl alcohol
Mercury
SAE 30 oil
Glycerin
Fixed plate
Fig. 1 Flow between parallel plates
fl₂
kg/(m.s)
8.8 E-6
1.8 E-5
V
2.9 E-4
1.0 E-3
1.2 E-3
1.5 E-3
0.29
1.5
P
kg/m³
0.084
1.20
680
998
789
13,580
891
1,264
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please show steps with explanation of the formulas and calculs for more understanding. Thank you!arrow_forwardShow detailed work in Handwritten format. Thanksarrow_forwardGlobal warming will produce rising sea levels partly due to melting ice caps and partly due to the expansion of water as average ocean temperatures rise. To get some idea of the size of this effect, calculate the change in length, Ah (in mm), of a column of water 1.5 km high for a temperature increase of 1.2 °C.Assume the column is not free to expand sideways. As a model of the ocean, that is a reasonable approximation, as only parts of the ocean very close to the surface can expand sideways onto land, and only to a limited degree. As another approximation, neglect the fact that ocean warming is not uniform with depth. Properties of water: 3 = 210 x 10 /C. c= 4186 J/kg - °C, L; = 334 kJ/kg, Le = 2256 kJ/kg Enter you answer below (to the nearest mm): Ah (in mm) = Type your answer.arrow_forward
- 2. The apparatus shown below is designed to measure the density of an unknown fluid (p2₂). The two sides of the device are separated by a movable, frictionless partition. The partition is attached to the immobile sidewalls of the device via springs (different spring constants) on either side. Before pouring fluid into the device, both springs are unstretched. The device has a rectangular cross-section and extends a width w into the page. Derive an expression for the unknown density p2 = f(p1, h₁, h₂, k₁, k2, Ax, g), where Ar is the displacement of the partition relative to its equilibrium location before the fluids are poured into the apparatus. h₁ P1 k₁ 5 P2 ли Ax k₂ h₂arrow_forwardthe equations given are not clear, can you display them clearly as it looks confusingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY