The equilibrium constant of a system, K, can be related to the standard free energy change, AG, using the following equation: AG-RT In K where T is a specified temperature in kelvins (usually 298 K) and R is equal to 8.314 J/(K.mol). Under conditions other than standard state, the following equation applies: AG AG + RT ln Q In this equation, Q is the reaction quotient and is defined the same manner as K except that the concentrations or pressures used are not necessarily the equilibrium values. Part A Acetylene, C₂ H₂, can be converted to ethane, C₂H6, by a process known as hydrogenation. The reaction is C₂H2(g) + 2H2(g) = C₂H6(g) Given the following data at standard conditions (all pressures equal to 1 atm and the common reference temperature 298 K), what is the value of K, for this reaction? Kp = Submit Substance Express your answer using two significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) 15. ΑΣΦ C₂ H₂(g) H₂(g) C₂H6(g) (kJ/mol) 209.2 0 -32.89 ?
The equilibrium constant of a system, K, can be related to the standard free energy change, AG, using the following equation: AG-RT In K where T is a specified temperature in kelvins (usually 298 K) and R is equal to 8.314 J/(K.mol). Under conditions other than standard state, the following equation applies: AG AG + RT ln Q In this equation, Q is the reaction quotient and is defined the same manner as K except that the concentrations or pressures used are not necessarily the equilibrium values. Part A Acetylene, C₂ H₂, can be converted to ethane, C₂H6, by a process known as hydrogenation. The reaction is C₂H2(g) + 2H2(g) = C₂H6(g) Given the following data at standard conditions (all pressures equal to 1 atm and the common reference temperature 298 K), what is the value of K, for this reaction? Kp = Submit Substance Express your answer using two significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) 15. ΑΣΦ C₂ H₂(g) H₂(g) C₂H6(g) (kJ/mol) 209.2 0 -32.89 ?
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
3L5

Transcribed Image Text:The equilibrium constant of a system, K, can be
related to the standard free energy change, AG,
using the following equation:
AG° = -RT In K
where T is a specified temperature in kelvins
(usually 298 K) and R is equal to 8.314
J/(K.mol).
Under conditions other than standard state, the
following equation applies:
AG=AG + RT In Q
In this equation, is the reaction quotient and is
defined the same manner as K except that the
concentrations or pressures used are not
necessarily the equilibrium values.
Part A
Acetylene, C₂ H2, can be converted to ethane, C₂H6, by a process known as hydrogenation. The reaction
is
C₂ H₂(g) + 2H2(g) = C₂H6(g)
Given the following data at standard conditions (all pressures equal to 1 atm and the common reference
temperature 298 K), what is the value of Kp for this reaction?
Kp
Express your answer using two significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
=
Submit
Substance
VE ΑΣΦ
C₂ H₂(g)
H₂(g)
C₂H6 (g)
=
Go
f
(kJ/mol)
209.2
0
-32.89
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
3L5.2
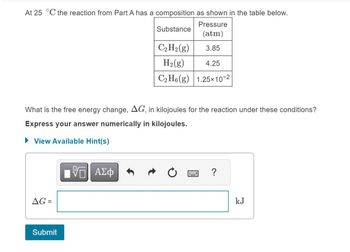
Transcribed Image Text:At 25 °C the reaction from Part A has a composition as shown in the table below.
Substance
Pressure
(atm)
3.85
What is the free energy change, AG, in kilojoules for the reaction under these conditions?
Express your answer numerically in kilojoules.
► View Available Hint(s)
AG=
Submit
C₂ H₂(g)
H₂(g)
4.25
C₂H6(g) 1.25x10-2
{—| ΑΣΦ
?
kJ
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON